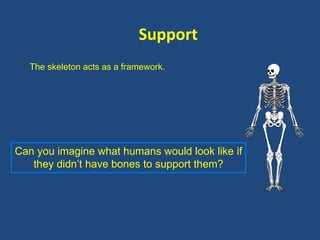
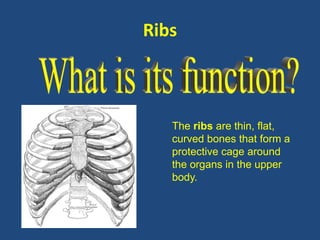
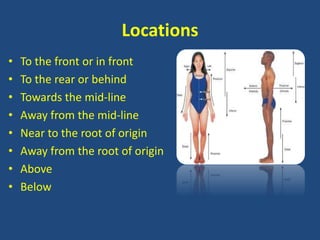
This document provides an overview of a unit on anatomy and physiology related to the skeletal system. It outlines four learning outcomes focusing on identifying skeletal functions and bones. Several in-class activities are described, including identifying what students already know about anatomy, discussing skeletal functions, and having students label bones on a diagram. Formative assessments include writing about skeletal functions and defining anatomical terms. Additional resources for further reading are also provided.