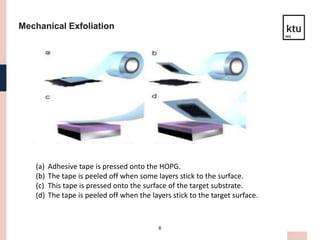
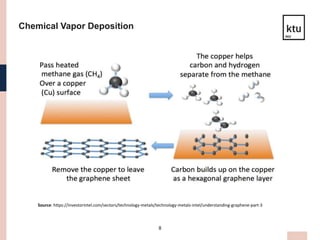
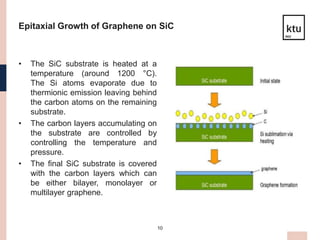
This presentation discusses graphene material for aerospace technology. Graphene is a single-atom thick sheet of carbon that is one of the strongest yet lightest materials. It has high electrical and thermal conductivity. There are three main production methods - mechanical exfoliation, chemical vapor deposition, and epitaxial growth on silicon carbide. Graphene has applications in aircraft and satellite structures and systems due to its strength and lightweight properties. Issues include controlling the number of layers and high production temperatures required. Further development could enable graphene fuel tanks and composite materials for aerospace.