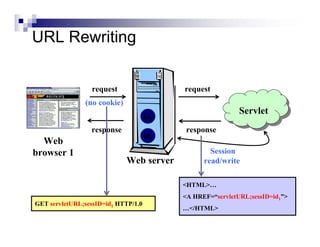
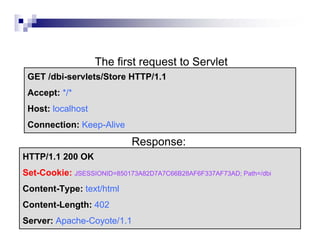
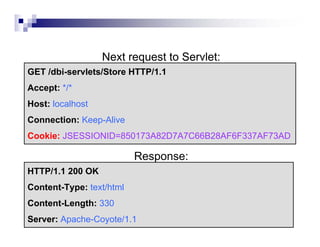
Cookies allow servers to store and retrieve information on the client side. Servers send cookies in HTTP responses and browsers send the cookie back with subsequent requests. There are two main methods for managing sessions between clients and servers - using session cookies or URL rewriting. With session cookies, the server embeds a session ID in a cookie it sends to the client, and the client sends the cookie back on future requests to identify the session. With URL rewriting, the server encodes the session ID directly into the URLs of links and redirects. The session data itself is stored server-side and associated with the client via the session ID.


![Managing Cookies
Get the cookies from the service request:
Cookie[] HttpServletRequest.getCookies()
Add a cookie to the service response:
HttpServletResponse.addCookie(Cookie cookie)
Cookie getter methods:
getName(), getValue(), getPath(), getDomain(),
getMaxAge, getSecure…
Cookie setter methods:
setValue() , setPath(), setDomain()…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/servletsessions-121001005314-phpapp02/85/Servlet-sessions-3-320.jpg)
![public class WelcomeBack extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String user = req.getParameter("username");
if (user == null) {
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
for (int i = 0 ; cookies!=null && i < cookies.length ; i++) {
if (cookies[i].getName().equals("username"))
user = cookies[i].getValue(); }
} else res.addCookie(new Cookie("username", user));
if (user != null) {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
out.println("<html><body><H1>Welcome Back " + user +
“</H1></html></body>");
} else { res.sendRedirect("/dbi-servlets/login.html"); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/servletsessions-121001005314-phpapp02/85/Servlet-sessions-4-320.jpg)