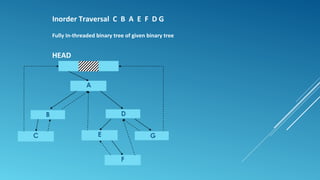
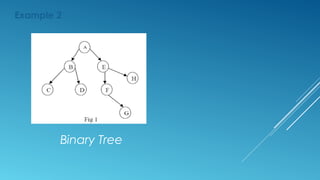
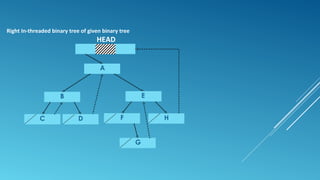
A threaded binary tree is a binary tree that removes NULL pointers and replaces them with threads. Threads are pointers that connect nodes in a specific traversal order, such as inorder. For inorder traversal, threads connect each node to its predecessor and successor. This allows faster traversal without a stack. Threaded binary trees distinguish threads from structural links using negative addresses or boolean flags per pointer. While faster for some operations, they are slower for insertions and deletions and cannot share subtrees.