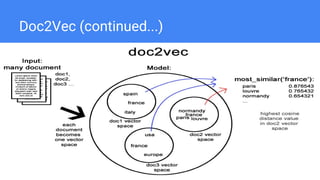
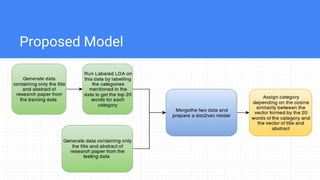
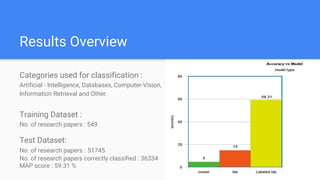
The document describes a project to semantically annotate research papers with ACM classification categories. It discusses using cosine similarity, latent Dirichlet allocation, and a proposed model combining labeled LDA and doc2vec. The proposed model trains a supervised topic model to learn document representations that capture semantic relationships between papers and categories. The model achieved 59.31% mean average precision and 45.03% NDCG on a test dataset, demonstrating an improvement over baselines.