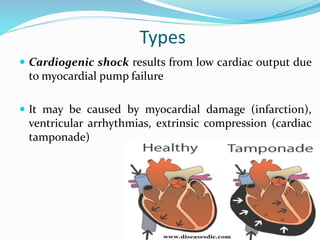
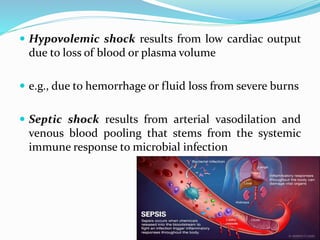
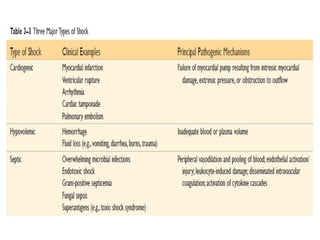
Shock is characterized by systemic hypoperfusion of tissues due to diminished cardiac output or reduced circulating blood volume. Prolonged shock leads to irreversible tissue injury and can be fatal if left untreated. There are several types of shock including cardiogenic, hypovolemic, septic, neurogenic, and anaphylactic shock. Septic shock results from vasodilation and blood pooling due to the immune response to infection, which can cause organ dysfunction if not corrected. Shock progresses through initial compensatory, progressive, and irreversible stages that can lead to cell injury and death without treatment.





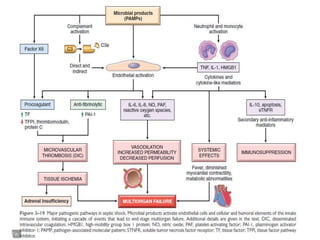
![Factors contributing to the pathophysiology of
septic shock
Inflammatory mediators: Cells of the innate
immune system express receptors (e.g., Toll-like
receptors [TLRs]
That recognize a host of microbe-derived substances
containing so-called pathogen-associated molecular
patterns (PAMPs)
Activation of pathogen recognition receptors by PAMPs
triggers the innate immune responses that drive sepsis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock-200612182516/85/Shock-10-320.jpg)