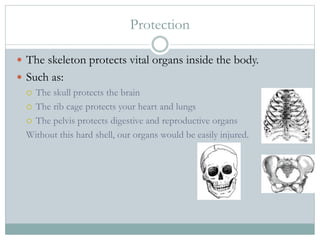
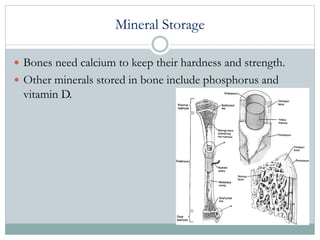
The human skeleton has 206 bones that perform several essential functions: providing structure and shape to the body like a framework; protecting vital organs like the brain and lungs; enabling movement through joints and muscles pulling on bones; producing blood cells in the marrow; and storing important minerals like calcium. The skeleton is critical to survival, as without it our organs would be easily injured and our bodies would have no structure or ability to move.