Embed presentation
Download to read offline

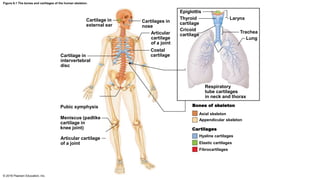


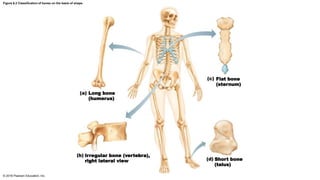
The human skeleton is divided into two groups: 1) The axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage along the long axis of the body. 2) The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs and are attached to the axial skeleton by girdles. Bones are also classified into four shapes: long bones in the limbs, short cube-shaped bones in the wrists and ankles, flat and slightly curved bones like the sternum and ribs, and irregularly shaped bones like the vertebrae and hip bones.




