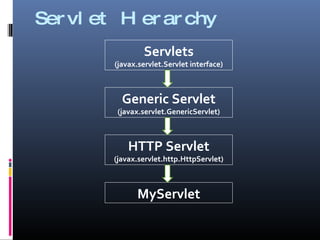
This document provides an overview of Java servlets, including what servlets are, their advantages over other technologies like CGI scripts, their lifecycle and program structure, deploying servlets on Tomcat, HTTP request methods, accessing request data, and redirecting URLs. Servlets are Java classes that extend functionality to handle HTTP requests and responses. They have advantages like faster performance than CGI scripts and reuse of the Java platform. The servlet lifecycle involves initialization, processing requests, and destruction. Servlets are deployed on a web container like Tomcat by compiling, configuring in web.xml, and placing in the webapps folder.








![[Screencast] Create simple servlet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaservlet-100529204624-phpapp01/85/Knowledge-Sharing-Java-Servlet-10-320.jpg)
![[Showcase] Servlet Lifecycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaservlet-100529204624-phpapp01/85/Knowledge-Sharing-Java-Servlet-11-320.jpg)
![[Showcase] Servlet Lifecycle (cont.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaservlet-100529204624-phpapp01/85/Knowledge-Sharing-Java-Servlet-12-320.jpg)
![[Showcase] Servlet Lifecycle (cont.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaservlet-100529204624-phpapp01/85/Knowledge-Sharing-Java-Servlet-13-320.jpg)










![URL Redirecting (cont.) sendRedirect() It will updates the browser history. RequestDispatcher If use RequestDispatcher to forward from Servlet-2 to JSP-3, the user's address bar will read http://[host]/Servlet-2. A reload/refresh will execute both Servlet-2 and JSP-3. Both kinds of redirections are useful, depending on the precise effect you want. http://www.theserverside.com/discussions/thread.tss?thread_id=26425](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaservlet-100529204624-phpapp01/85/Knowledge-Sharing-Java-Servlet-26-320.jpg)
