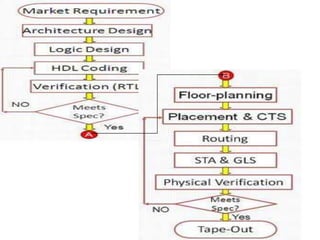
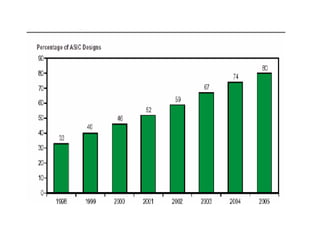
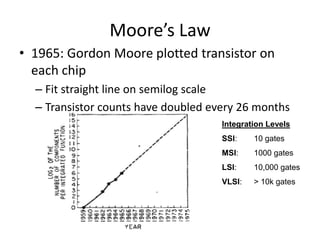
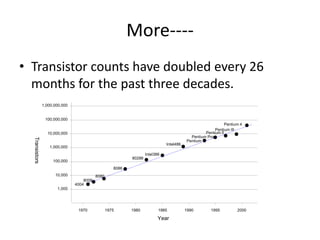
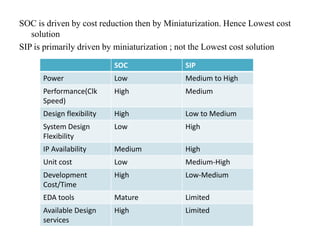
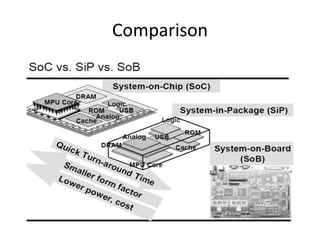
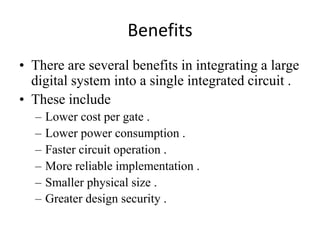
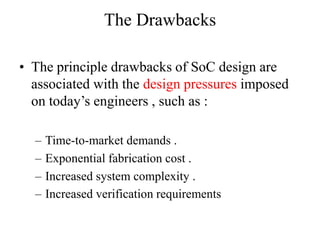
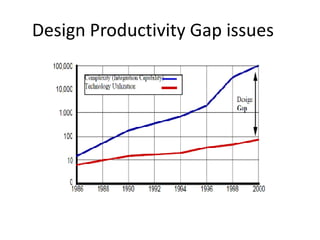
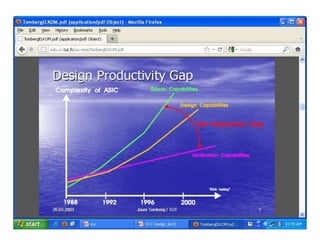
System on Chip (SoC) design aims to integrate heterogeneous components like processors, memory, analog circuits onto a single chip to achieve benefits like lower cost, power consumption, and physical size. Moore's law has allowed increasing transistor counts on chips over decades. Early SoCs integrated thousands of gates while modern ones integrate millions of transistors. Challenges include meeting time-to-market demands and managing increasing design complexity and verification requirements. Solutions involve raising the design process to higher abstraction levels, reusing pre-verified intellectual property blocks from different vendors to simplify verification.