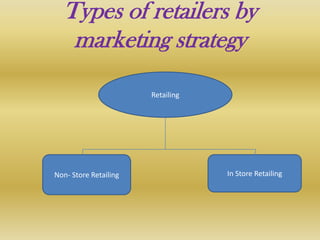
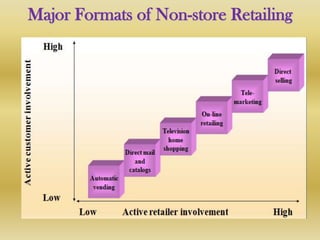
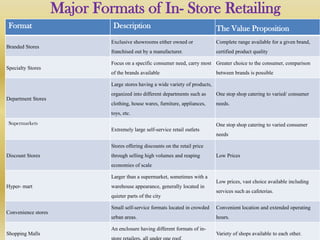
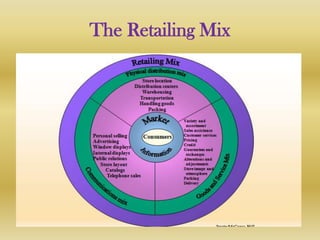
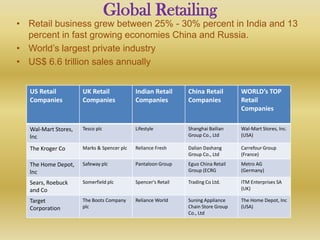
Retail is the sale of goods and services from individuals or businesses to the end user. There are two main types of retailing: in-store and non-store. In-store includes department stores, supermarkets, discount stores, and hypermarkets. Non-store includes vending machines, direct mail/catalogs, TV shopping, online retail, and telemarketing. Retailers must choose a format and positioning strategy to attract customers. Globally, retail is a large industry worth $6.6 trillion annually led by Walmart, Carrefour, and Metro AG. In India, retail makes up 14-15% of GDP but is fragmented with 96% of stores small. The industry faces challenges around infrastructure