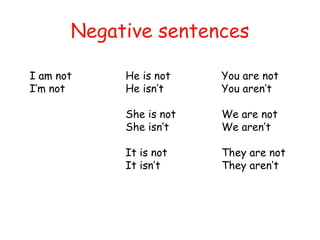
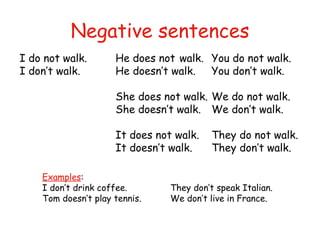
The document covers the usage of present simple and present continuous tenses in English, including affirmative, negative, and interrogative forms. It provides examples related to daily habits, routines, and actions happening at the moment, as well as spelling rules for verbs in these tenses. Additionally, it emphasizes the distinction between general facts and actions in progress.