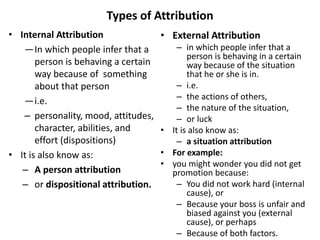
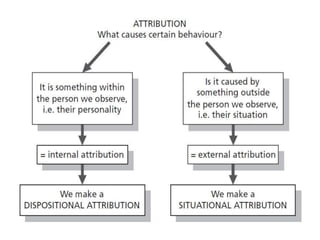
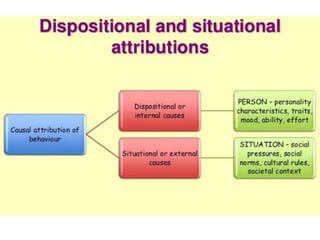
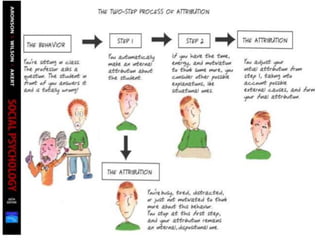
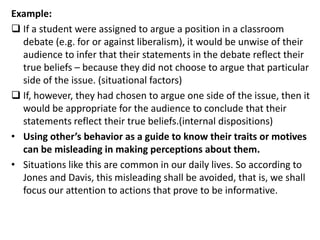
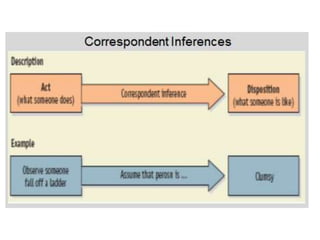
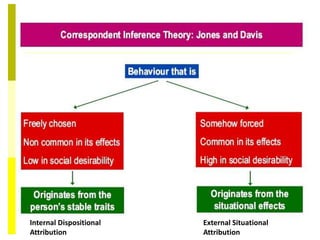
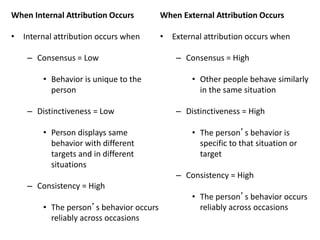
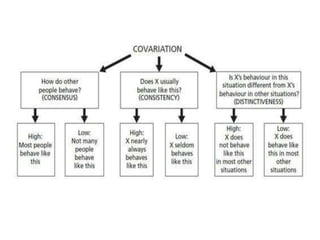
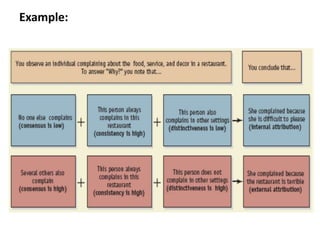
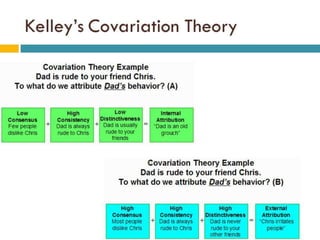
This document discusses social perception and attribution theory. It defines attribution as explaining the causes of behaviors and events. There are two types of attribution: internal attribution, which attributes behaviors to internal factors like personality; and external attribution, which attributes behaviors to external situational factors. Two influential theories are discussed: Jones and Davis' theory of correspondent inference, which outlines factors like behavior being freely chosen that lead to internal attributions; and Kelley's covariation model, which uses three factors - consensus, distinctiveness, and consistency - to determine if a behavior is attributed to internal or external causes. Common attribution errors like the correspondence bias and actor-observer effect are also outlined.