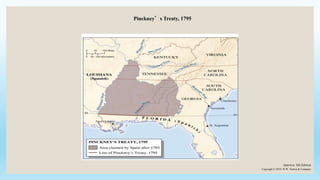
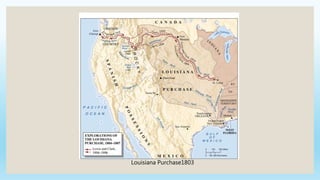
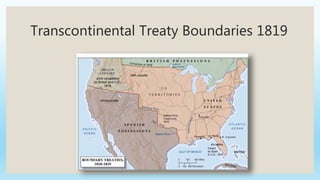
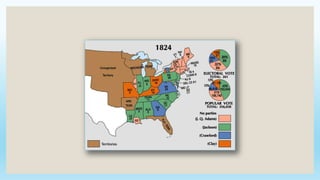
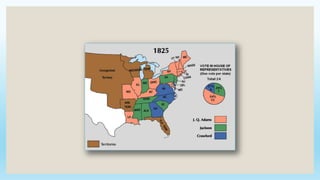
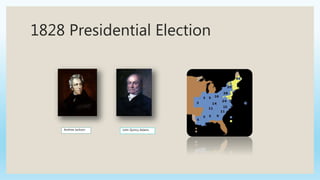
This document provides an overview of key political, economic, and social developments in the early United States from 1800 to 1850. It discusses the rise of the first political parties, Hamilton's vision for an American economy centered around manufacturing and finance, the Whiskey Rebellion in response to Hamilton's taxes, and the election of 1800 which resulted in Thomas Jefferson becoming president and the Democratic-Republican party gaining power. The document also summarizes events like the Louisiana Purchase, the War of 1812, settlement of new western lands, and the emergence of sectional differences between the North and South.