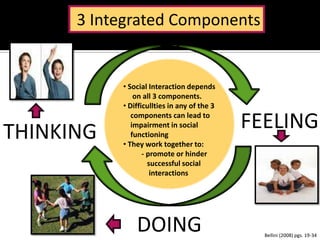
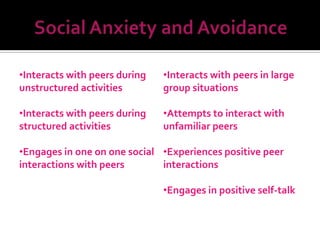
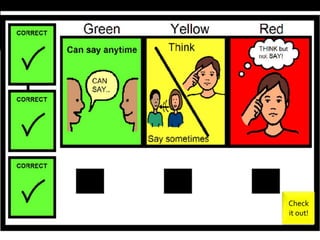
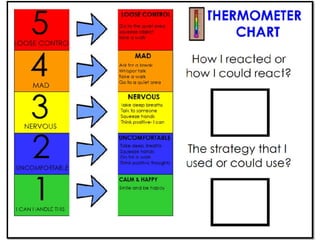
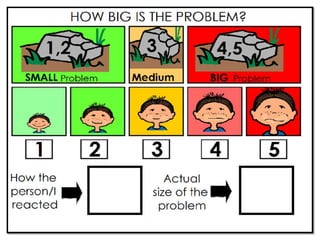
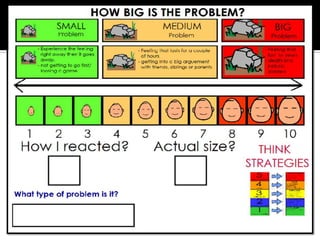
The document discusses social skills interventions for students. It provides:
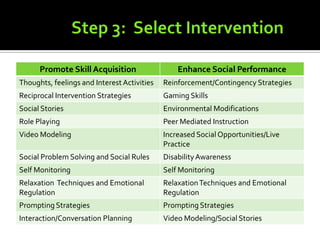
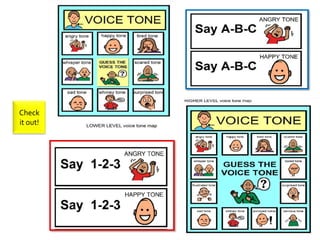
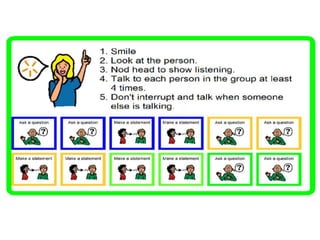
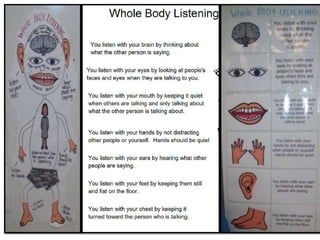
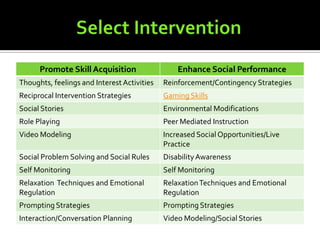
1) A variety of intervention strategies to either promote skill acquisition or enhance social performance, such as social stories, video modeling, and reinforcement.
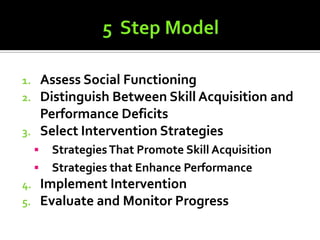
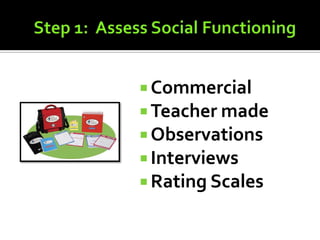
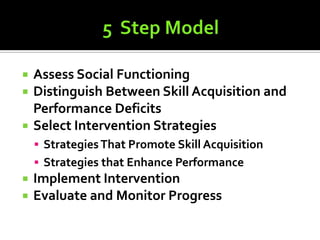
2) Methods for assessing students' social functioning and determining if deficits are due to skills not being learned or performance issues.
3) A process for developing social skills interventions that includes assessing the student, selecting appropriate strategies, implementing interventions, and monitoring progress.