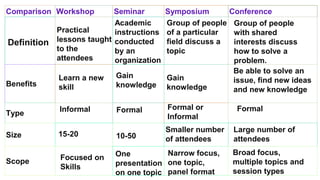
This document provides information about organizing different types of formal events like workshops, conferences, panel discussions, and roles like the master of ceremonies (MC). It discusses the key differences between workshops, seminars, symposiums and conferences. It also outlines the important elements to consider when planning these events such as purpose, participants, agenda, logistics and evaluations. The roles of the MC, chairperson, presenters, panelists and moderator during the event are explained. The document concludes with an exercise that simulates organizing a conference with panel discussions to demonstrate these concepts.