This power point presentation summarizes elimination reactions, specifically 1,2 elimination reactions. It defines elimination reactions as reactions where two atoms or groups are removed from a reactant to form an unsaturated product. 1,2 elimination reactions eliminate atoms or groups from the 1 and 2 positions on a molecule. Three possible mechanisms are discussed: E2, E1, and E1cb. Evidence for the E2 mechanism includes kinetic isotope effects, the element effect showing dependence on leaving group ability, and the lack of hydrogen exchange. The Saytzeff rule and factors influencing its application, like stability and transition state crowding, are also covered.

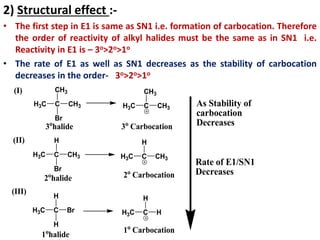
![Three Possible Mechanisms
1) The E2 Mechanism: (Elimination Bimolecular)
The breaking of Cα–Y bond, formation of the Л bond between
Cα-Cβ and breaking of Cβ–H bond takes place simultaneously.
c c
Alkene
cß ca
Y
H
+ H-B+
+ Y-
B:
E2,Base
Slow
c c
Y
H
B
T.S.
Substrate
Rate α [Substrate] [Base]
This mechanism has some similarities with SN2 mechanism-
a.It is bimolecular.
b.All bond formation and bond breakings are concerted.
c.Proceed through single T.S.
d.It is one step process.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-220127065636/85/1-5-elimination-reaction-4-320.jpg)
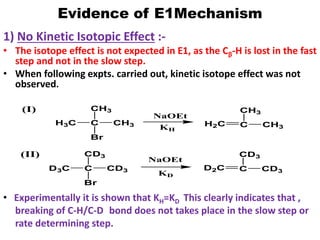
![2) The E1 Mechanism:
(Elimination Unimolecular)
The breaking of Cα–Y bond taks place in the slow step to
form a carbonium ion, which is then followed by fast breaking
of Cβ–H bond and formation of Cα-Cβ Л bond .
Rate α [Substrate]
This mechanism has some similarities with SN1 mechanism-
a.It is Unimolecular.
b.Formation of carbonium ion occurs in the slow step.
c.It is two step process.
c c
Alkene
cß ca
Y
H
+ H-B
E1
Slow
c c
H
Substrate Carbonium ion
+ Y
c c
H
Base
Fast
Carbonium ion
B:
(a)
(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-220127065636/85/1-5-elimination-reaction-5-320.jpg)
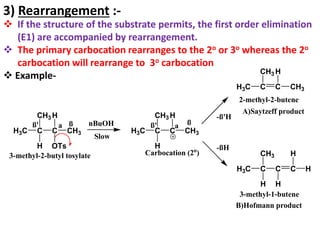
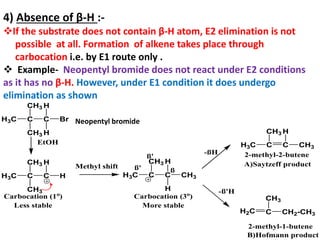
![3) The E1cB Mechanism:
(Elimination Proceeding through Conjugate base)
The breaking of Cβ–H bond taks place first to form a carbanion
or conjugate base of the substrate, followed by simultenious
formation of Cα-Cβ Л bond and breaking of Cα–Y bond.
Rate α [Substrate] [Base]
E2 and E1 mechanisms are very commonly observed but E1cB
mechanism is very rarely observed
c c
Alkene
cß ca
Y
H
+ H-B
E1cB
Slow
c c
Substrate Carbanion
+ Y
Base
Fast
B:
(a)
(b)
Y
Carbanion
c c
Y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-220127065636/85/1-5-elimination-reaction-6-320.jpg)
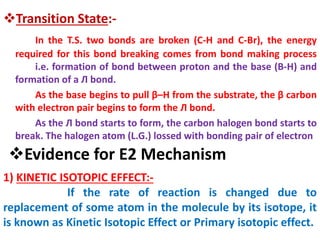
![The E2 Mechanism
Consider the following 1,2 elimination –
H3C CH
Br
CH3 + NaoMe H2C CH CH3 + NaBr + MeOH
a ß
ß
2-bromopropane Propene
Kinetics :- Rate α [Substrate] [Base]
Rate =K2 [2-bromopropane] [NaOMe]
Mechanism:- It is one step mechanism. The leaving group i.e. halogen atom
lossed with bonding e pair and β–H lossed without bonding e pair, to form
the double bond. All these operations occur simultaneously, in a single step
via single T.S.
c c
H
H3C H
H
Alkene
ca cß
H
H
H
Br
H
H3C + MeOH + Br-
MeO Base
Slow
c c
H
H
H3C
H
T.S.
2-bromopropane
Br H
OMe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-220127065636/85/1-5-elimination-reaction-7-320.jpg)
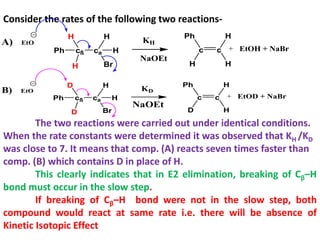


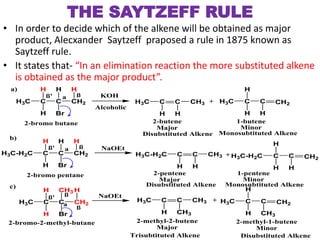

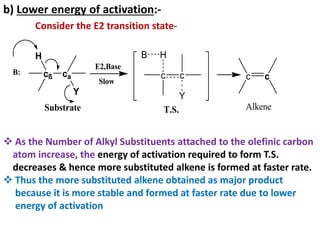
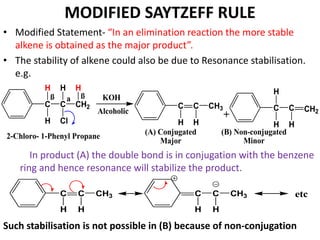

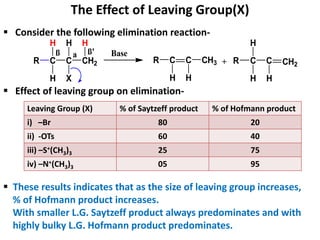
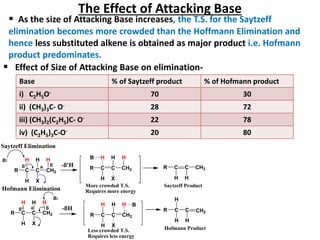
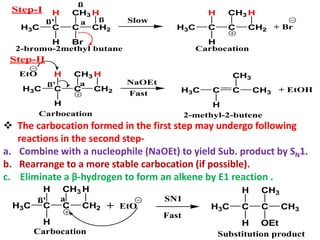
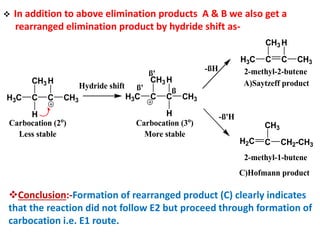
![The E1 Mechanism
Consider the following elimination reaction-
H3C C
H
C
H Br
ß' a
CH2
CH3 H
ß
H3C C C
H
ß
2-bromo-2methyl butane
NaOEt
EtOH
CH3
CH3
2-methyl-2-butene
+ NaBr + EtOH
Kinetics :- Rate α [Substrate]
Rate = K1 [2-bromo-2-methyl-butane]
Mechanism :-
The First step involves hetrolysis of Cα-Br bond to form carbocation
which is well stabilized by +I effect of alkyl groups.
This step is slow step and contains only one molecule and hence it
is unimolecular reaction.
The Second Step is a fast step and involves abstraction of β-
hydrogen by base to form an alkene.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-220127065636/85/1-5-elimination-reaction-21-320.jpg)