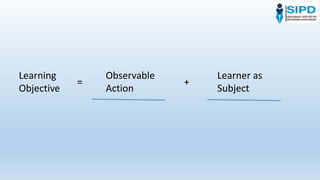
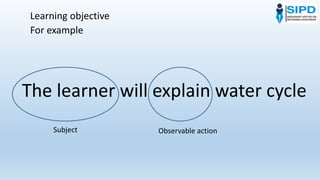
This document discusses learning objectives and how to write them effectively. It defines learning objectives as a statement describing what the learner will be able to do by the end of a lesson or course. Learning objectives should include an observable action, the learner as the subject, and conditions like time limits or resources. Objectives help learners understand what they will learn and keep teachers focused. Well-written objectives are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. The document provides examples of weak versus strong objectives and recommends using verbs that indicate higher-order thinking skills.