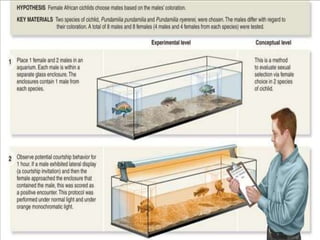
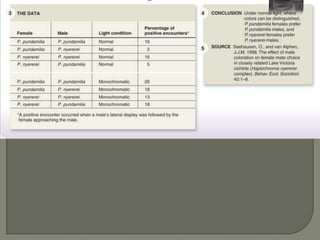
This document discusses sexual selection and sexual dimorphism, specifically focusing on two methods: intrasexual selection and intersexual selection. Intrasexual selection involves competition within one sex, usually males, for access to the opposite sex for mating. Intersexual selection involves mate choice by the opposite sex, usually females choosing visually appealing traits in males like antlers, claws, or bright colors. However, these traits are not always beneficial for survival as they can make males easier for predators to spot. The document also discusses research on coloration preferences in female cichlid fish and mate choice.