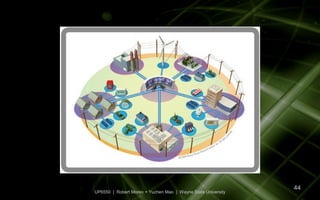
The document discusses the development of a smart grid in Michigan and its potential economic benefits, including job creation and enhanced energy efficiency through advanced technologies. It outlines the characteristics of the smart grid, its applications in consumer participation, and the role of key companies and public policies in fostering innovation in energy supply and management. It also highlights Michigan's initiatives, investment opportunities, and recommendations for workforce development in the smart grid sector.