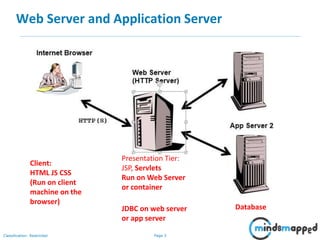
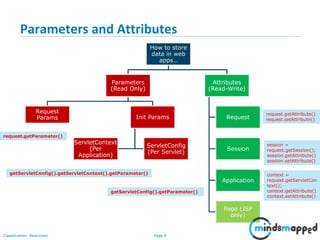
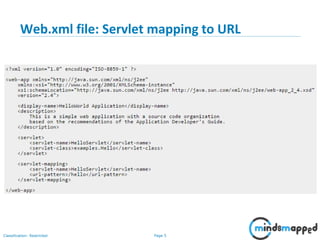
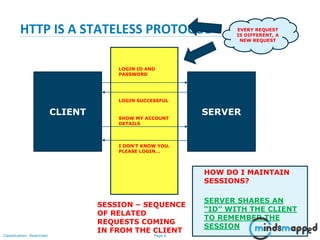
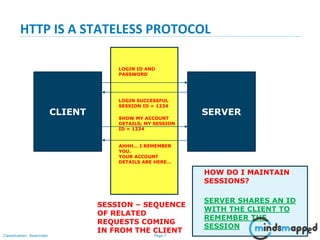
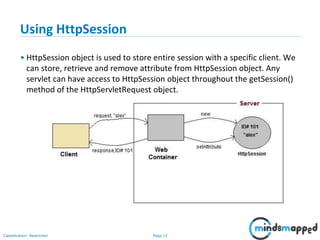
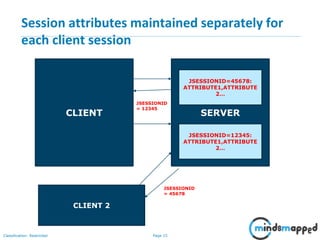
The document covers session management in Java EE applications using servlets, focusing on techniques such as cookies, hidden fields, URL rewriting, and the HttpSession object. It explains the significance of maintaining sessions in a stateless HTTP protocol and discusses practical implementations and advantages/disadvantages of each session tracking method. Additionally, it provides a demo of using HttpSession for managing user sessions and outlines topics for the next training session.