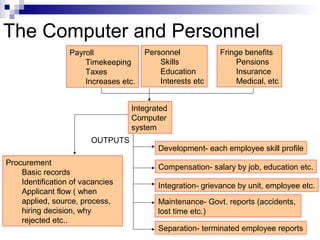
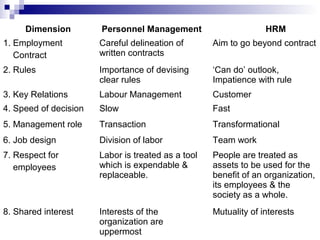
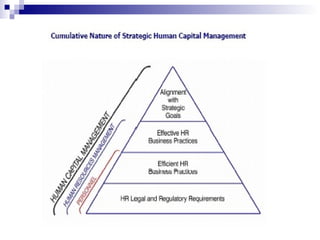
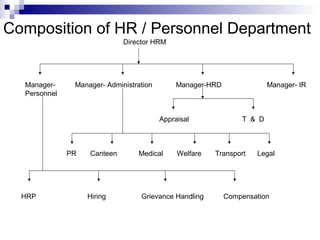
The document discusses the personnel function in an organization. It covers topics like recruitment, induction, placement, development, personnel policies, absenteeism, transfers, promotions, compensation plans, job structure, and morale studies. It defines personnel management and discusses the role of the personnel manager. It also covers challenges like a changing workforce, values, expectations, and government demands. It discusses approaches to personnel management like mechanical, paternalism, and social systems. It outlines organizing the personnel unit, planning the personnel program, and controlling the personnel unit.