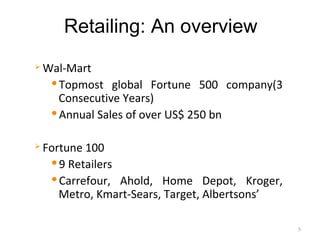
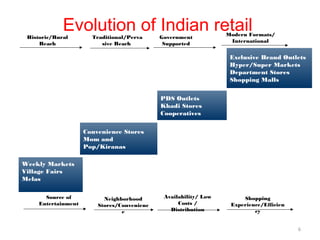
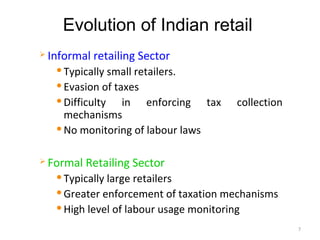
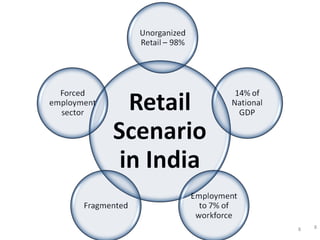
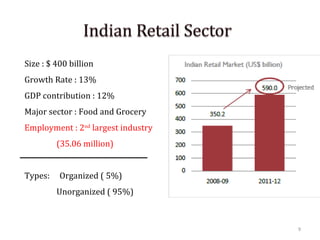
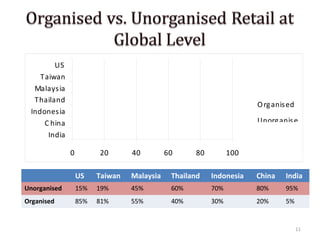
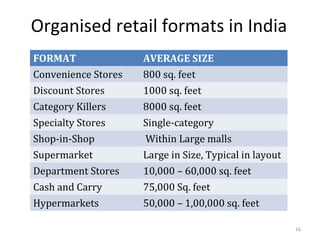
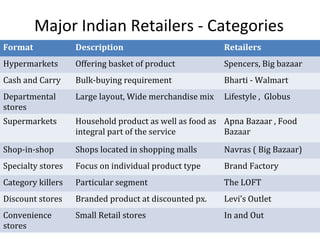
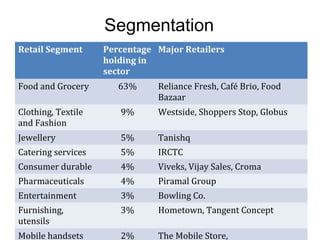
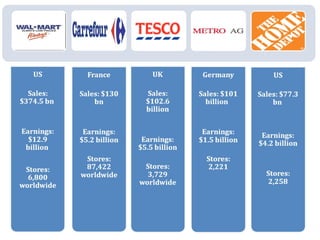
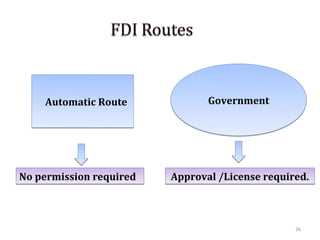
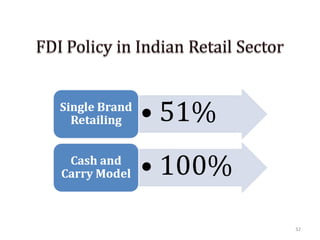
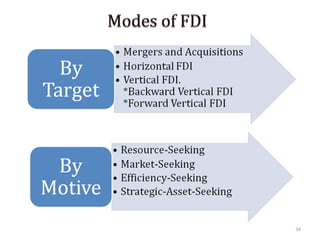
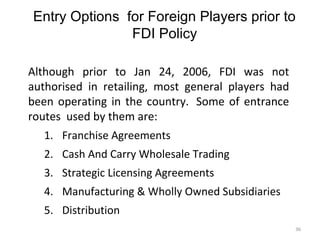
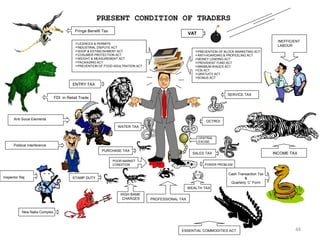
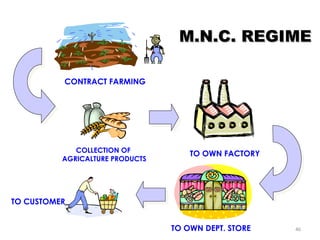
The document discusses FDI in the retail sector in India. It provides an overview of retailing globally and in India, including the size and growth of the Indian retail market. It then discusses the evolution of Indian retail from traditional to modern formats. The document outlines the categories of Indian retail from organized to unorganized sectors. It discusses the entry of FDI in retail and the various options foreign players had prior to the FDI policy change in 2006. Finally, it summarizes the present FDI policy for single brand and multi-brand retail in India.