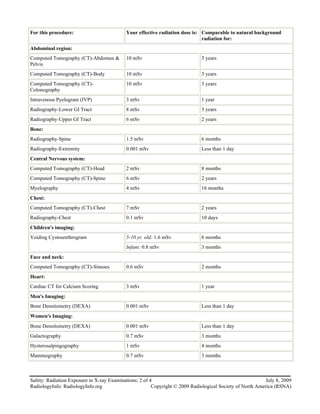
This document discusses radiation exposure from x-ray examinations. It explains that x-rays are a form of radiation that can penetrate the body and produce images. While x-rays are generally safe, different exams involve different levels of radiation. The radiation dose is measured in millisieverts and compared to natural background radiation. Pregnancy is an important factor to disclose for some exams due to potential risks to the developing baby. The risks of radiation must be weighed against the benefits of the medical information provided by all radiological procedures.