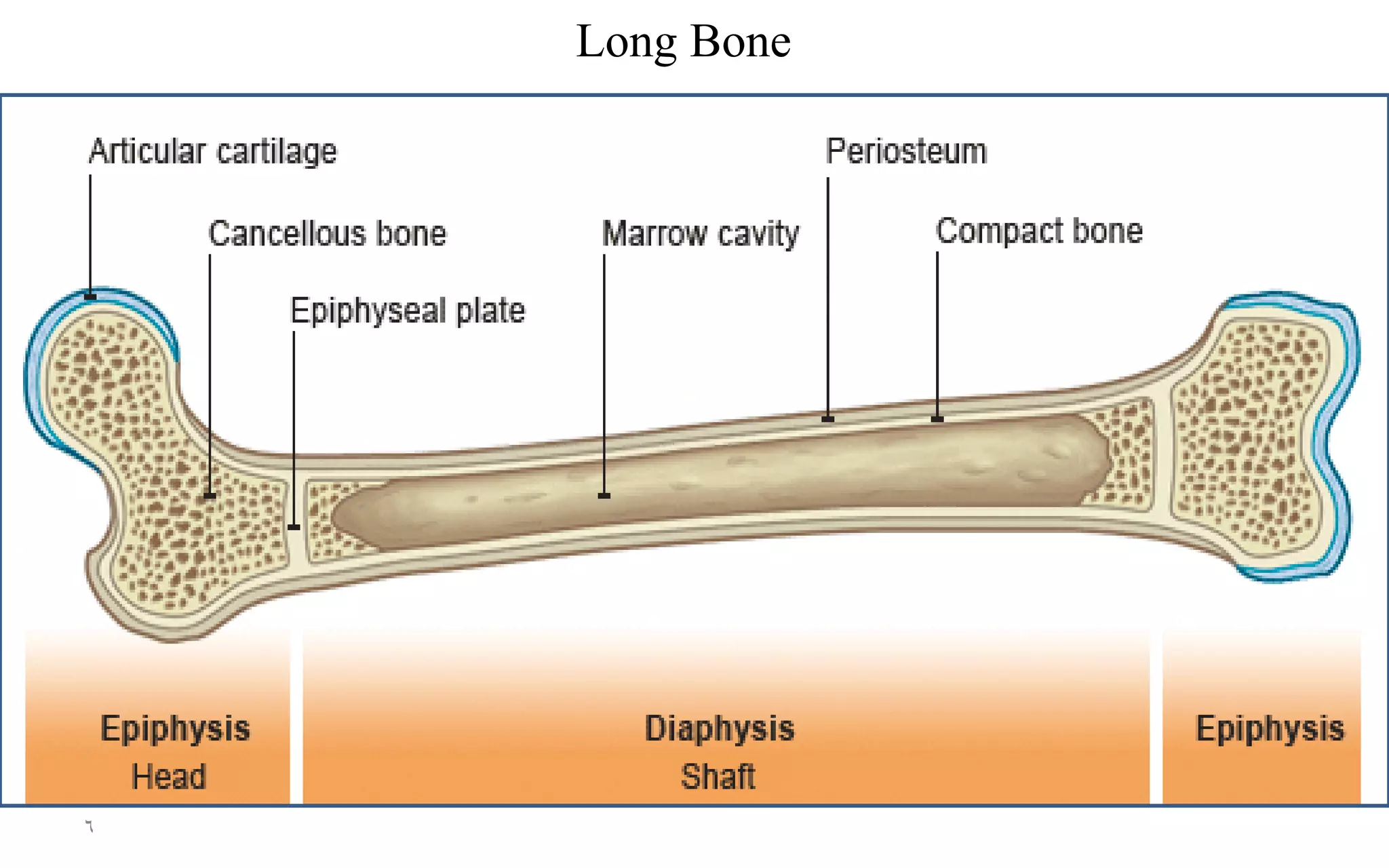
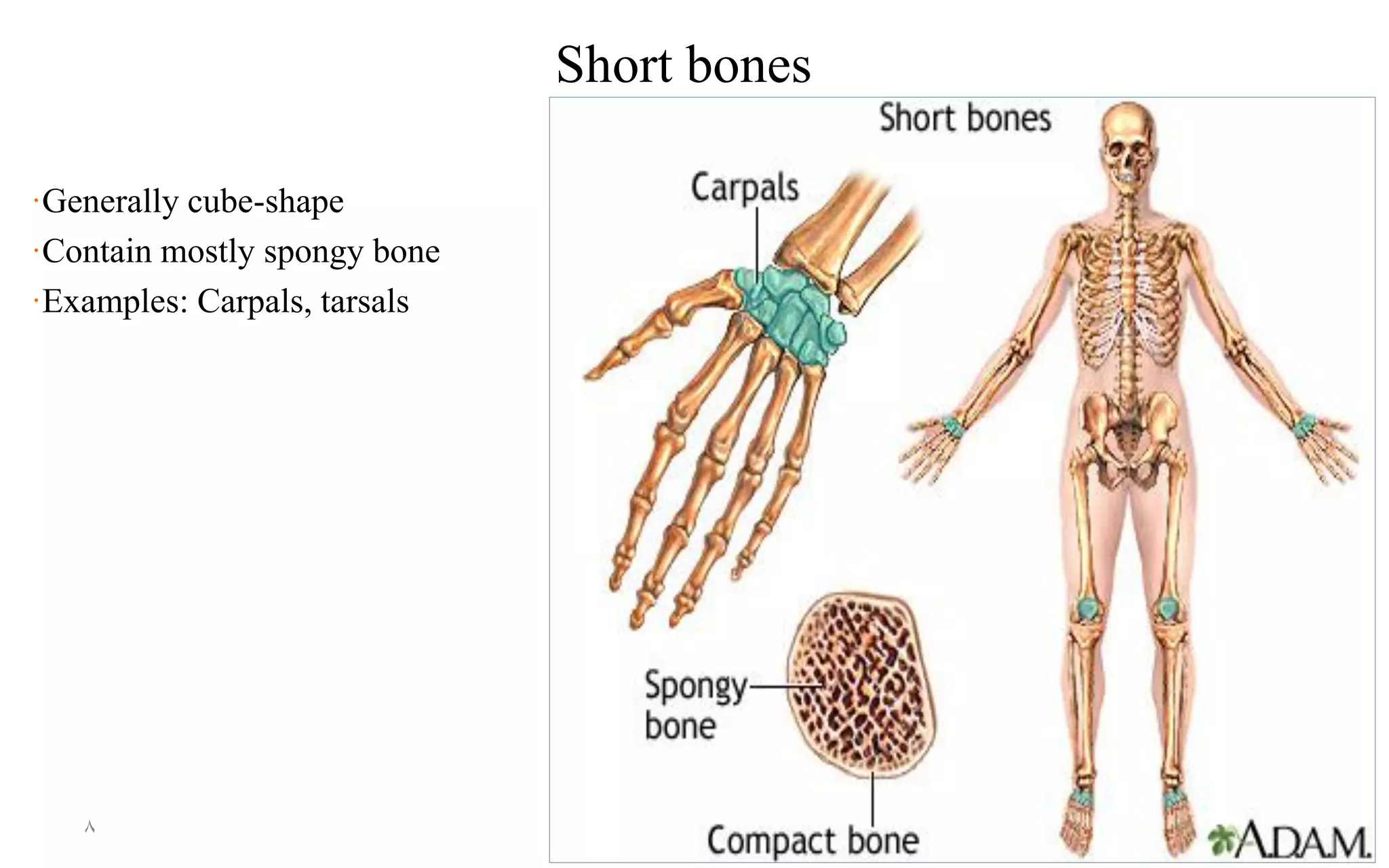
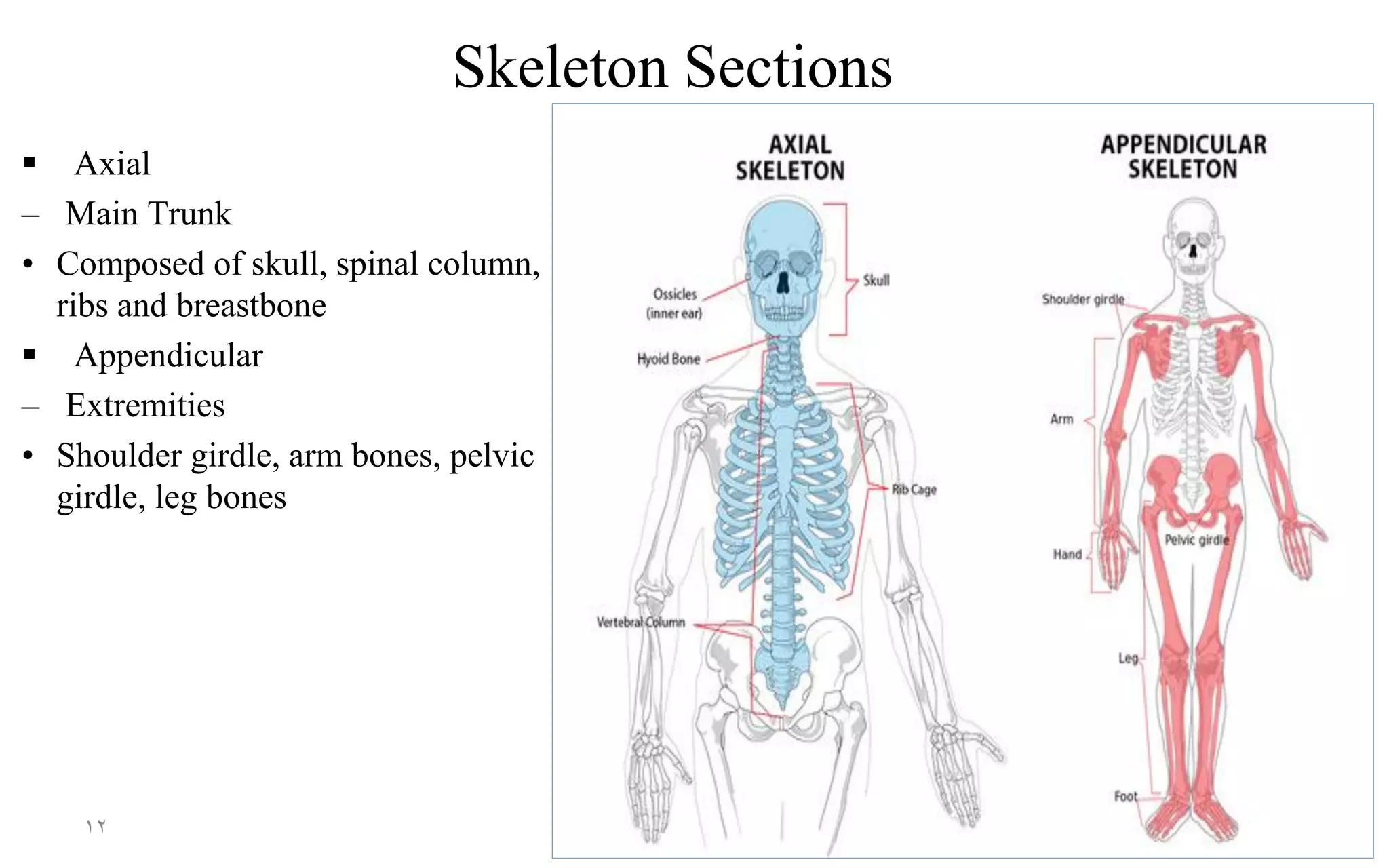
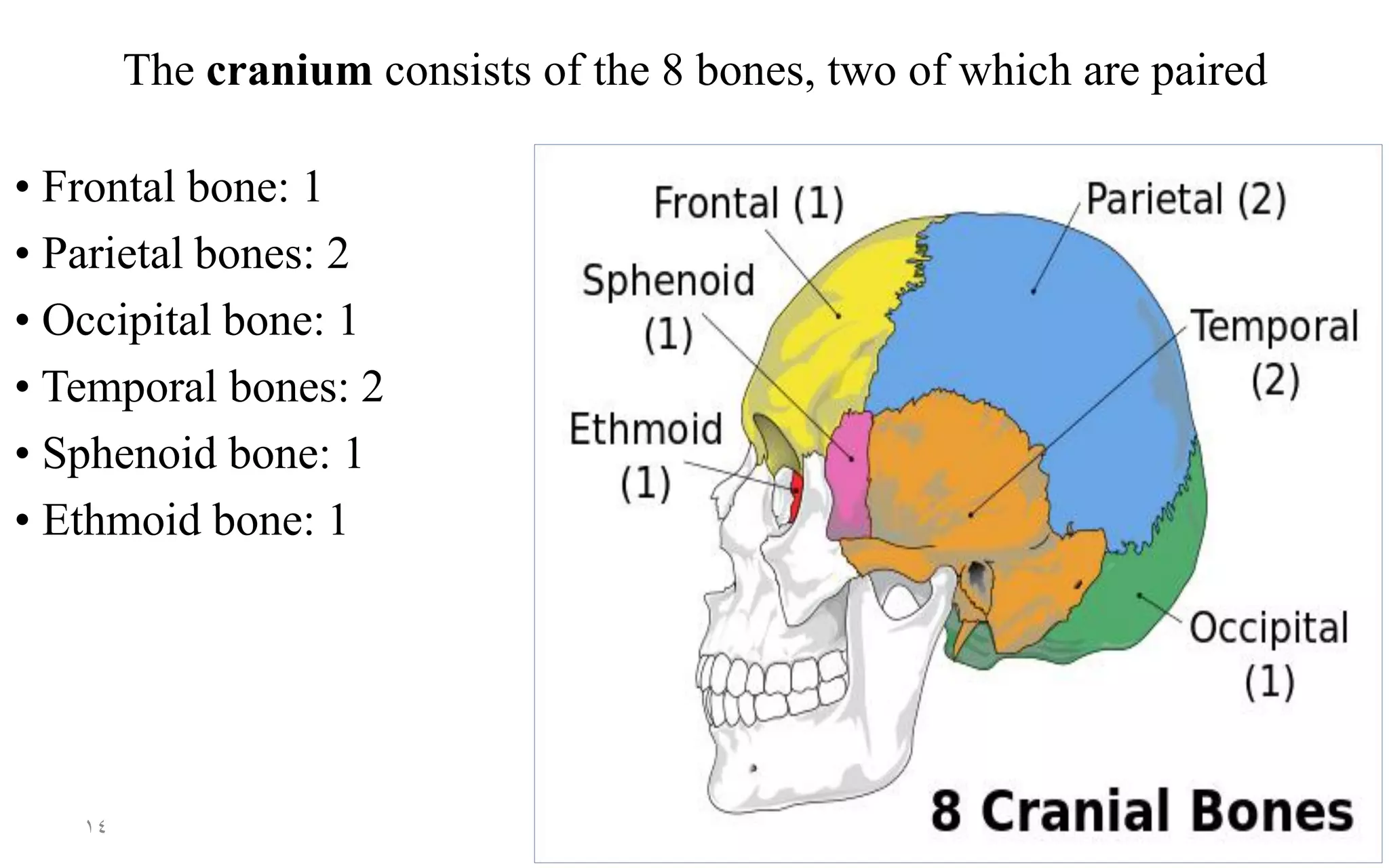
The skeletal system consists of 206 bones and connective tissues that connect them. It performs vital functions like providing a framework to support the body, protecting organs, enabling movement through muscle attachment to bones, producing blood cells, and storing minerals. The skeletal system includes long bones in the limbs, short bones in the hands and feet, flat bones like in the skull, and irregular bones like vertebrae. It is divided into the axial skeleton of the trunk and appendicular skeleton of the extremities. The skull contains cranium and facial bones that protect the brain and house senses.