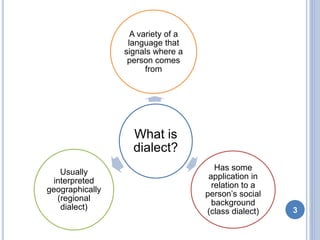
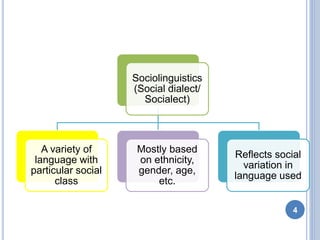
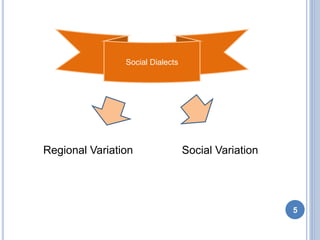
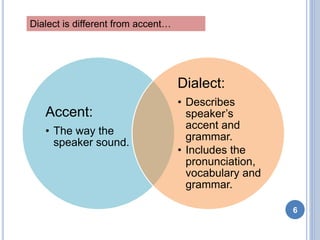
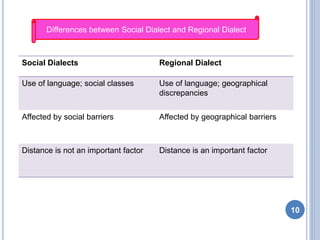
This document discusses social dialects and how they differ from regional dialects. It defines dialect as a variety of a language that signals where a person comes from and is influenced by their social background. Social dialect, also called sociolinguistics, refers to variations in language based on social factors like ethnicity, gender, age, and social class. Regional dialect depends more on the geographical area where a language is spoken. While both reflect social variations in language use, social dialects are influenced more by social barriers between groups rather than geographical distance.