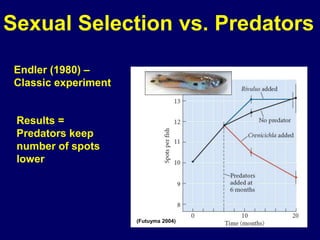
Sexual selection leads to sexual dimorphism as males and females evolve different traits to obtain mates. For example, male widowbirds have exceptionally long tail feathers while females lack tails. Studies show that female widowbirds prefer males with artificially longer tails, demonstrating they have stronger and more vigorous genes. However, traits that make males more attractive to females, like bright spots on male guppies, can also make them more visible to predators, creating conflict between sexual selection pressures and predation.