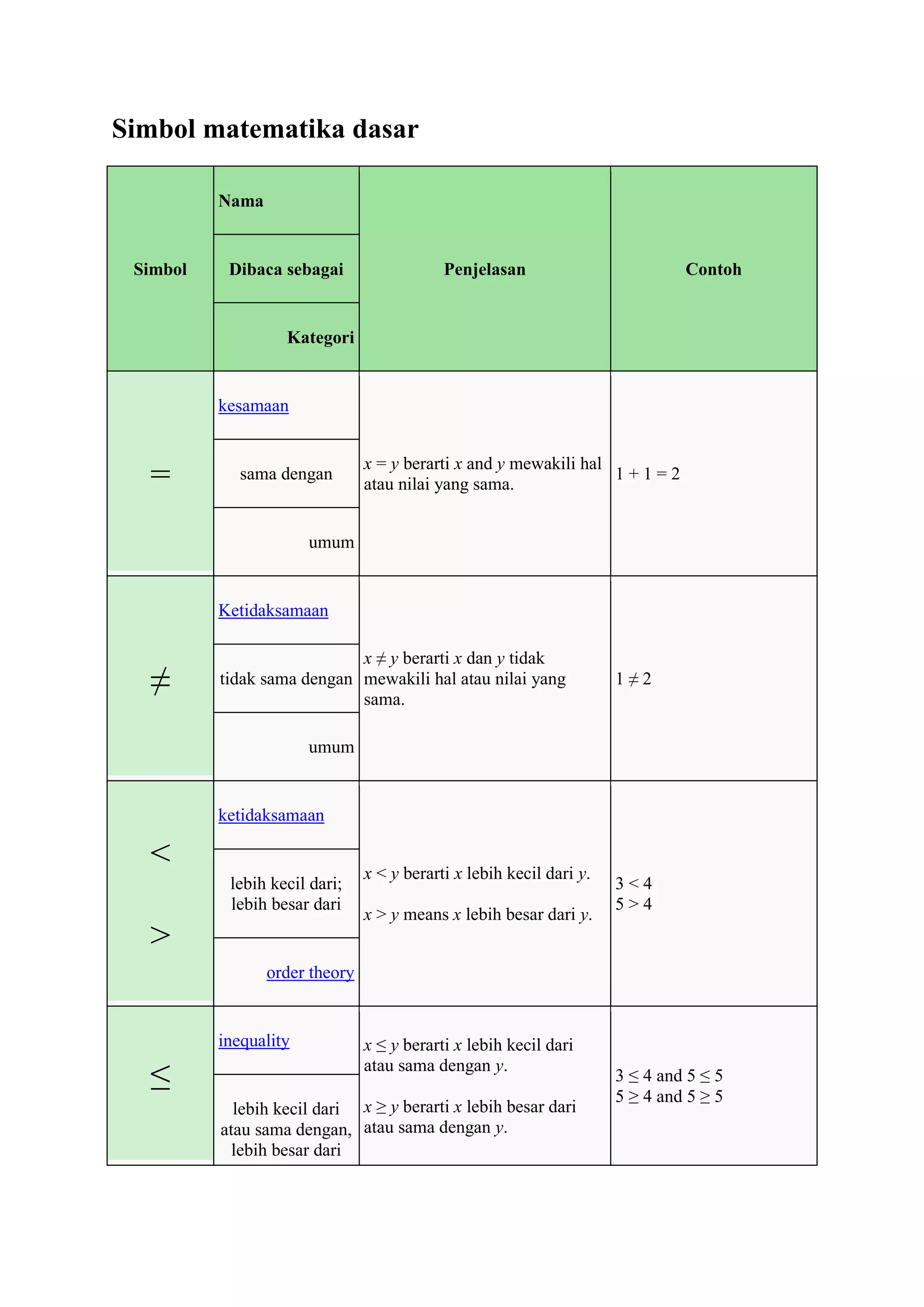
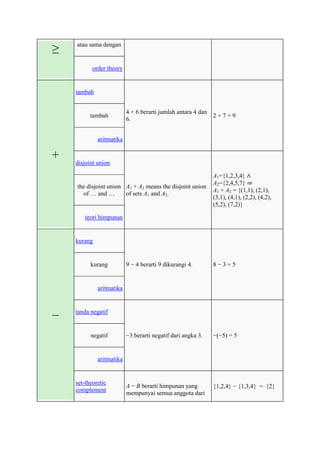
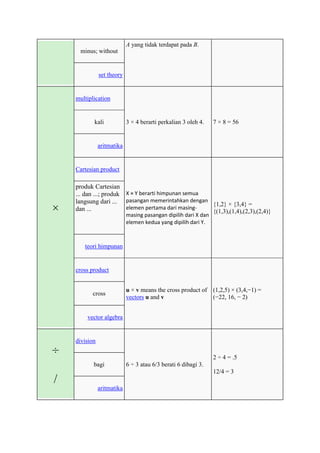
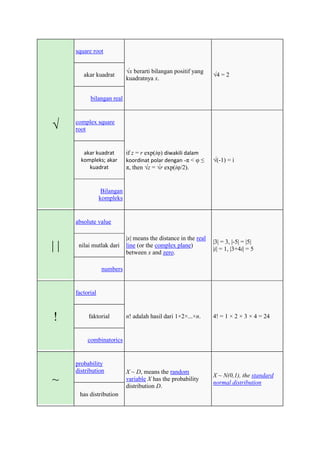
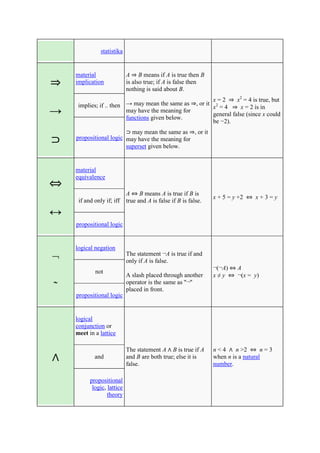
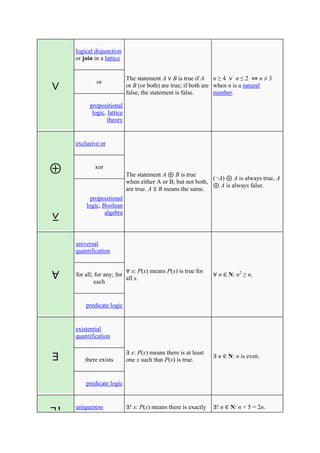
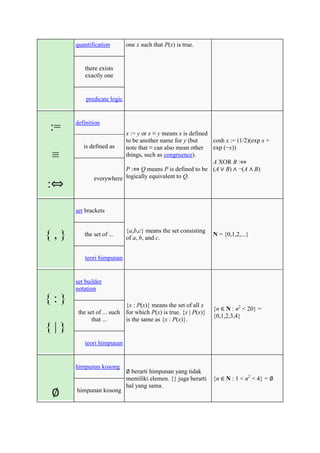
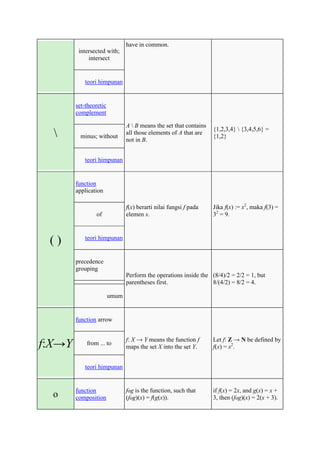
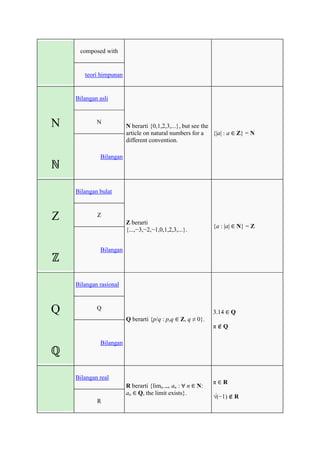
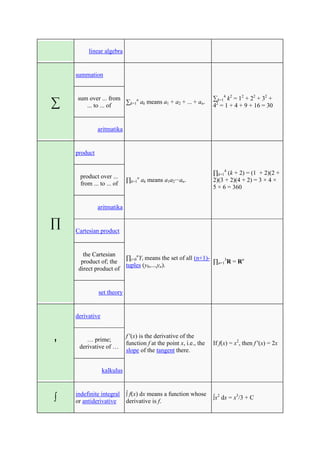
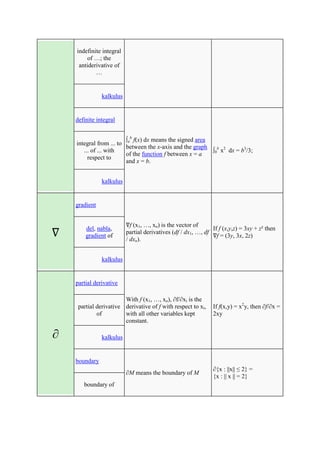
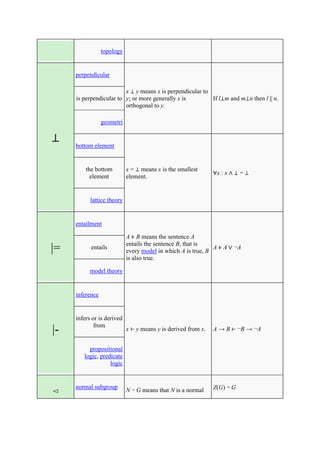
The document defines and provides examples of common mathematical symbols. Some key symbols and their meanings include:
= means equal to; ≠ means not equal to; < and > mean less than and greater than, respectively; + means addition; - means subtraction; × means multiplication; ÷ and / mean division. Other symbols covered include exponents, fractions, sets, logic, functions, and limits.