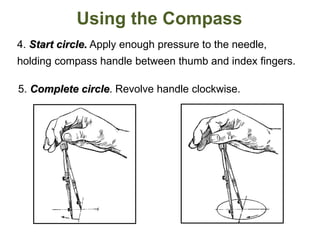
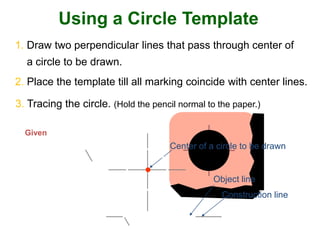
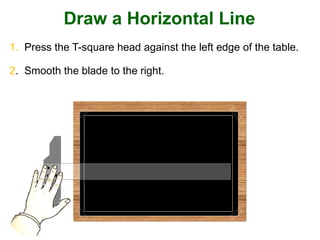
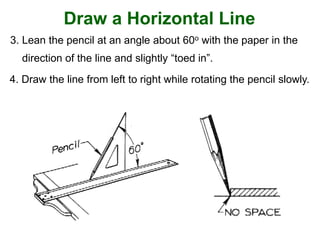
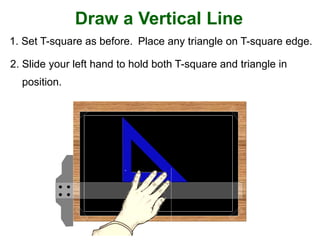
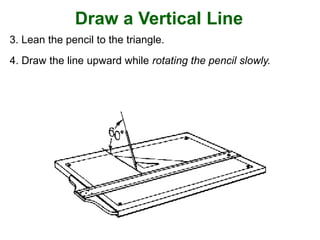
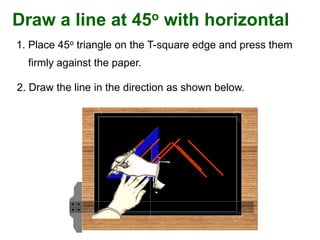
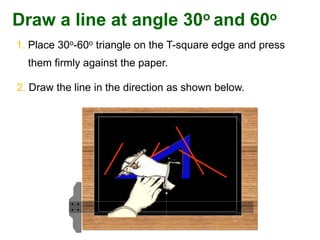
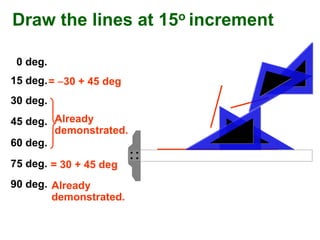
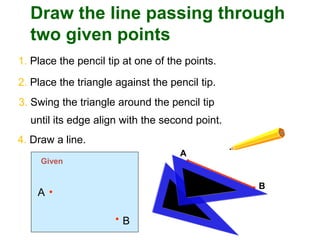
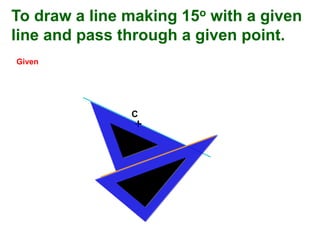
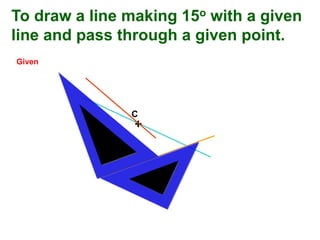
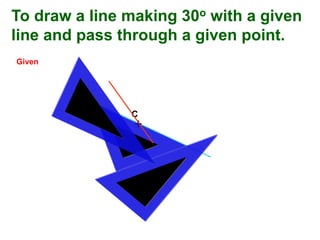
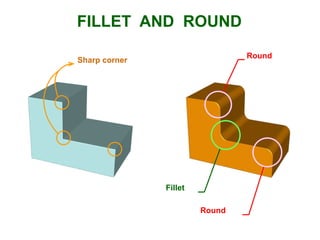
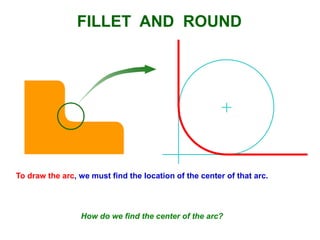
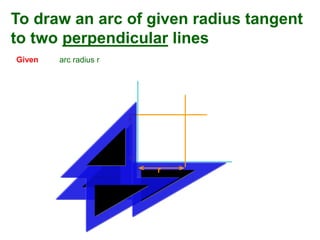
This document provides instructions for constructing and using different types of scales for technical drawing. It includes:
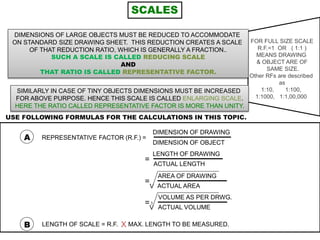
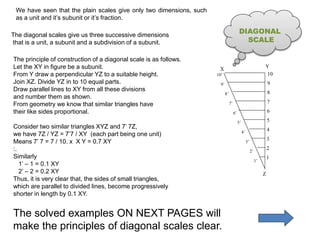
1. An overview of plain, diagonal, comparative, Vernier and cord scales. Plain scales can measure dimensions to one decimal place, while diagonal and Vernier scales provide more precision up to two decimals.
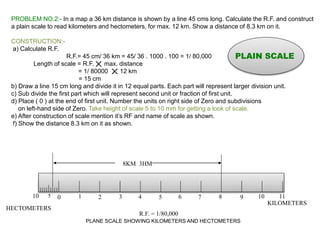
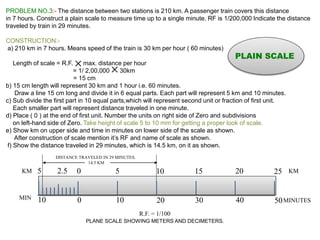
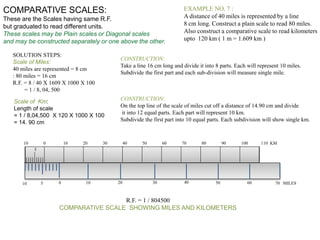
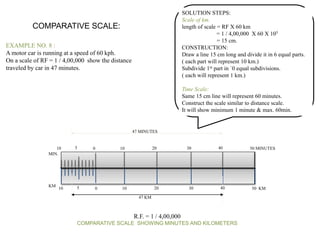
2. Examples of how to construct plain scales to specified ratios to measure distances and time intervals on technical drawings. This includes dividing lines into units, labeling scales, and indicating values.
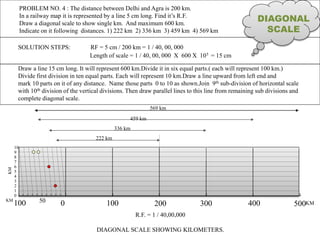
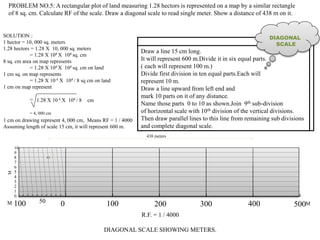
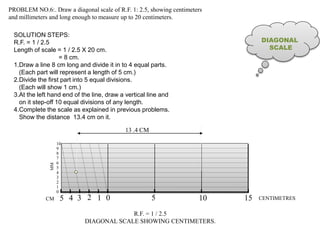
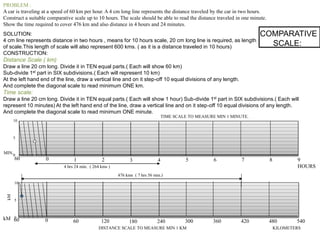
3. Three practice problems for students to construct plain scales showing distances, calculate representative factors, and indicate values on the scales. This helps students learn how to appropriately scale measurements for technical drawings.