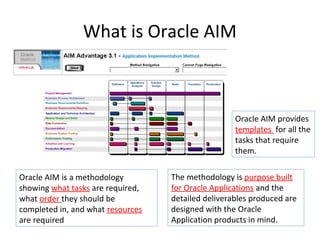
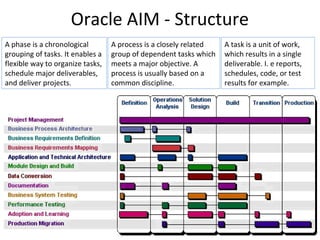
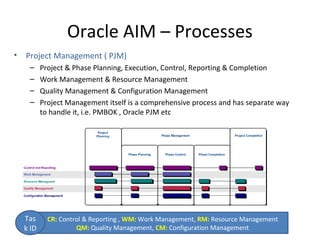
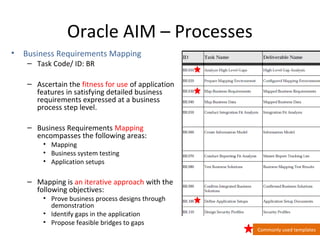
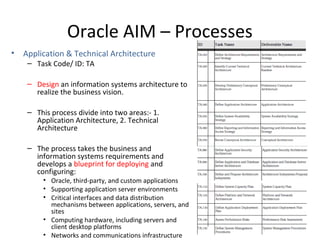
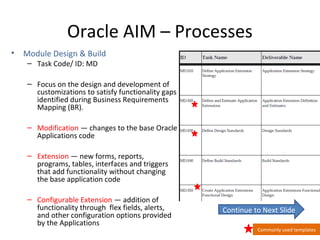
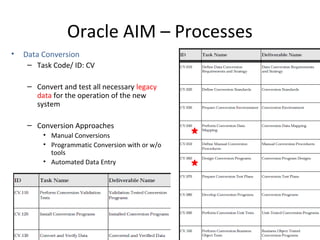
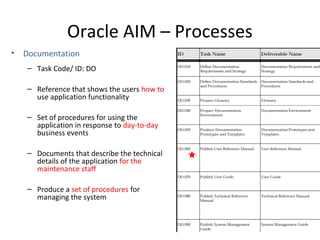
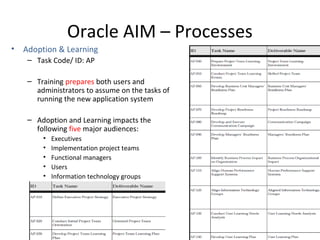
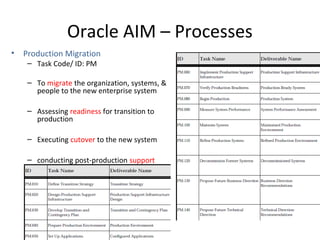
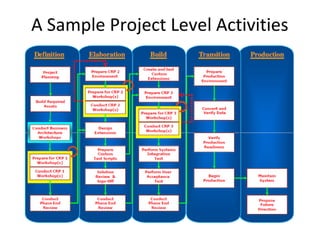
The document provides an overview of the Oracle AIM (Application Implementation Methodology) which is Oracle's methodology for implementing Oracle E-Business Suite applications. It discusses that Oracle AIM provides a proven process for implementation with high quality, quick ROI and short time to benefit. It then describes the key elements of Oracle AIM including its structure with phases, processes and tasks, as well as the advantages it provides to clients.