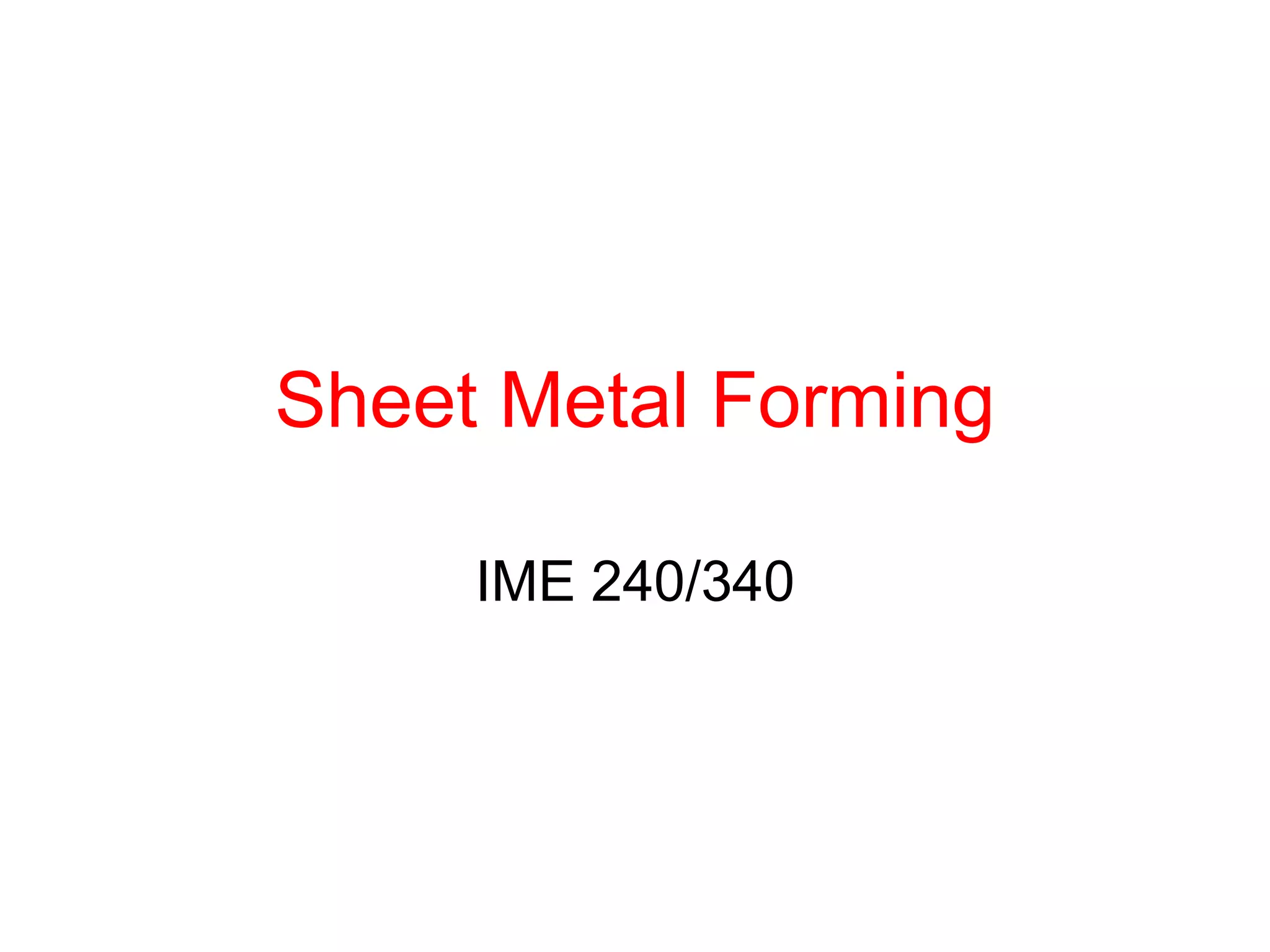
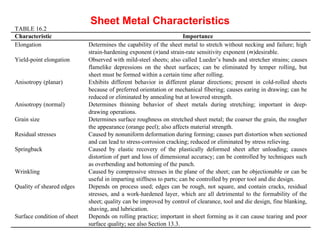
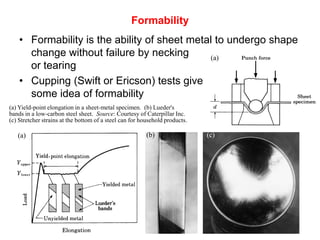
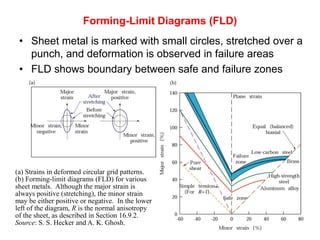
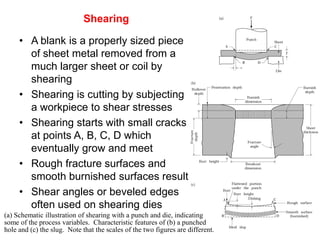
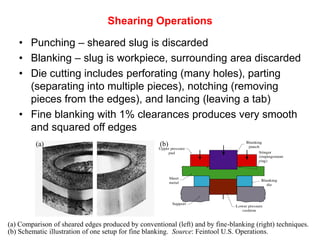
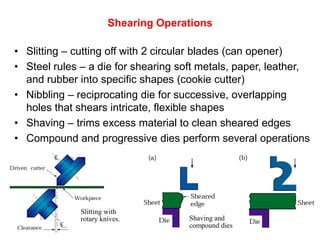
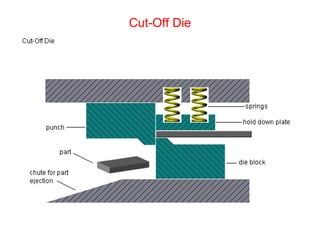
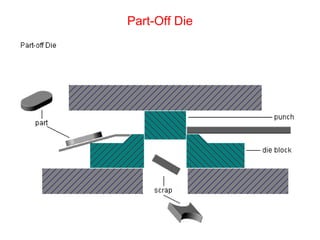
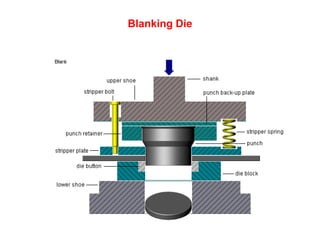
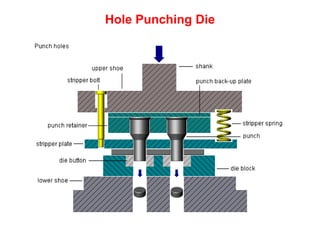
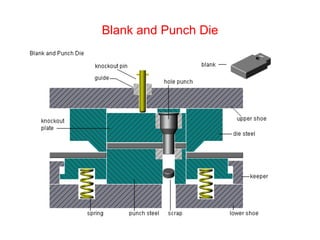
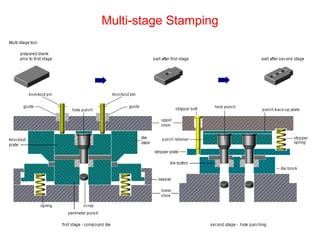
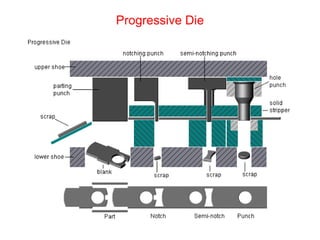
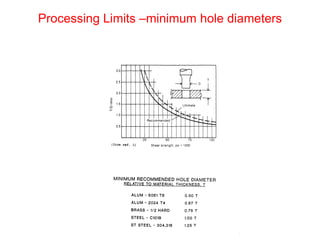
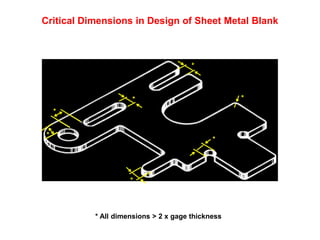
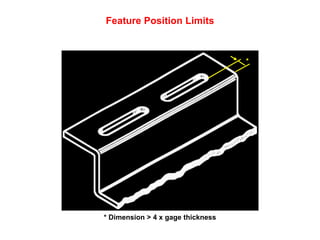
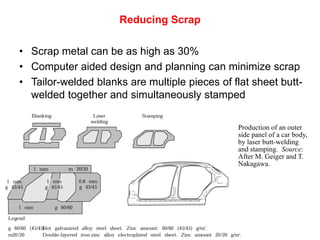
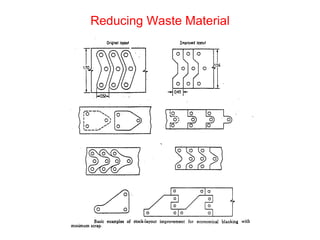
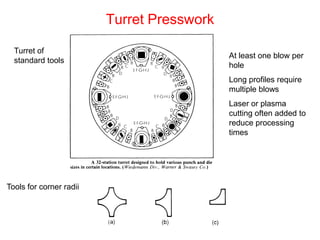
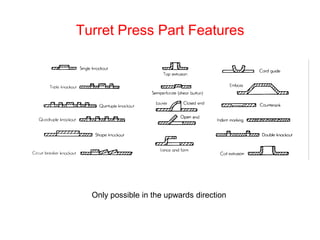
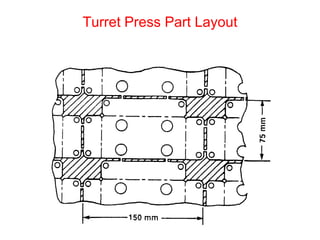
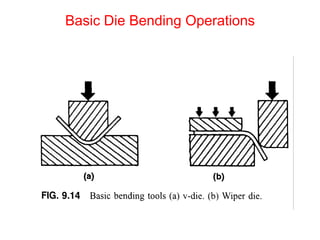
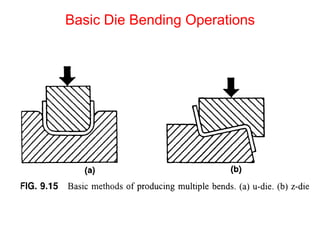
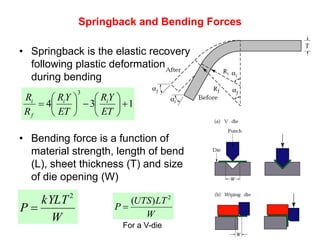
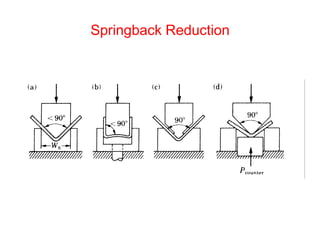
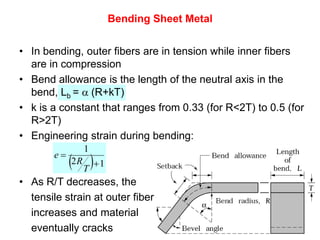
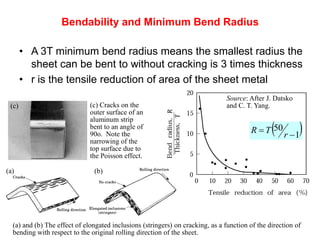
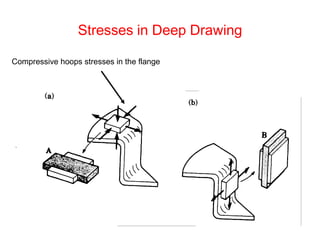
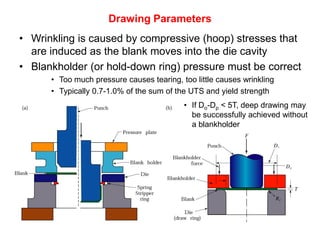
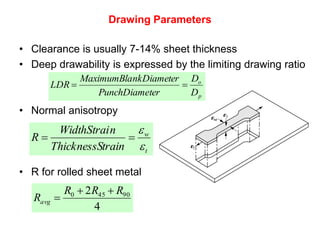
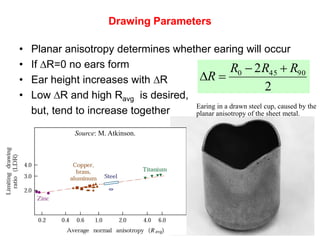
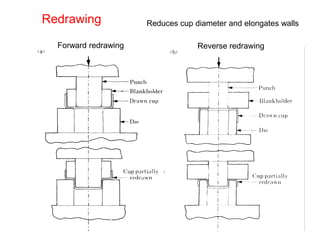
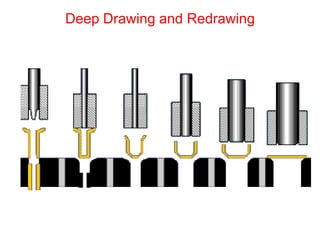
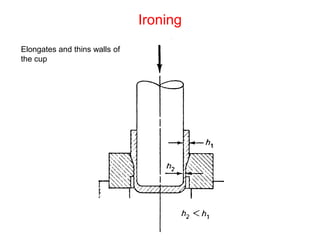
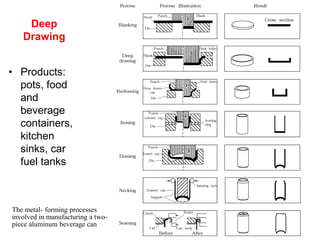
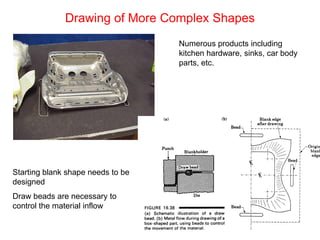
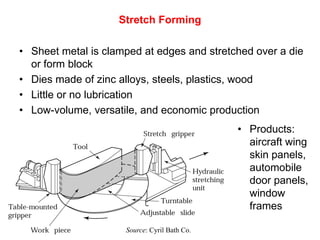
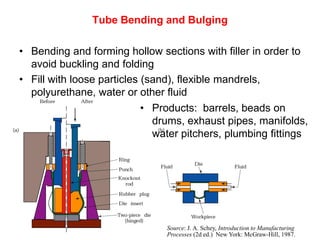
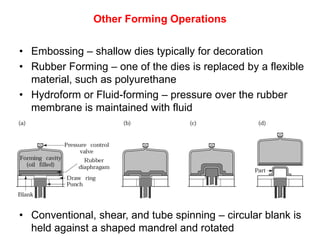
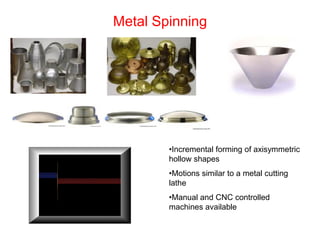
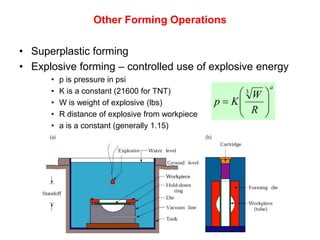
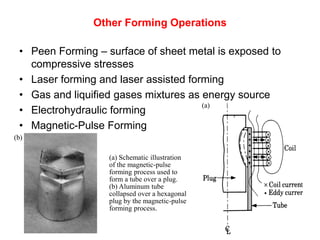
Sheet metal forming is a versatile manufacturing process used to produce lightweight parts with complex shapes. Common forming operations include punching, blanking, bending, deep drawing, and stamping. Key considerations in sheet metal forming include the material properties, forming limits, stresses induced during forming, and techniques to reduce waste and improve dimensional accuracy. Proper tool and die design is critical for successful forming of sheet metal parts.