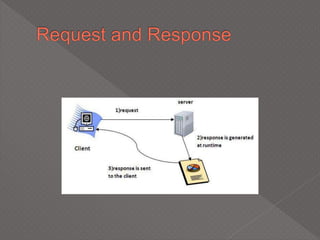
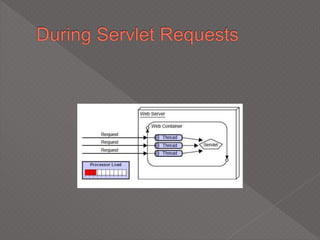
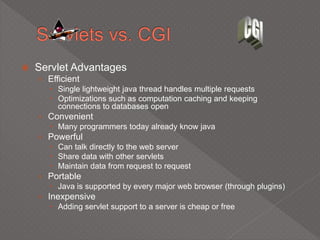
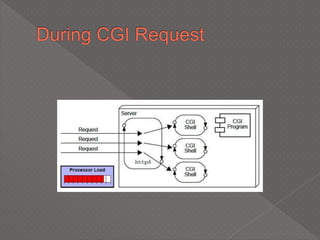
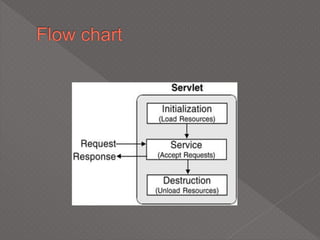
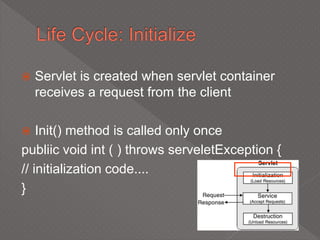
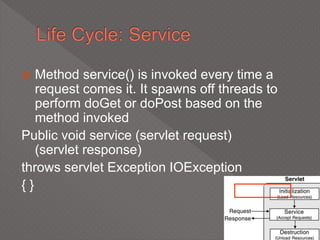
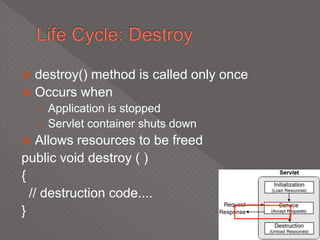
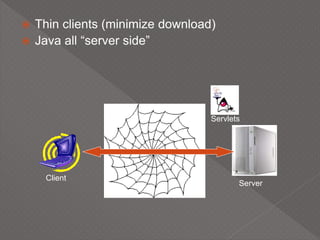
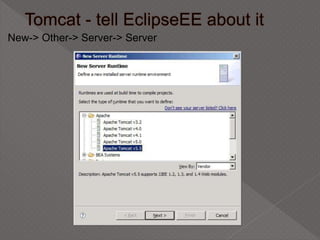
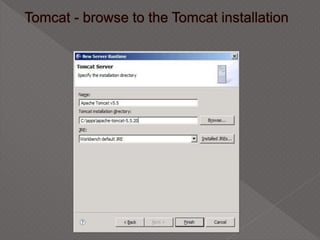
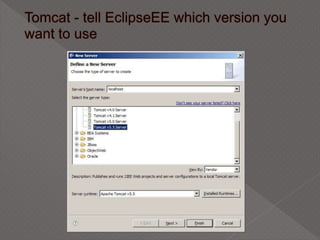
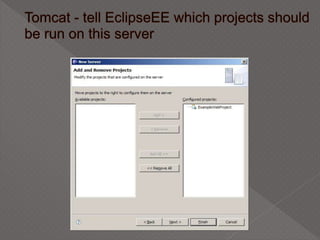
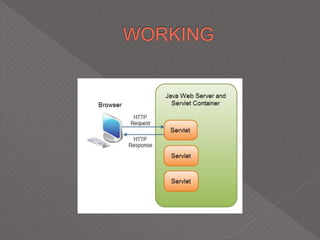
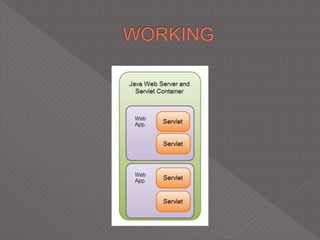
This document discusses servlets, which are Java programs that extend the capabilities of web servers to enable dynamic web content. Servlets run on the server-side and generate HTML responses to HTTP requests from clients. The document covers the basics of servlets, how they interface with web servers, their lifecycle including initialization and destruction, advantages over previous technologies like CGI, and implementation details.