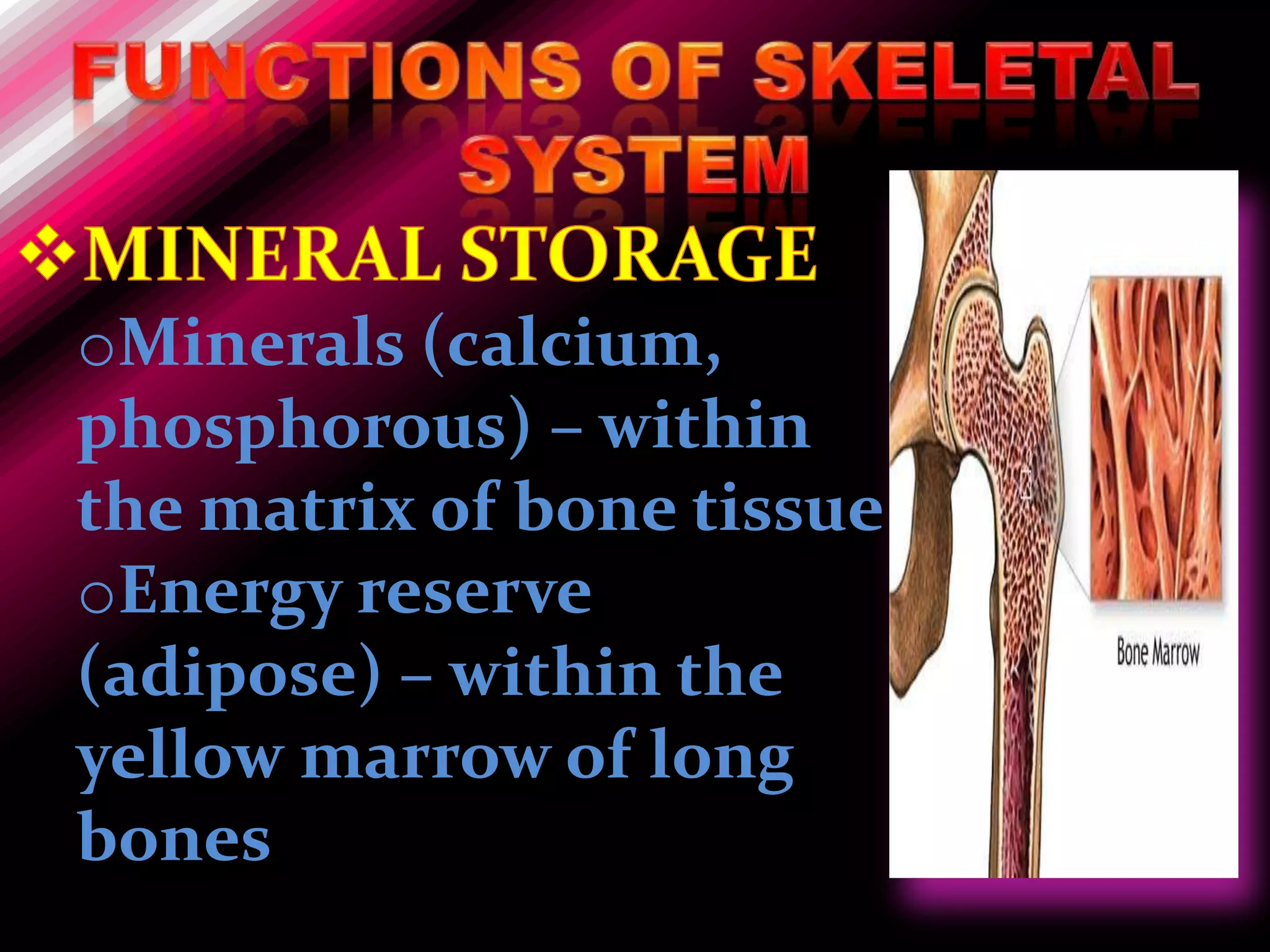
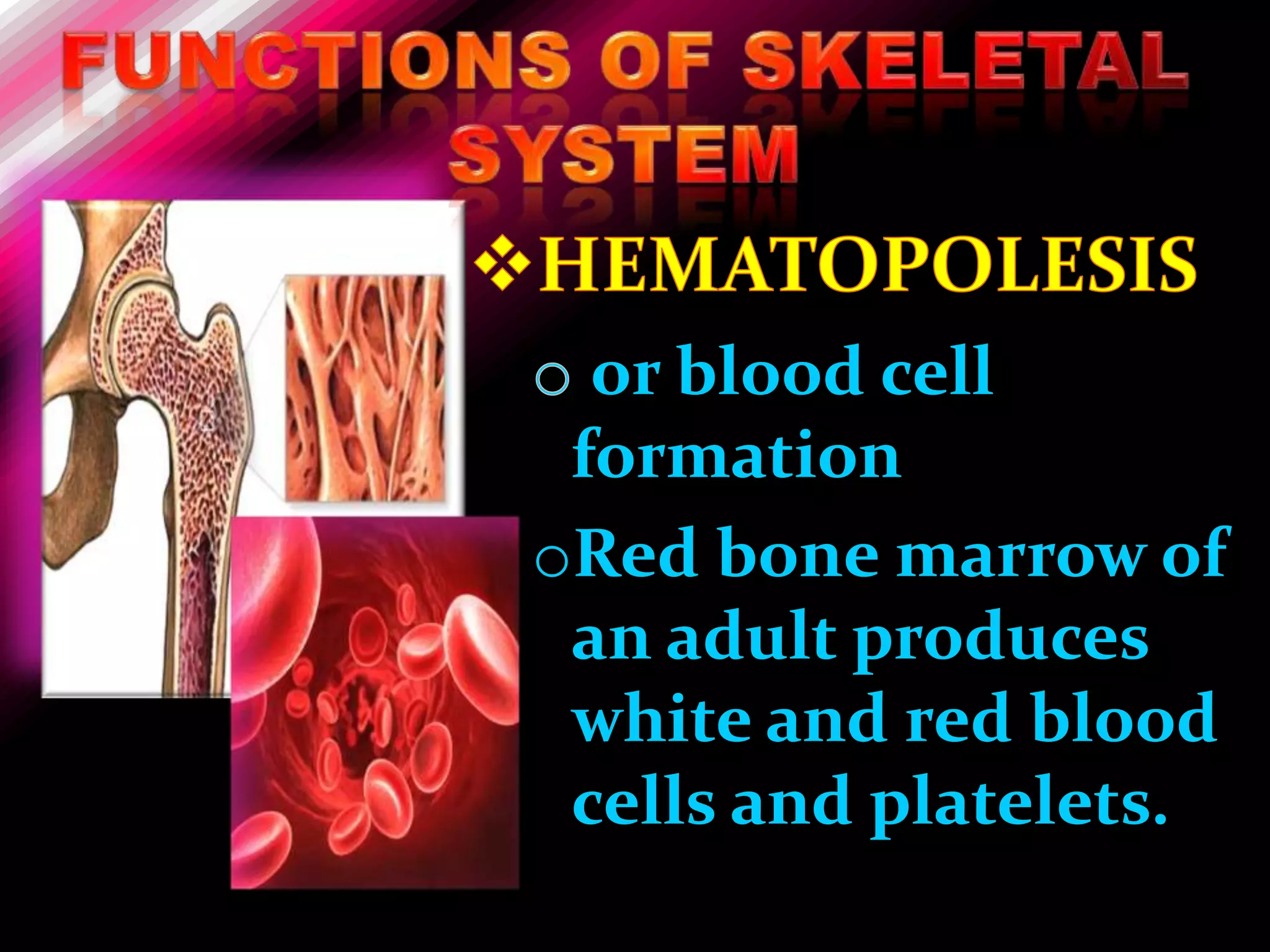
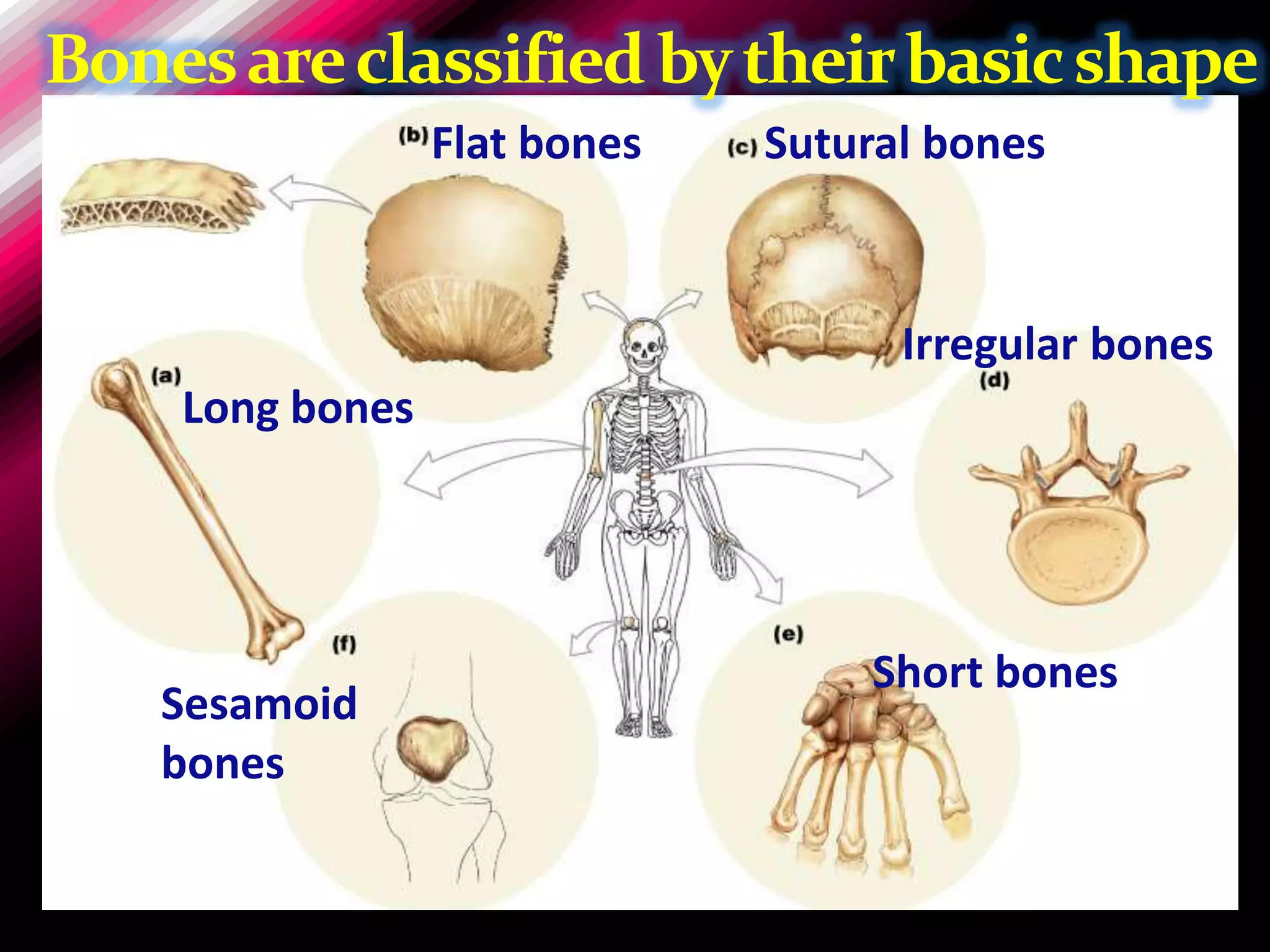
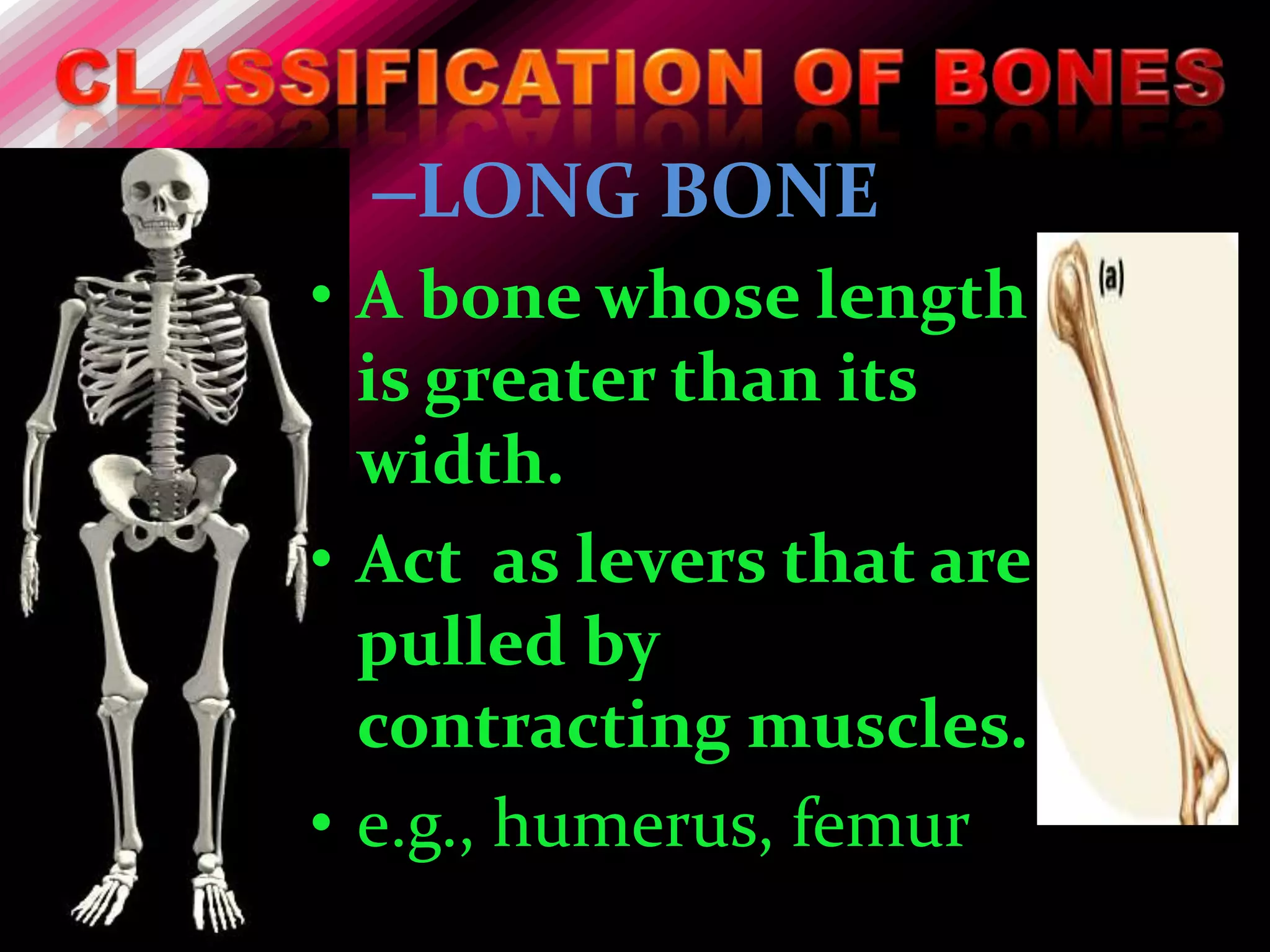
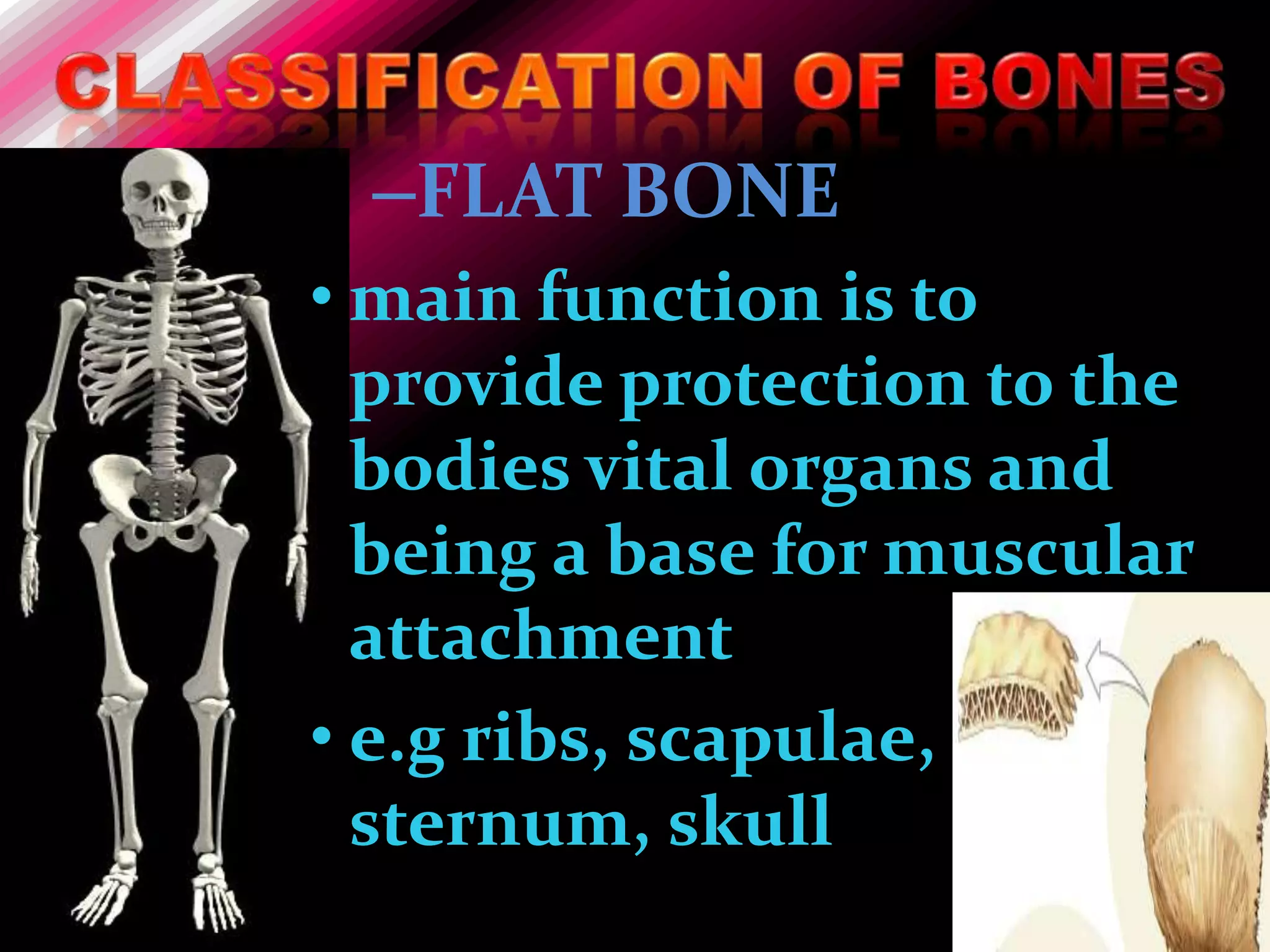
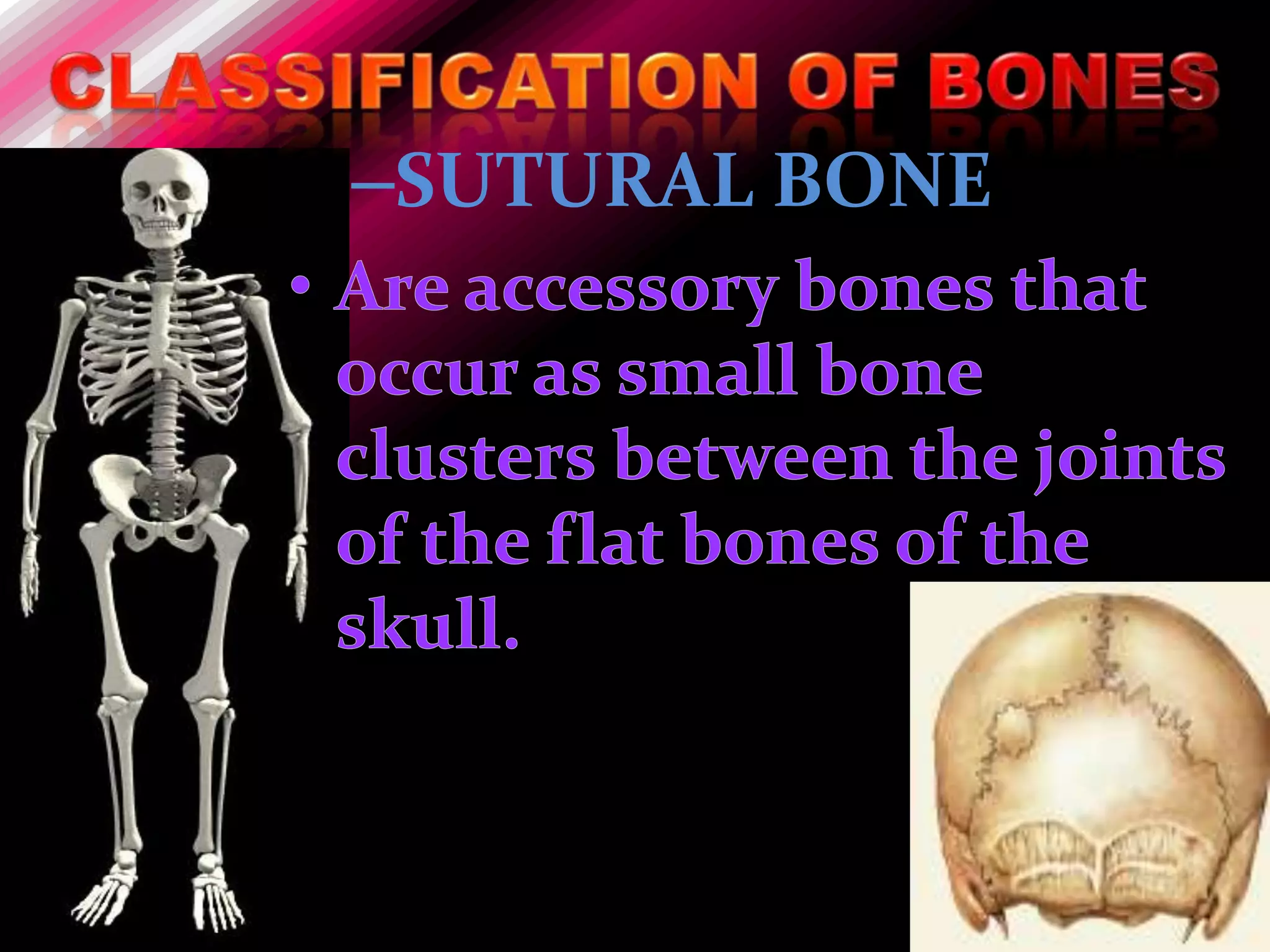
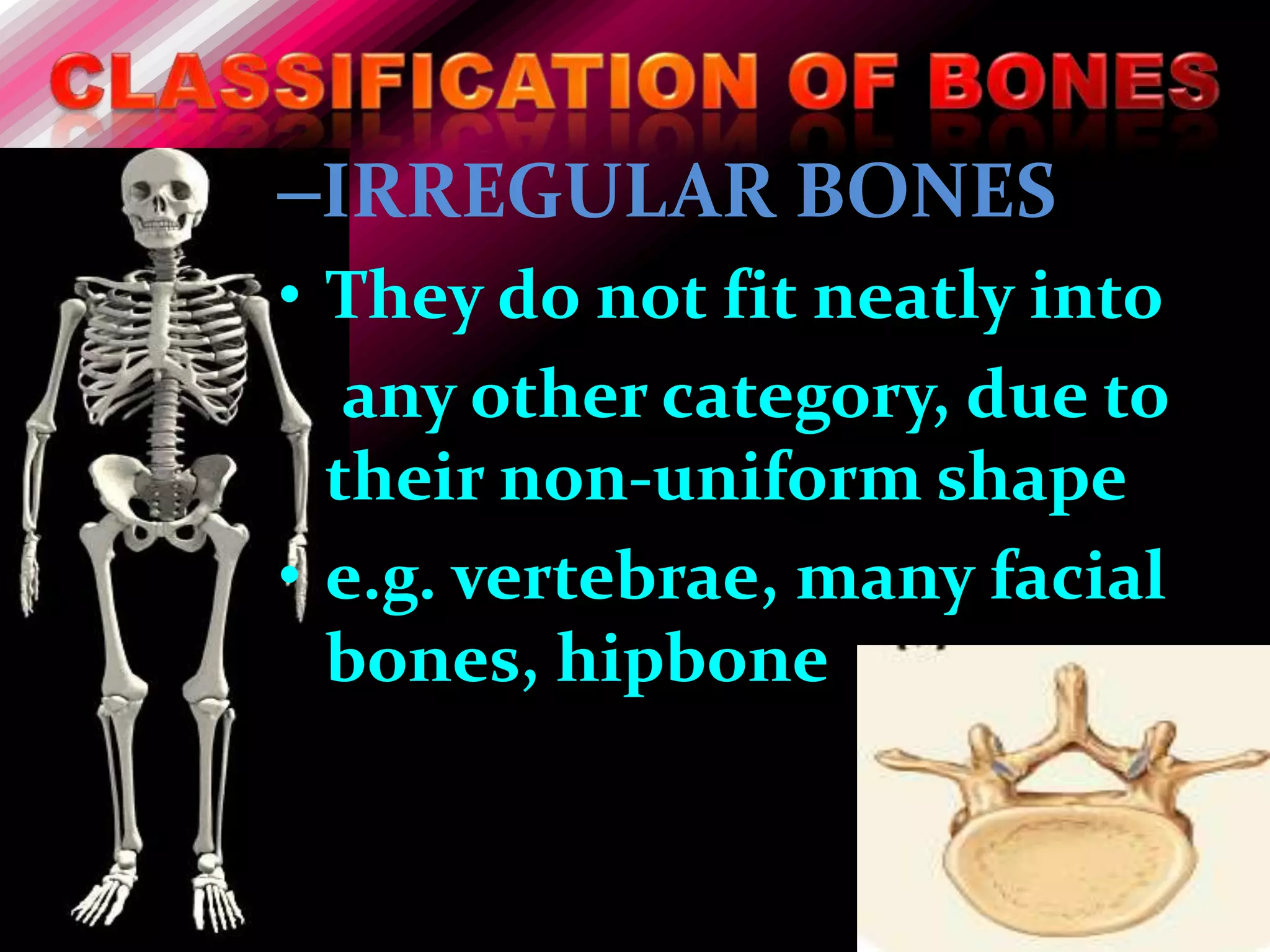
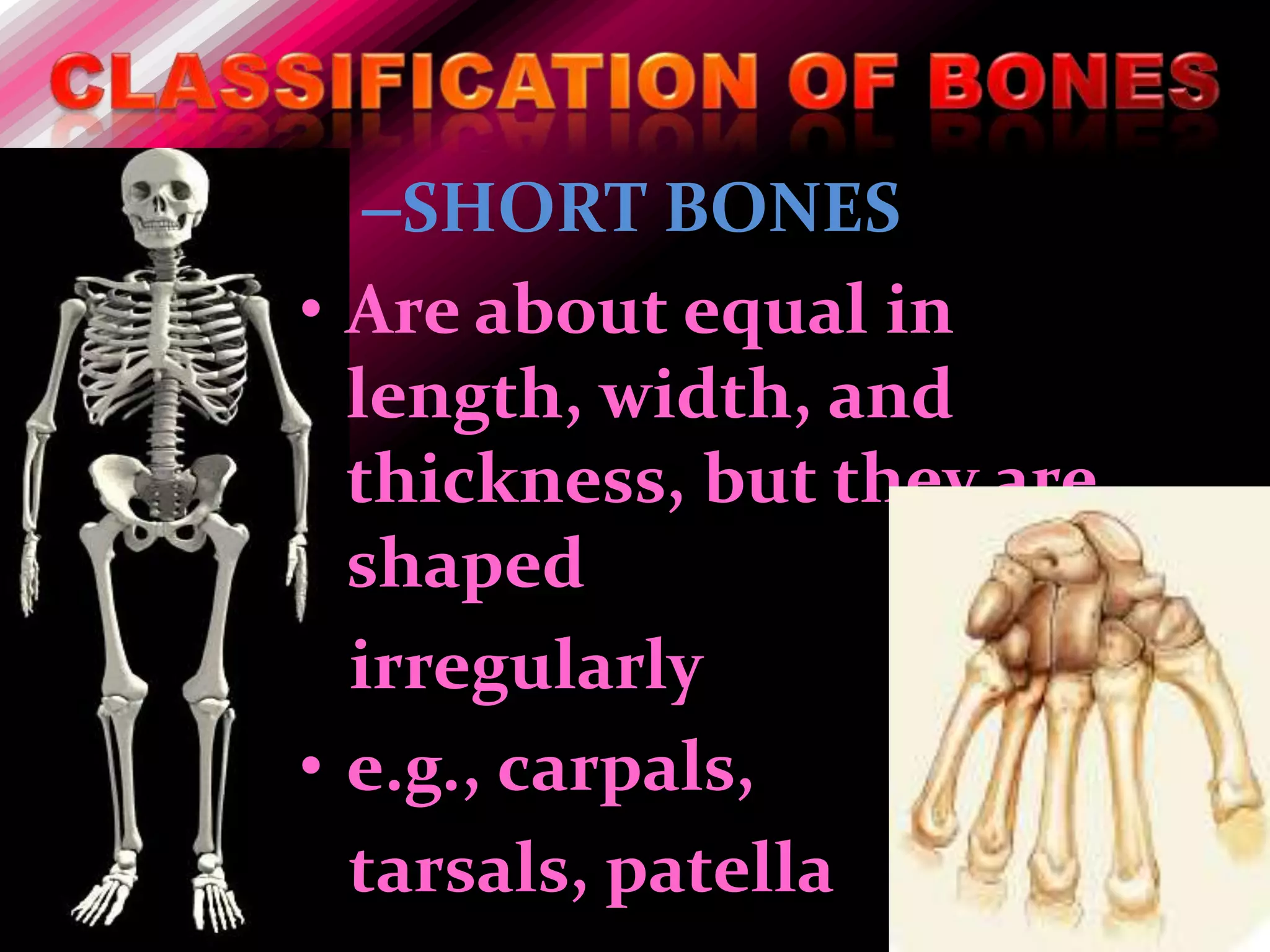
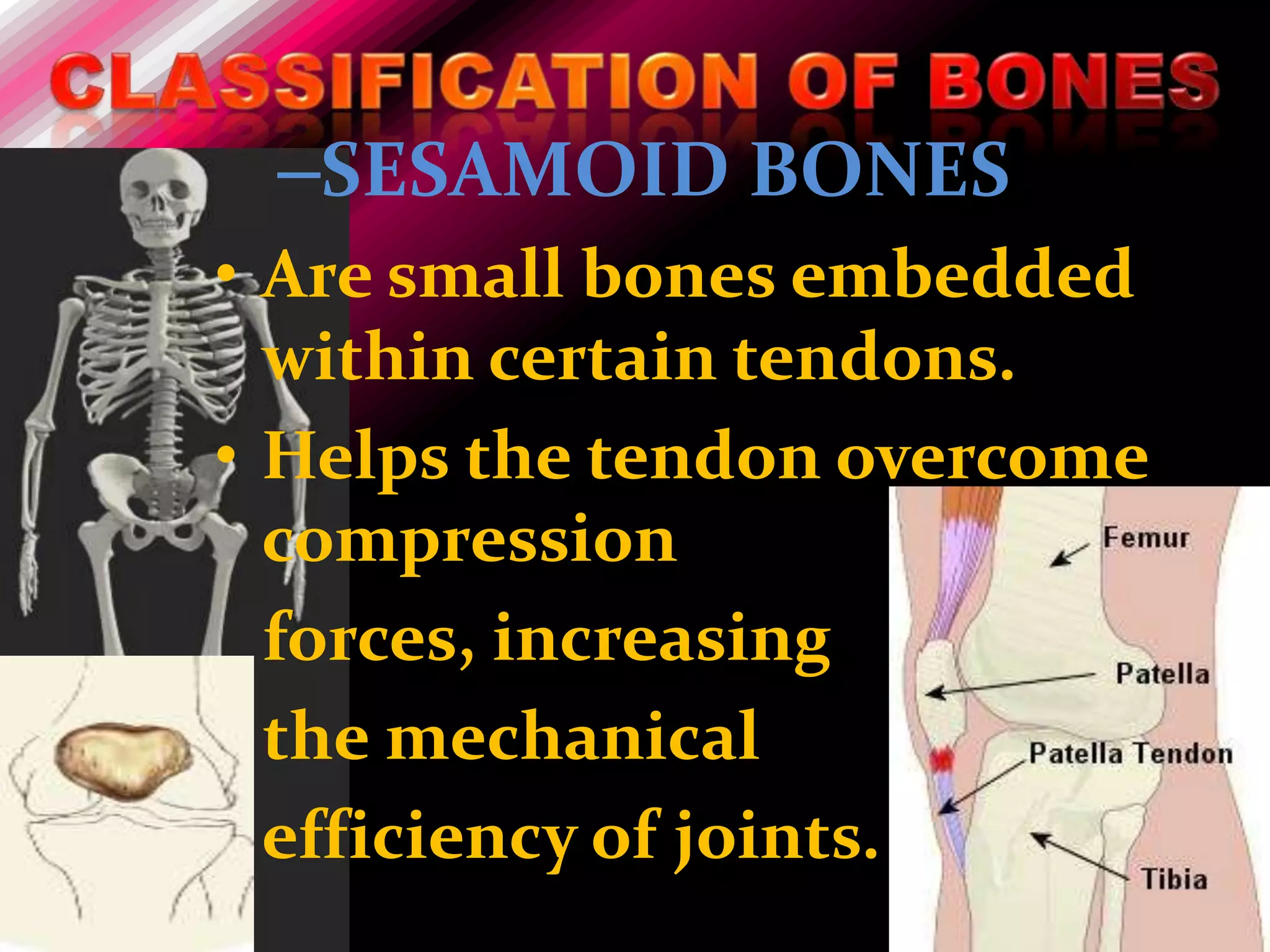
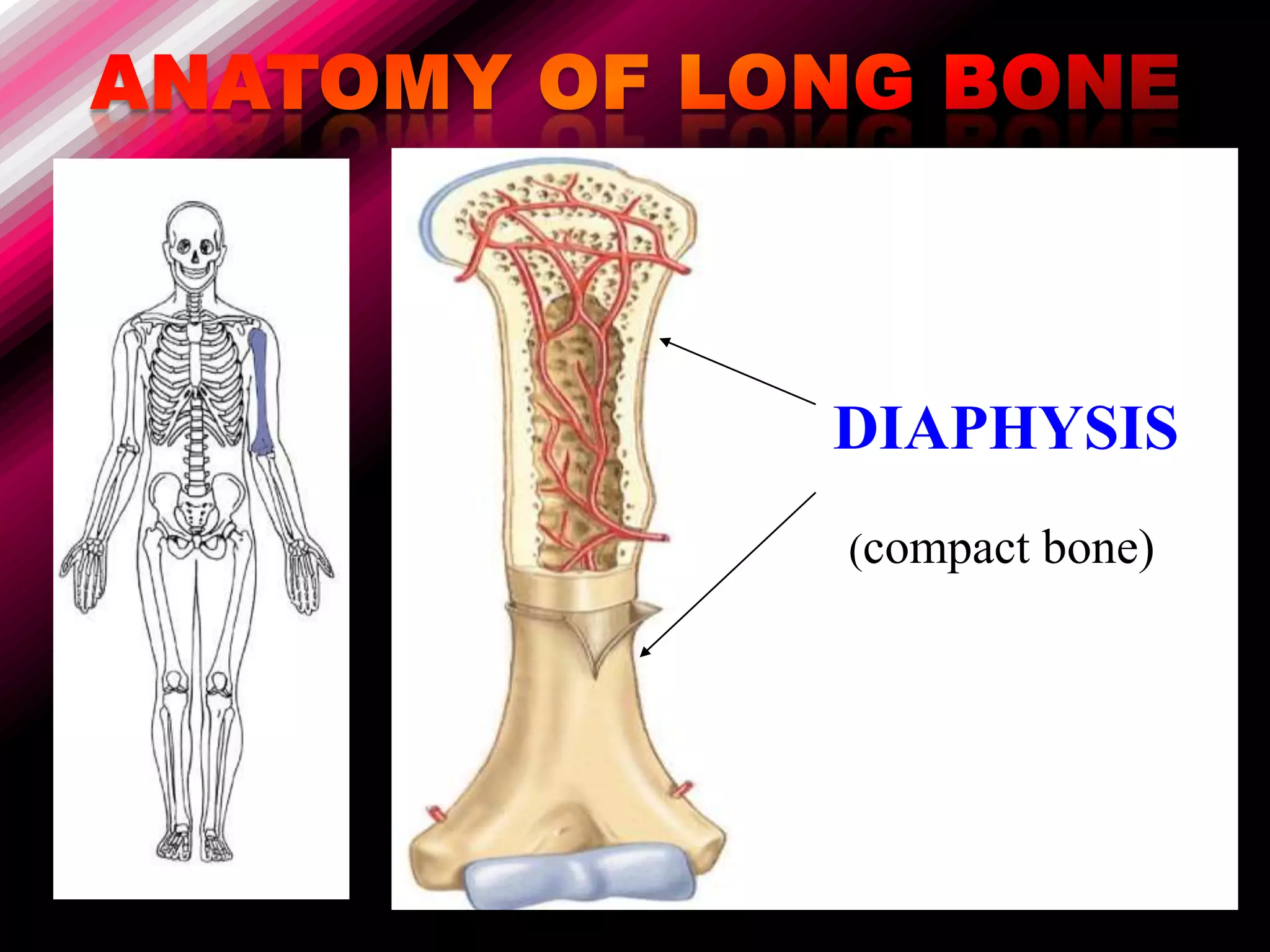
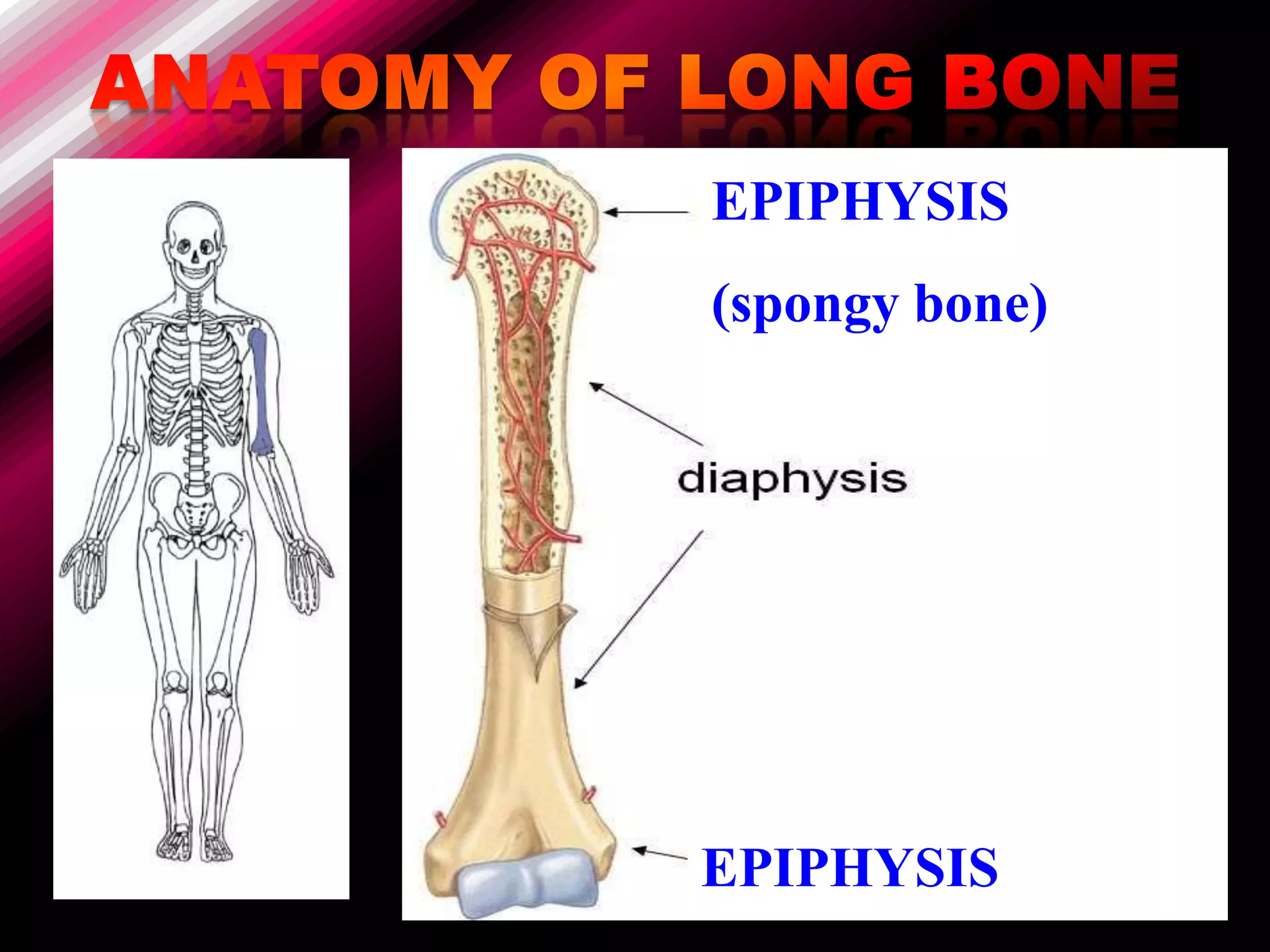
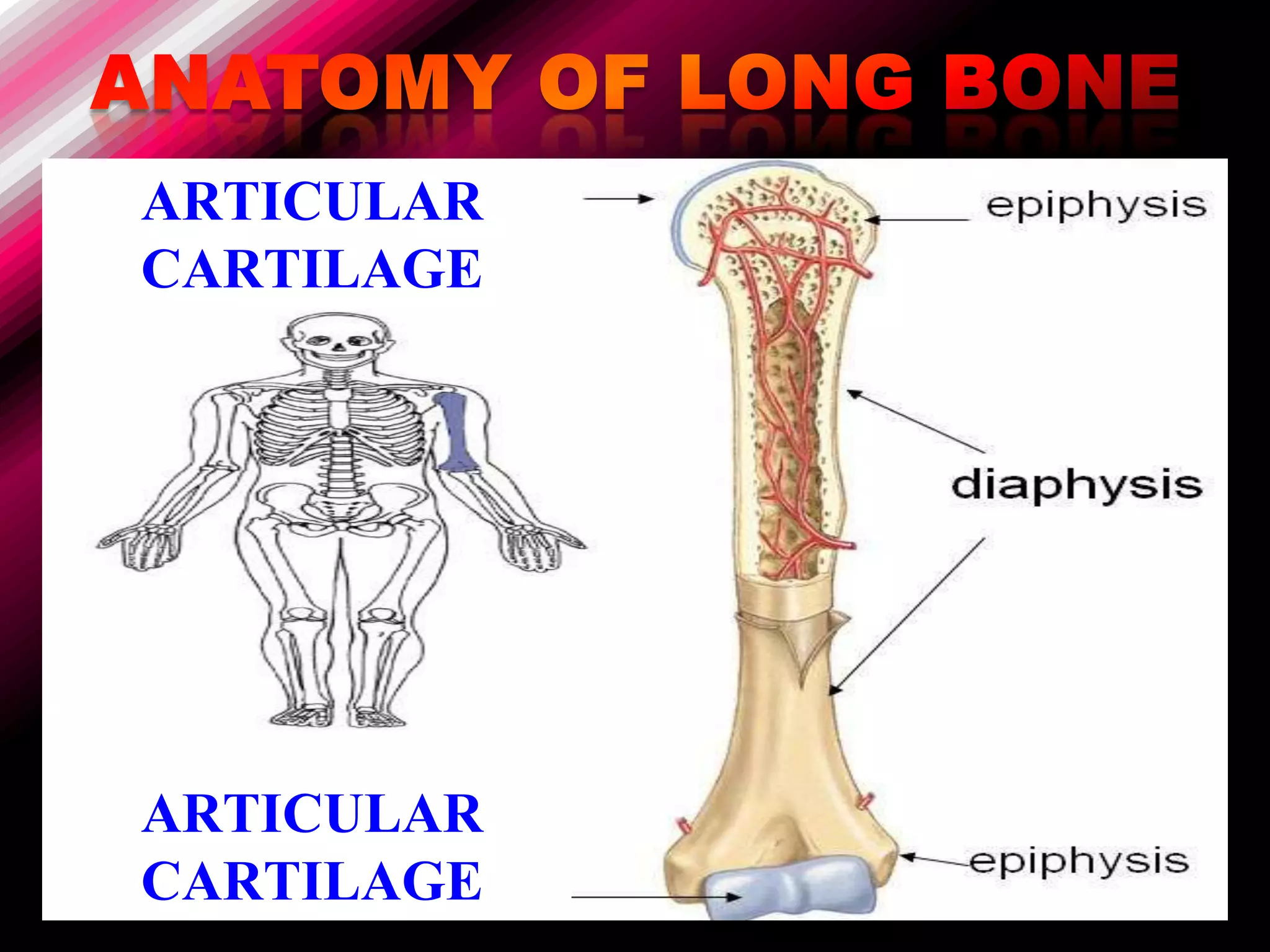
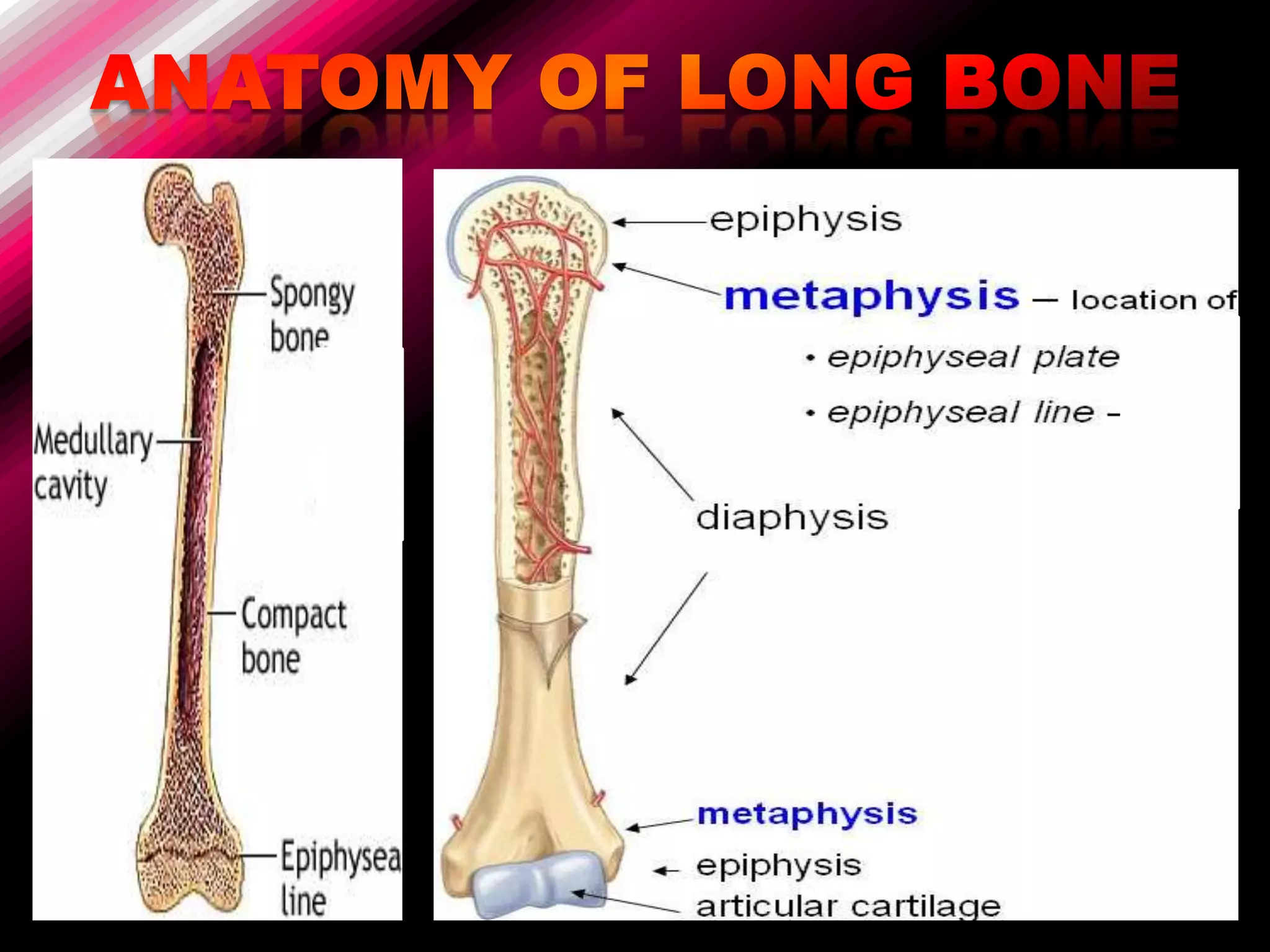
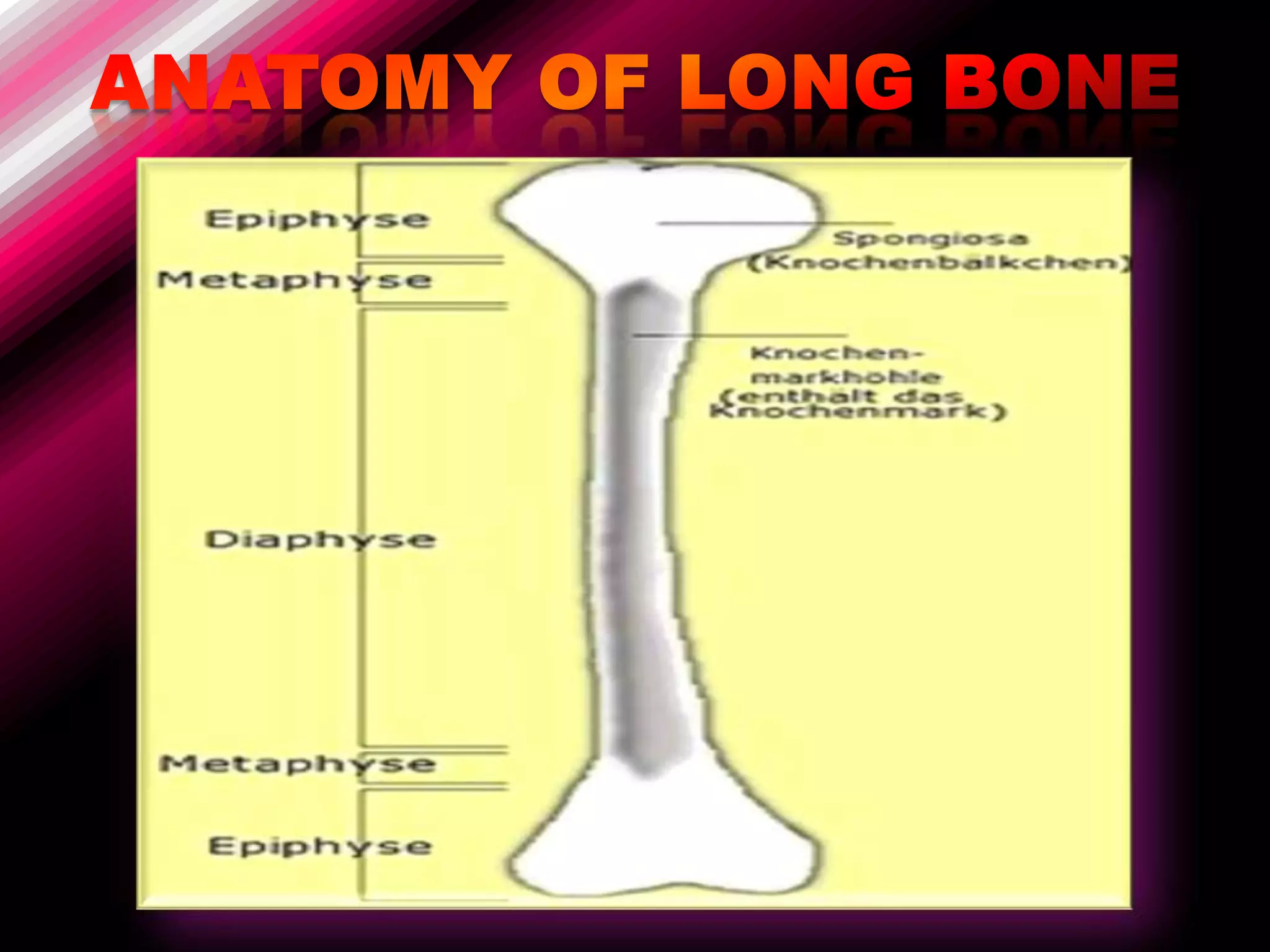
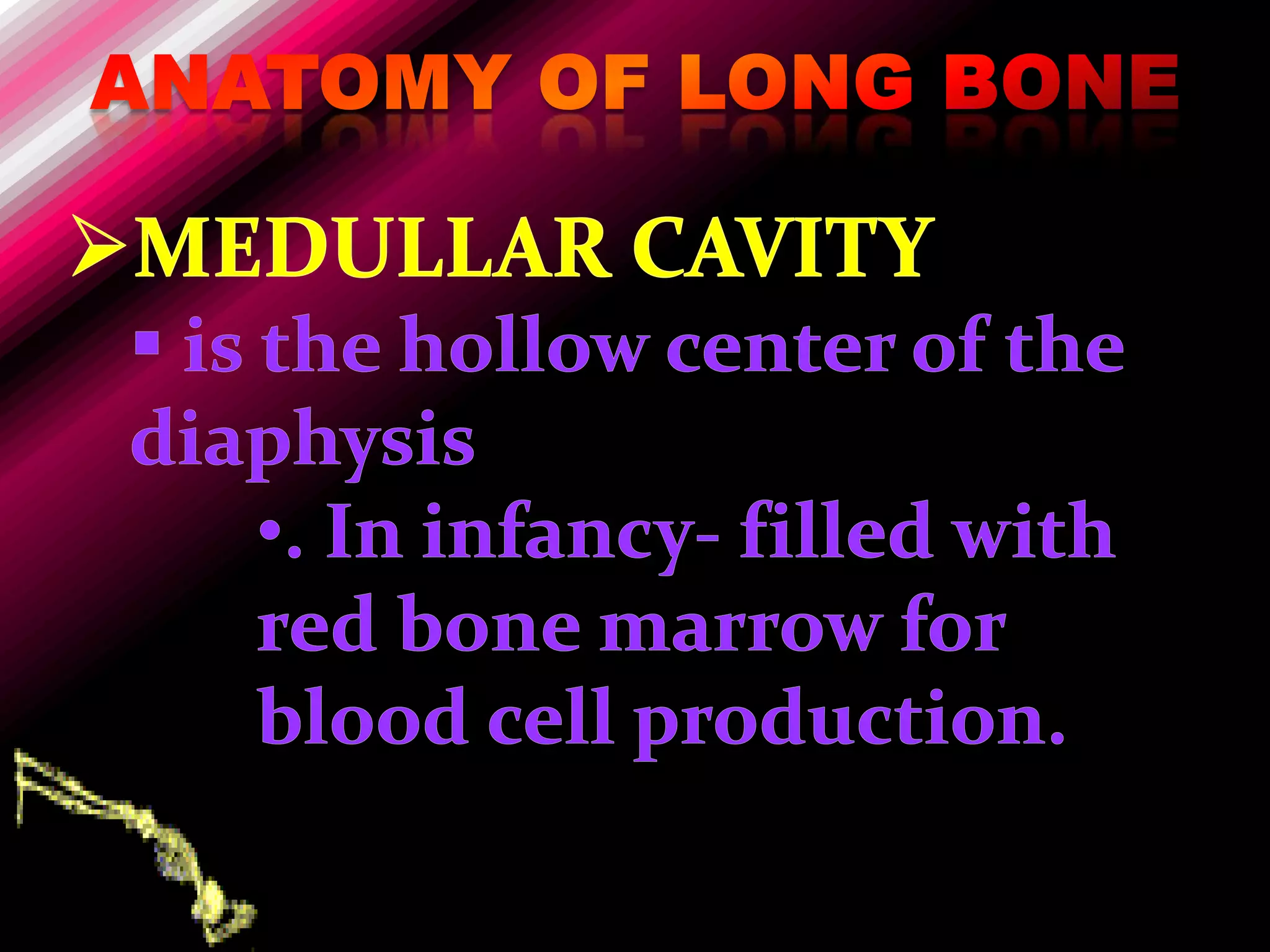
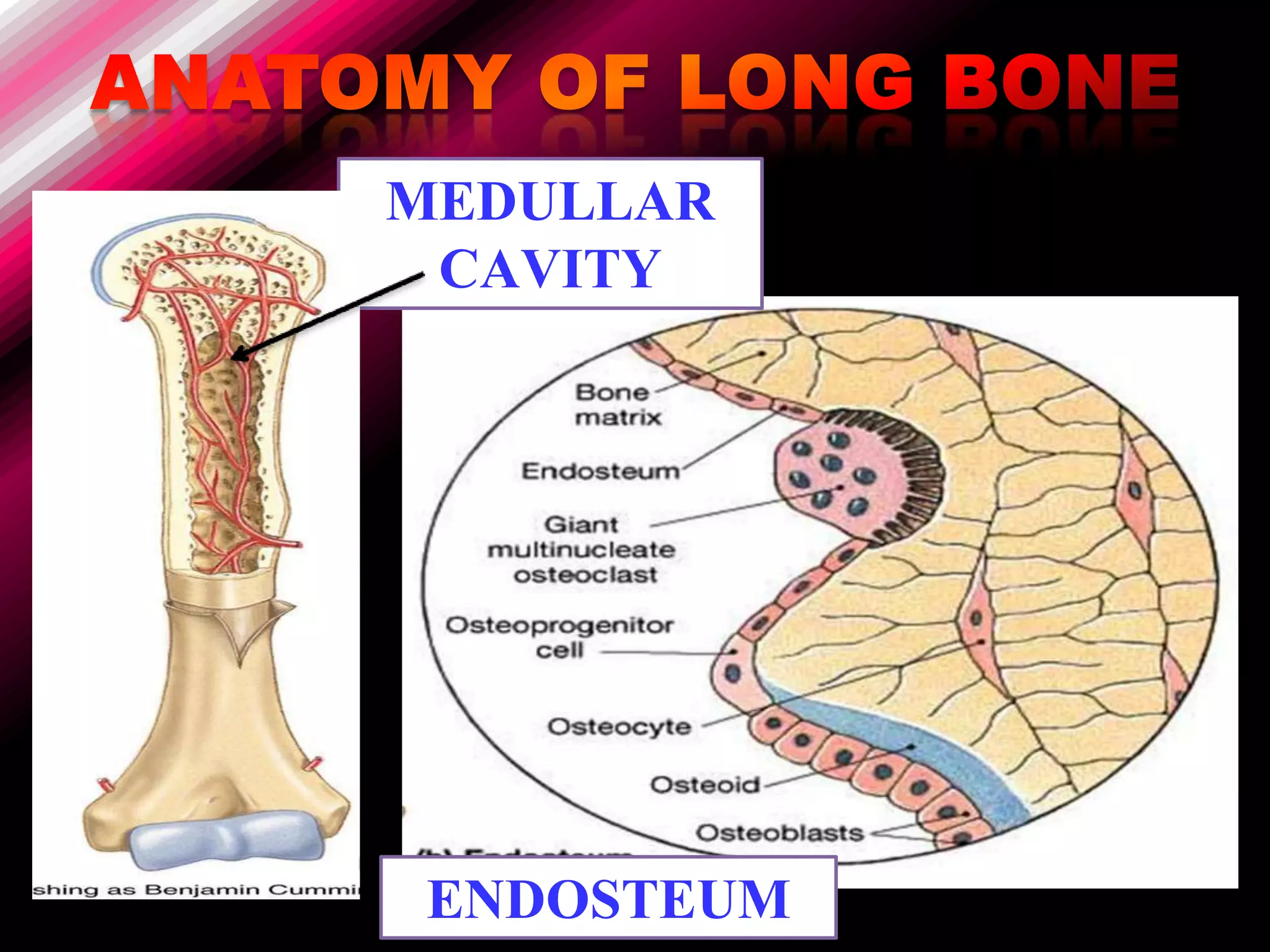
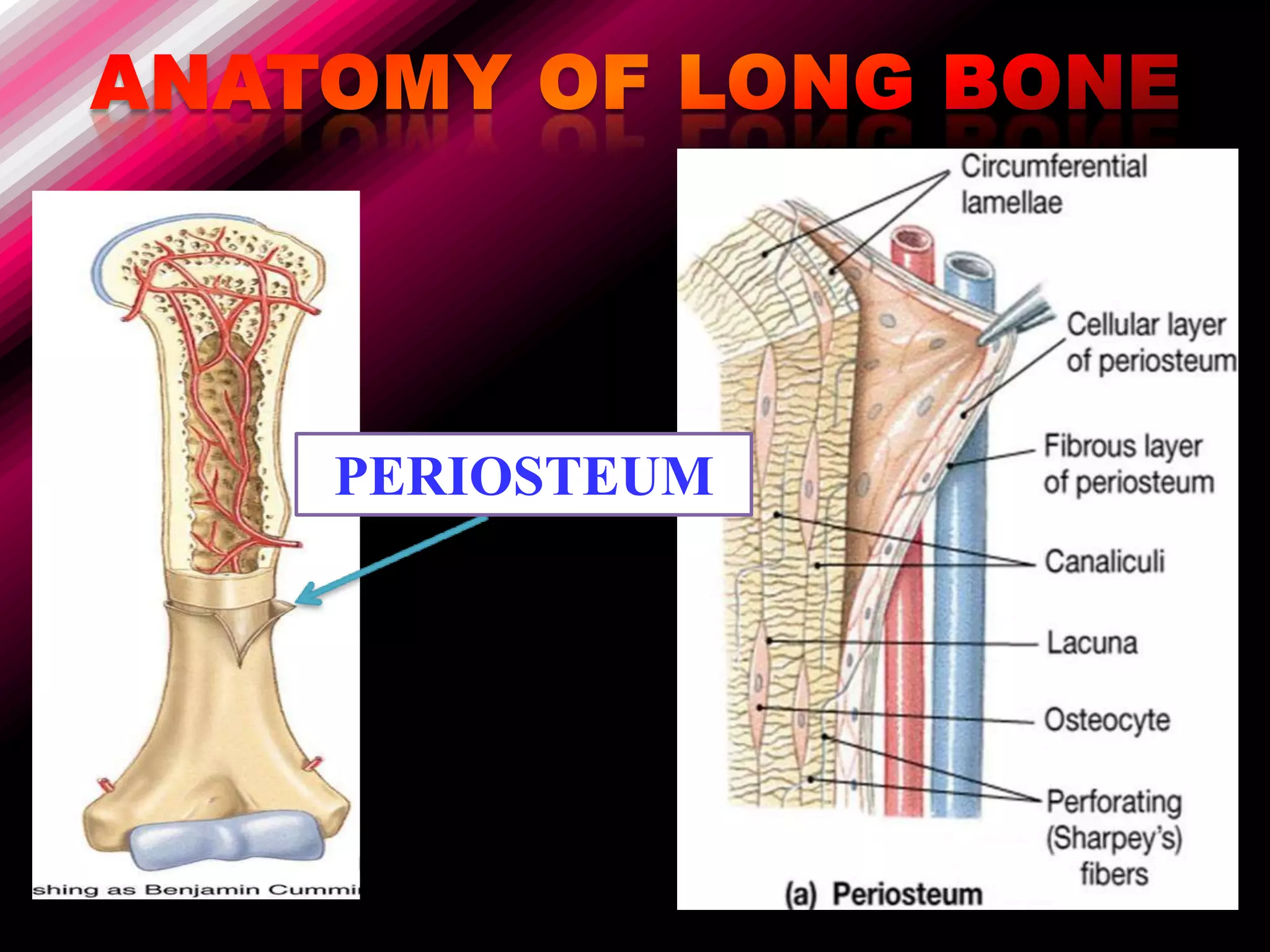
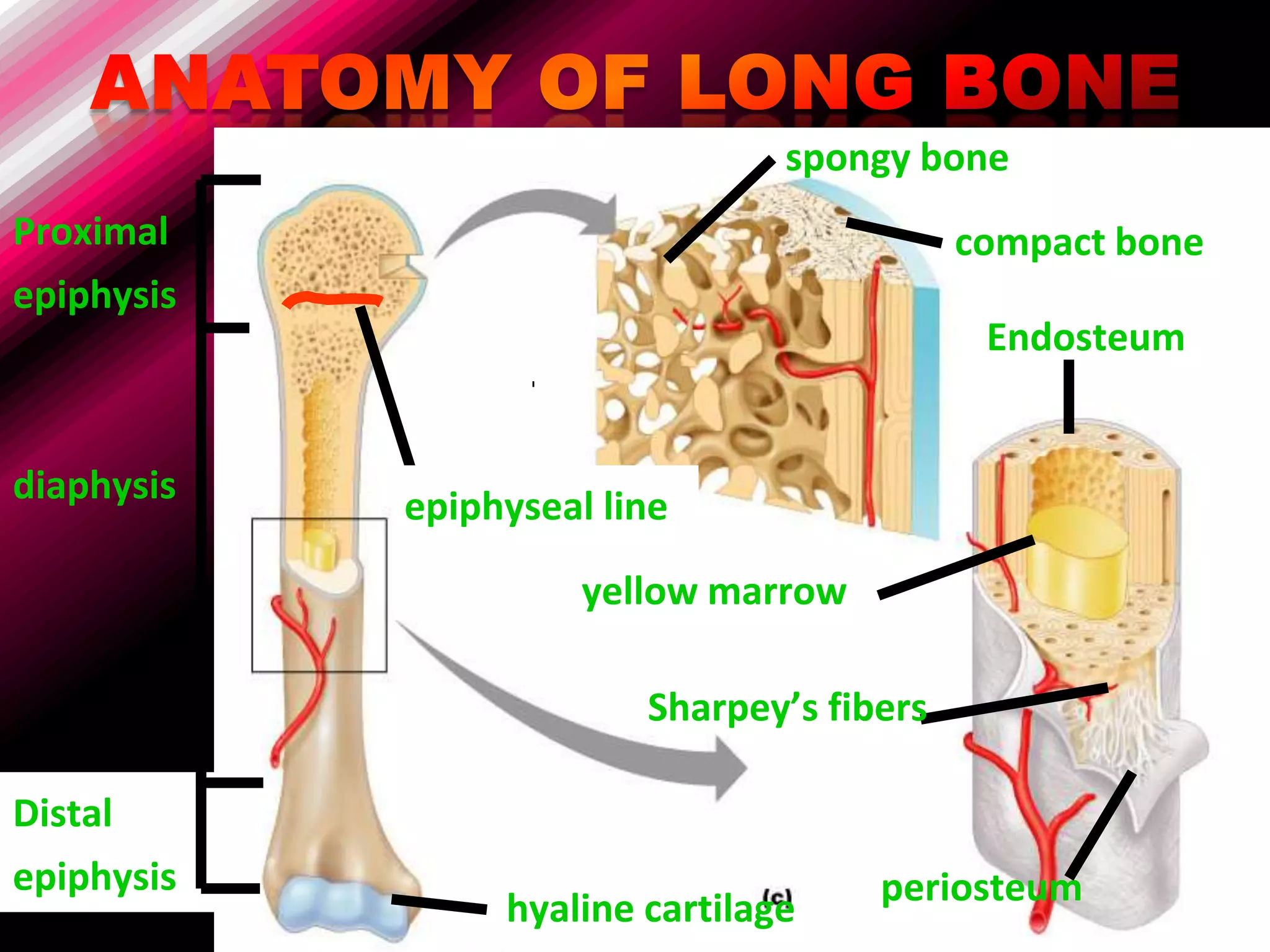
The skeleton is composed of bones that provide structure, protect organs, allow movement, and store minerals. Bones are classified by their shape as long, flat, irregular, short, or sesamoid. Long bones act as levers pulled by muscles and have a hollow shaft (diaphysis) of compact bone surrounded by spongy bone in the ends (epiphyses). Bones grow in childhood as the epiphyseal plate ossifies. The periosteum and endosteum lining bones are involved in growth, repair, and marrow production of red and white blood cells.