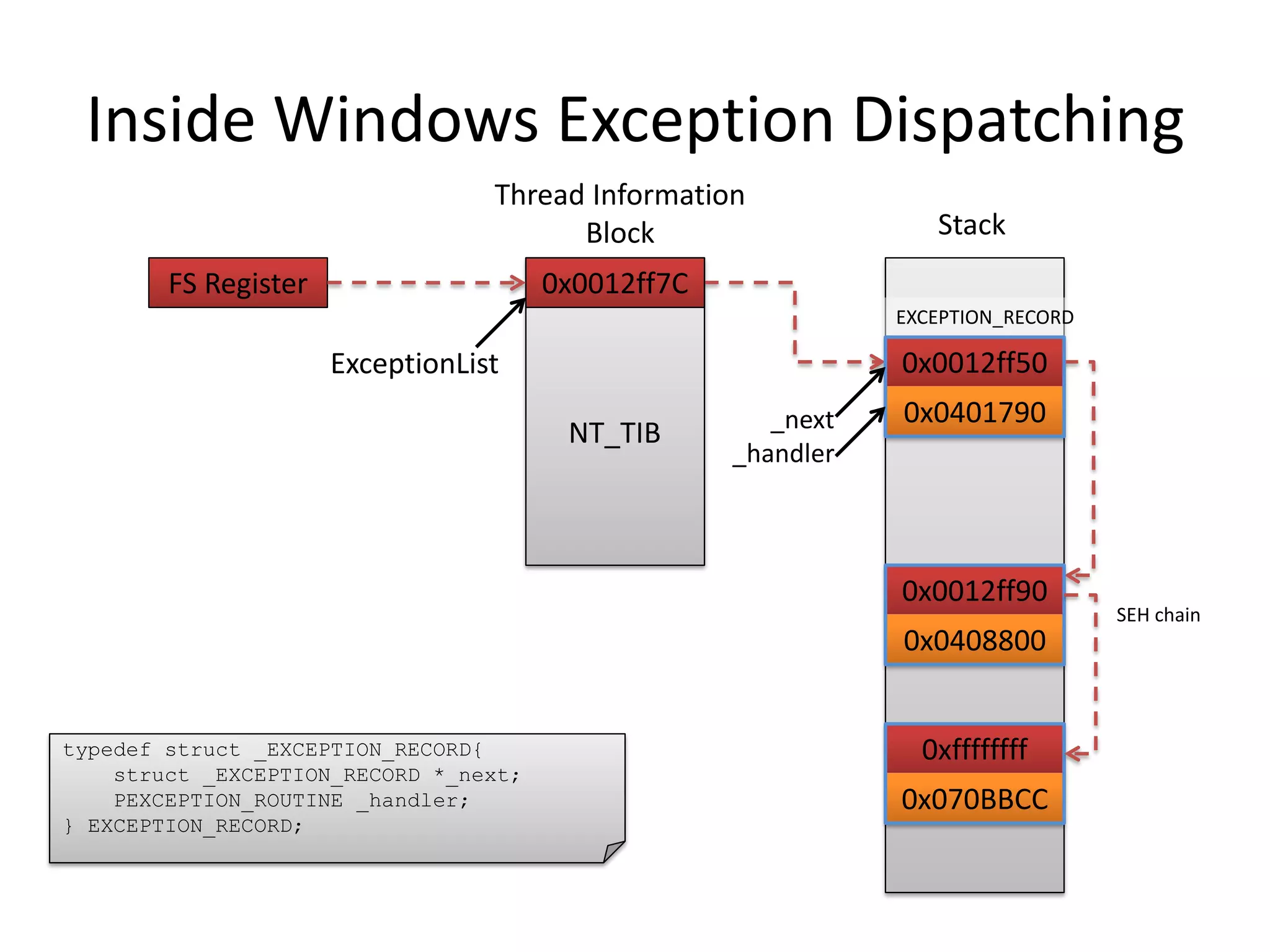
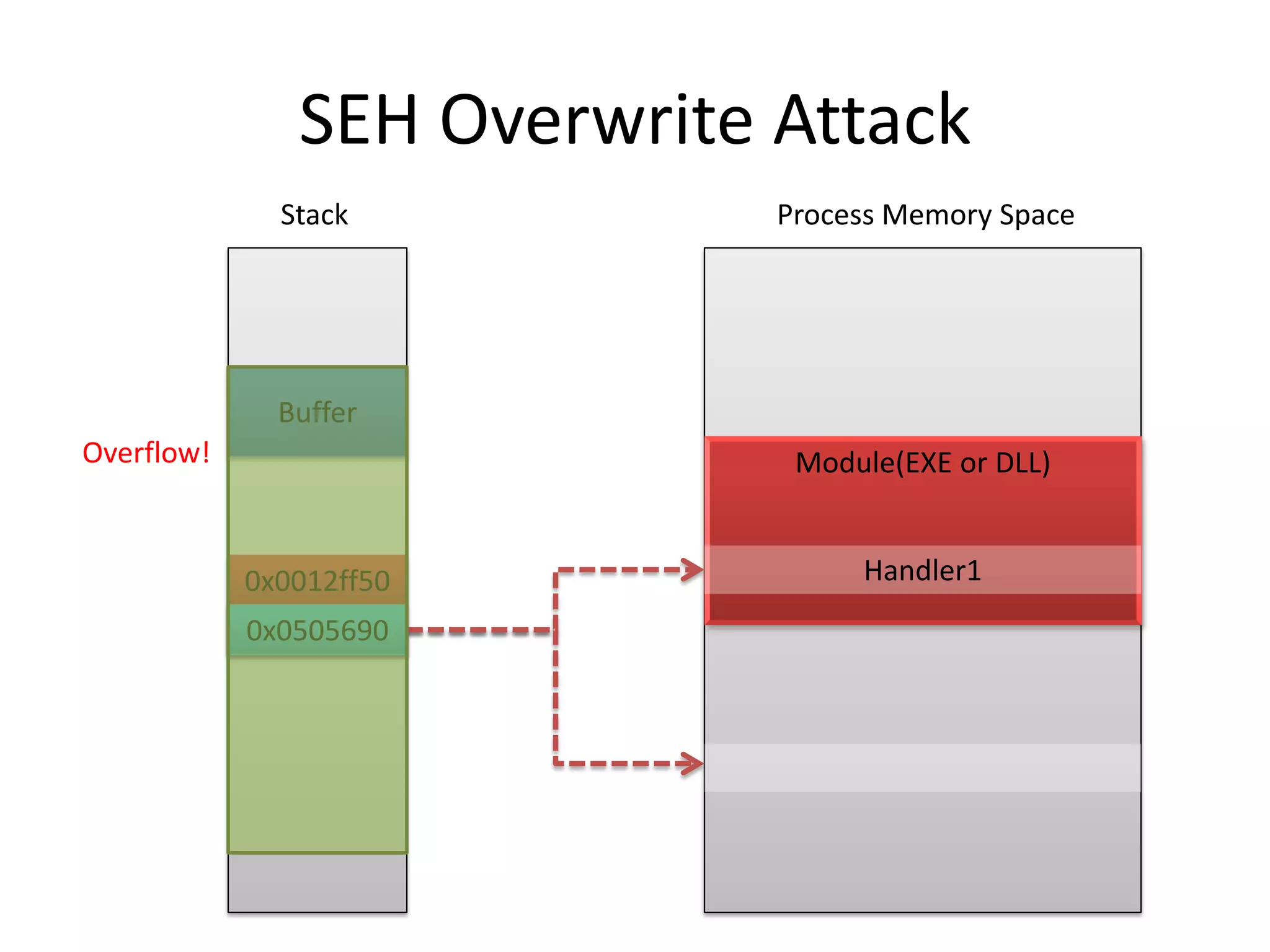
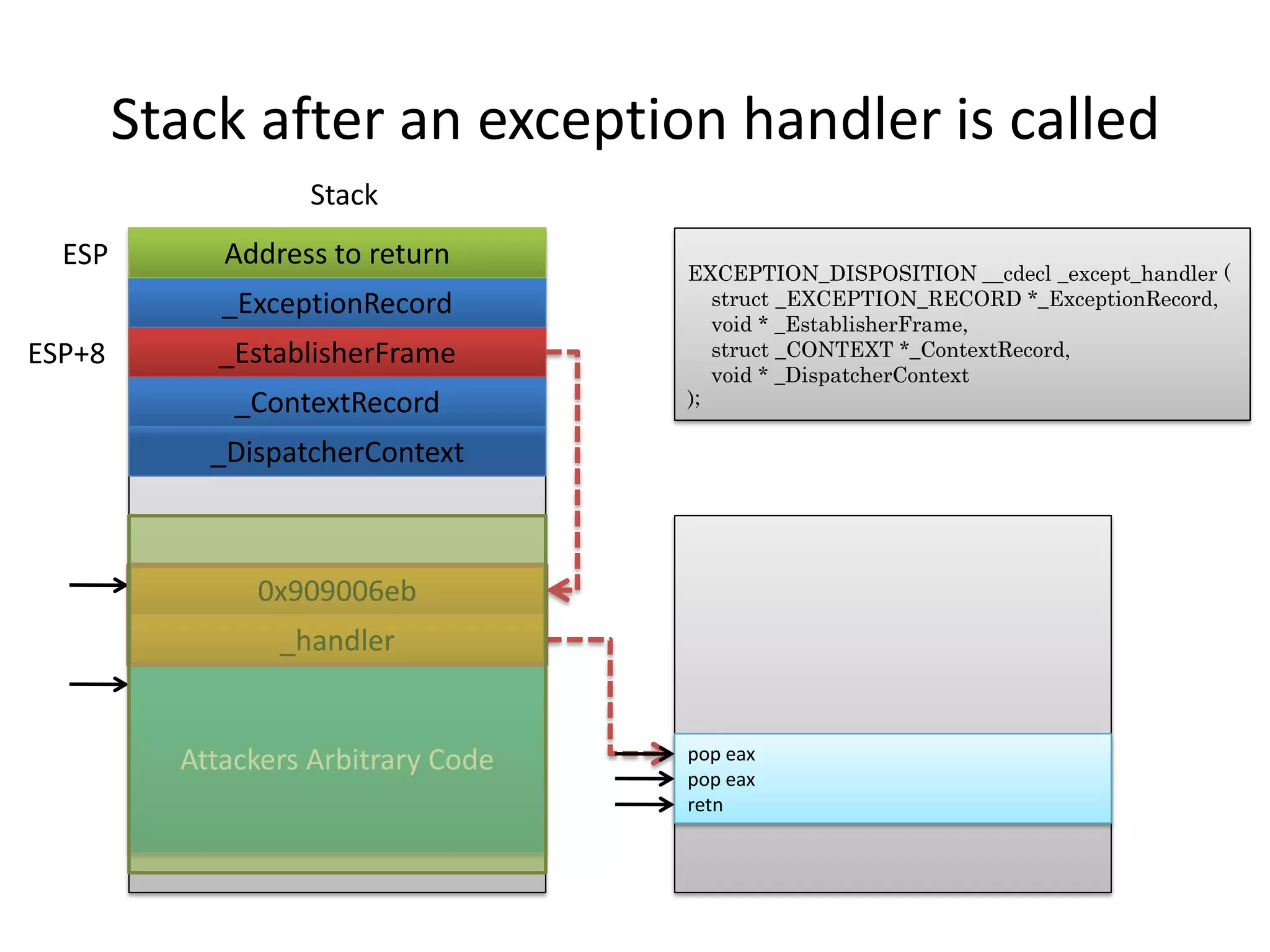
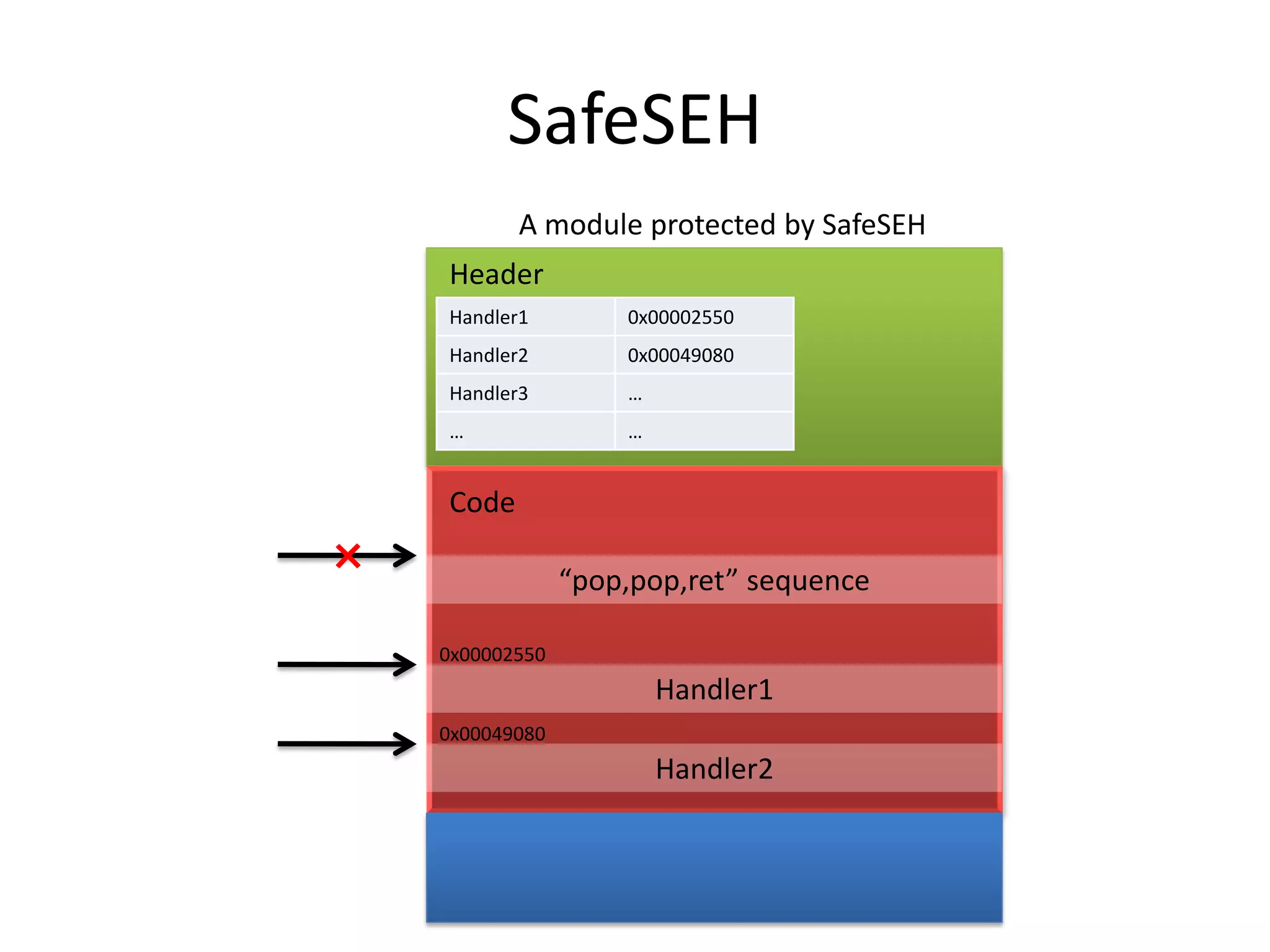
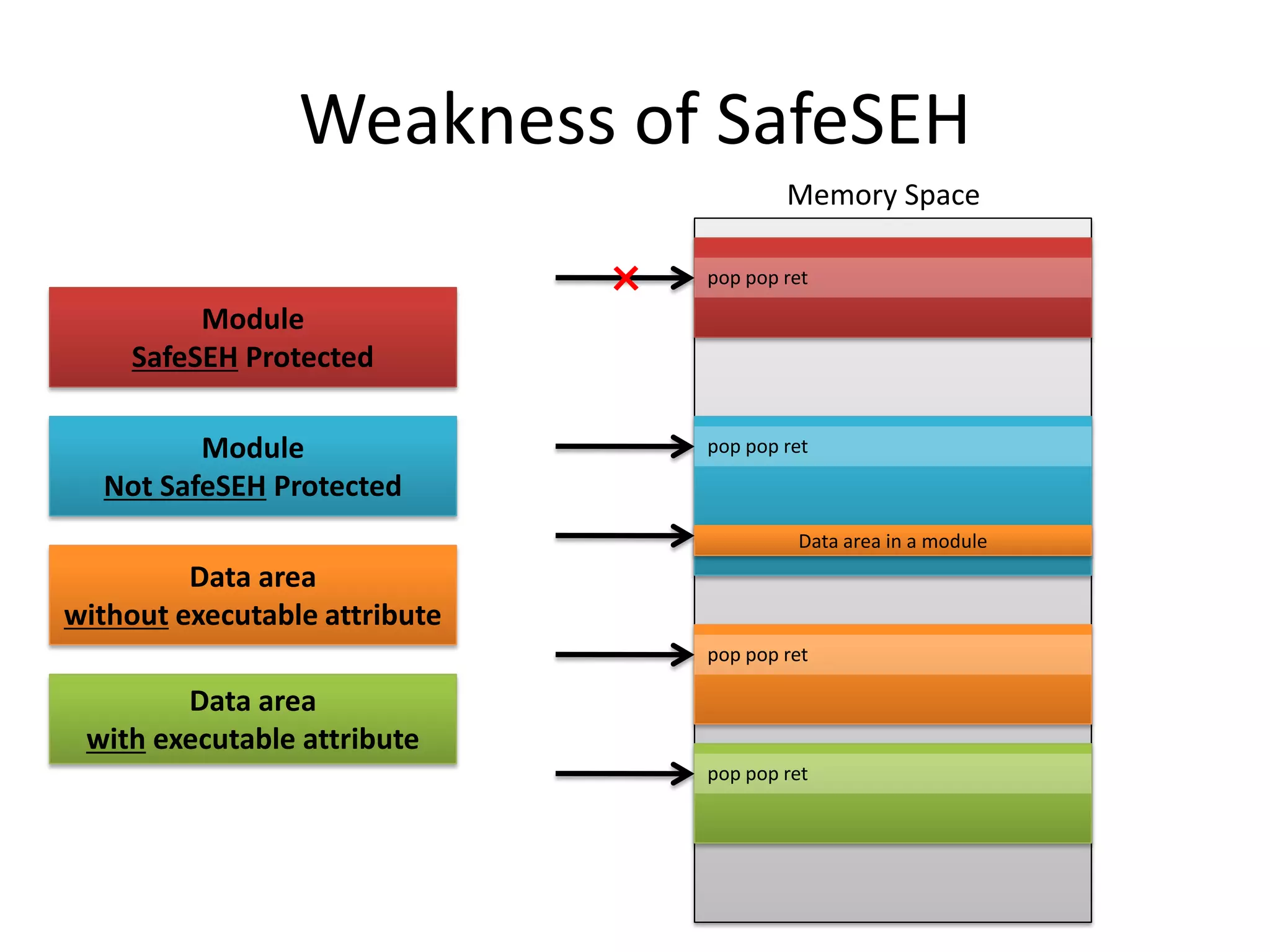
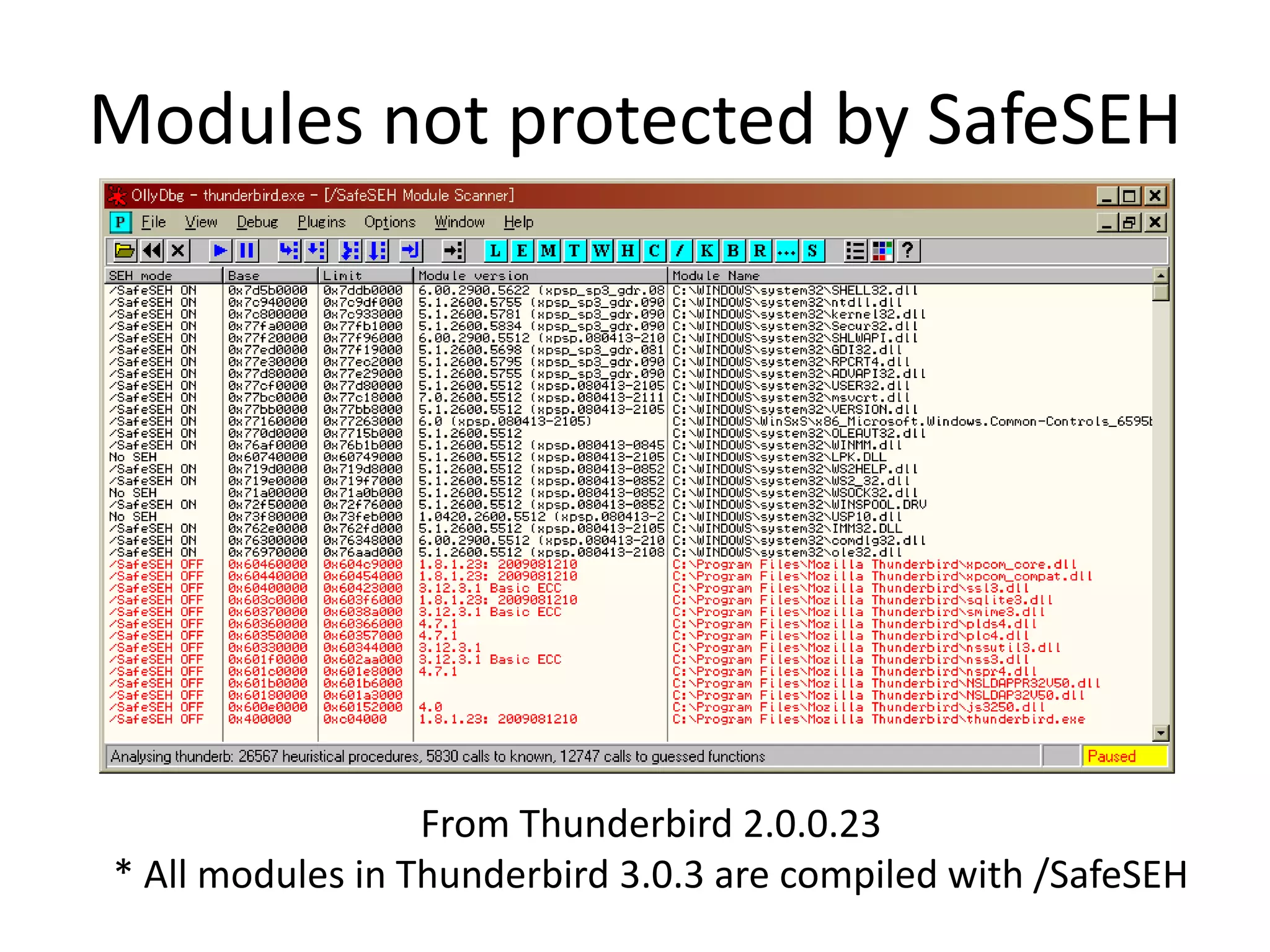
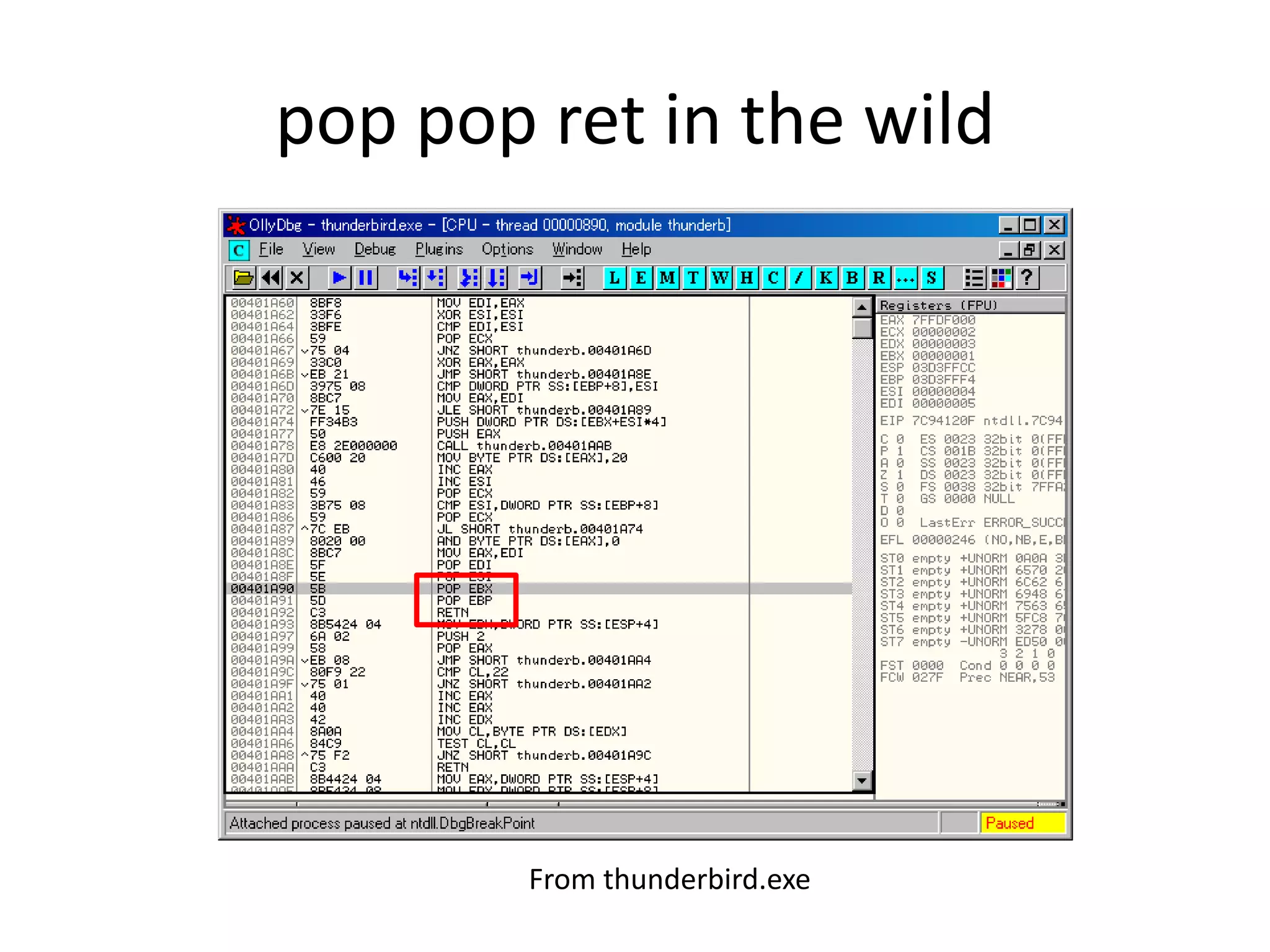
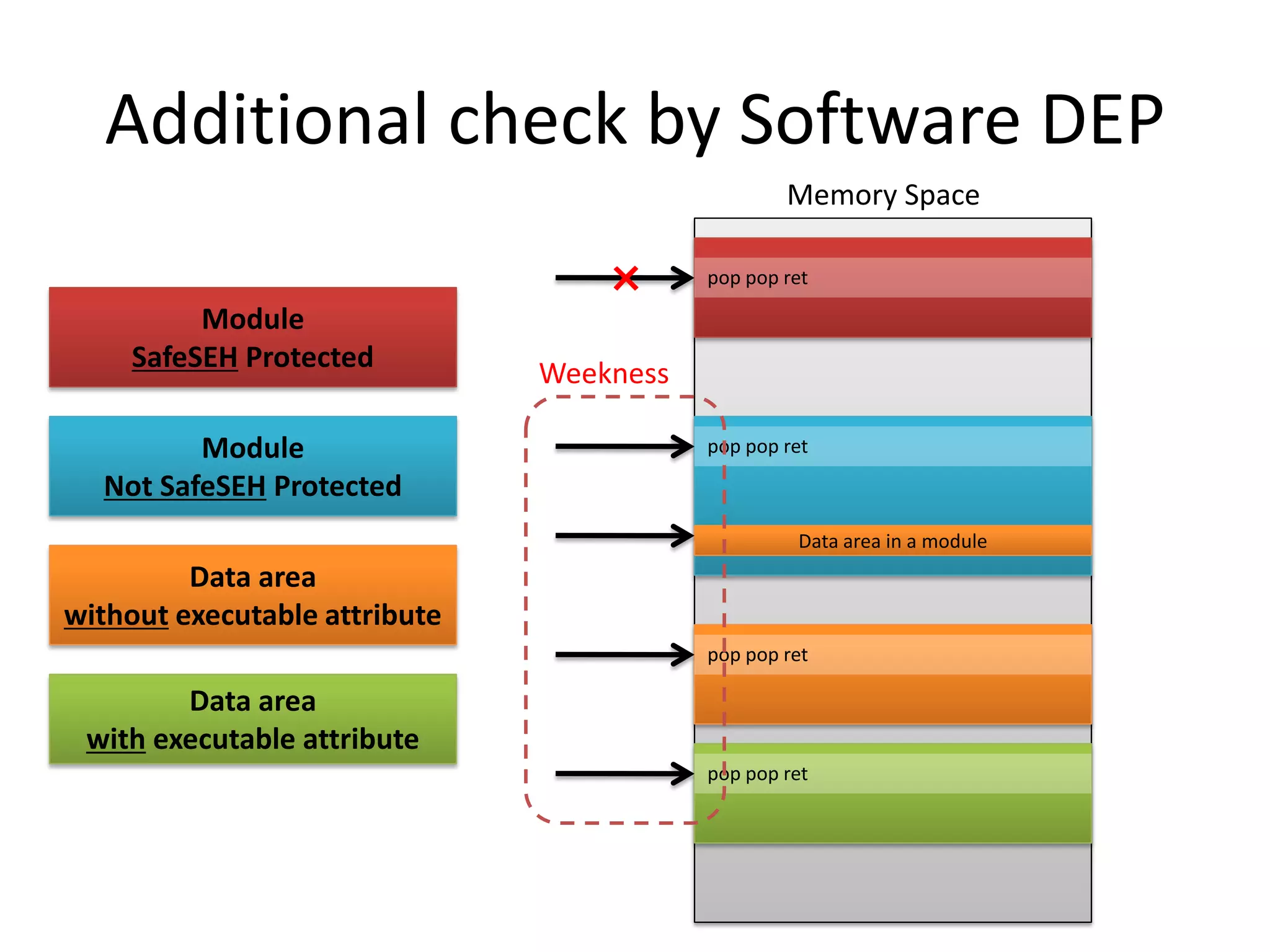
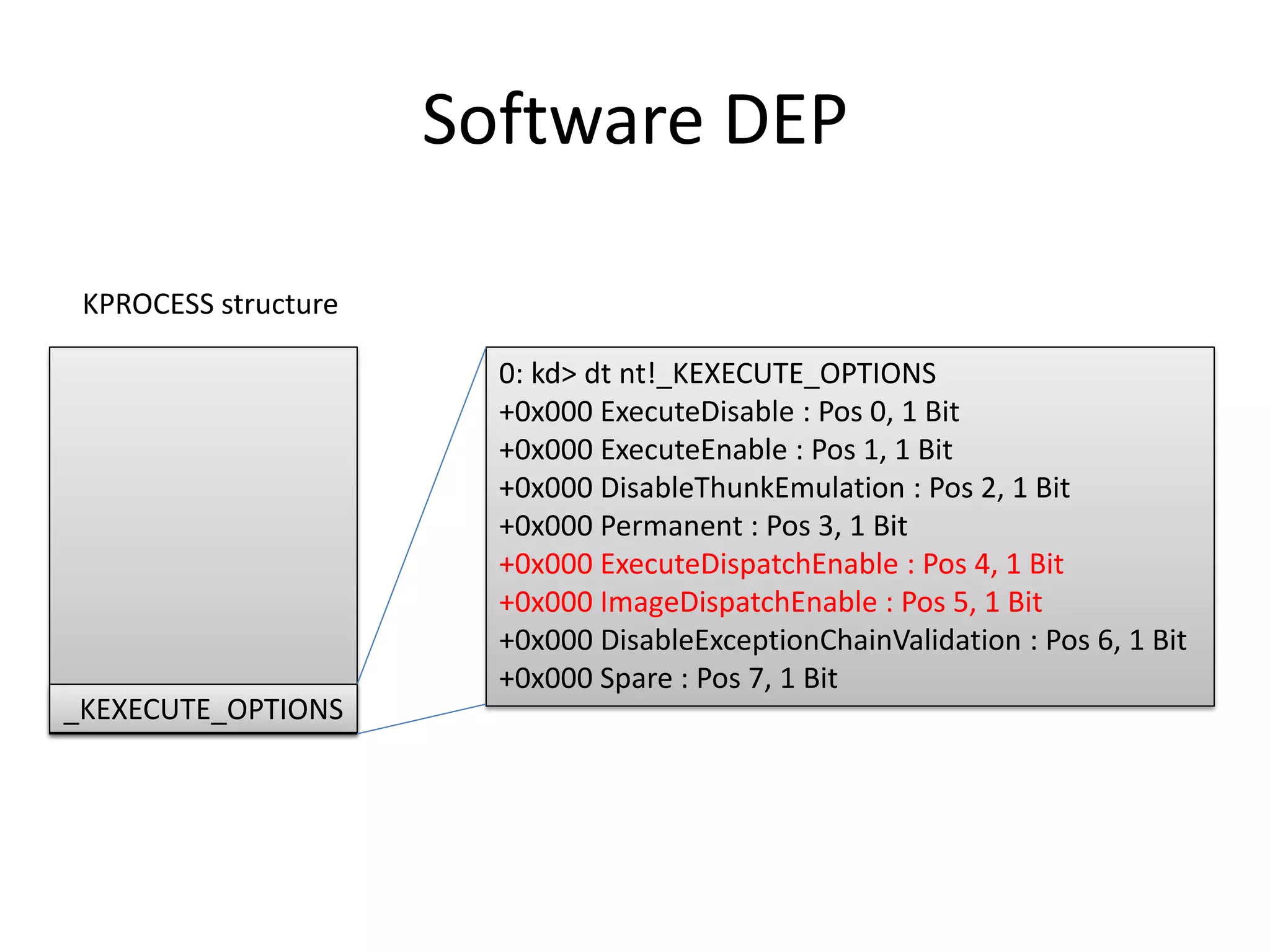
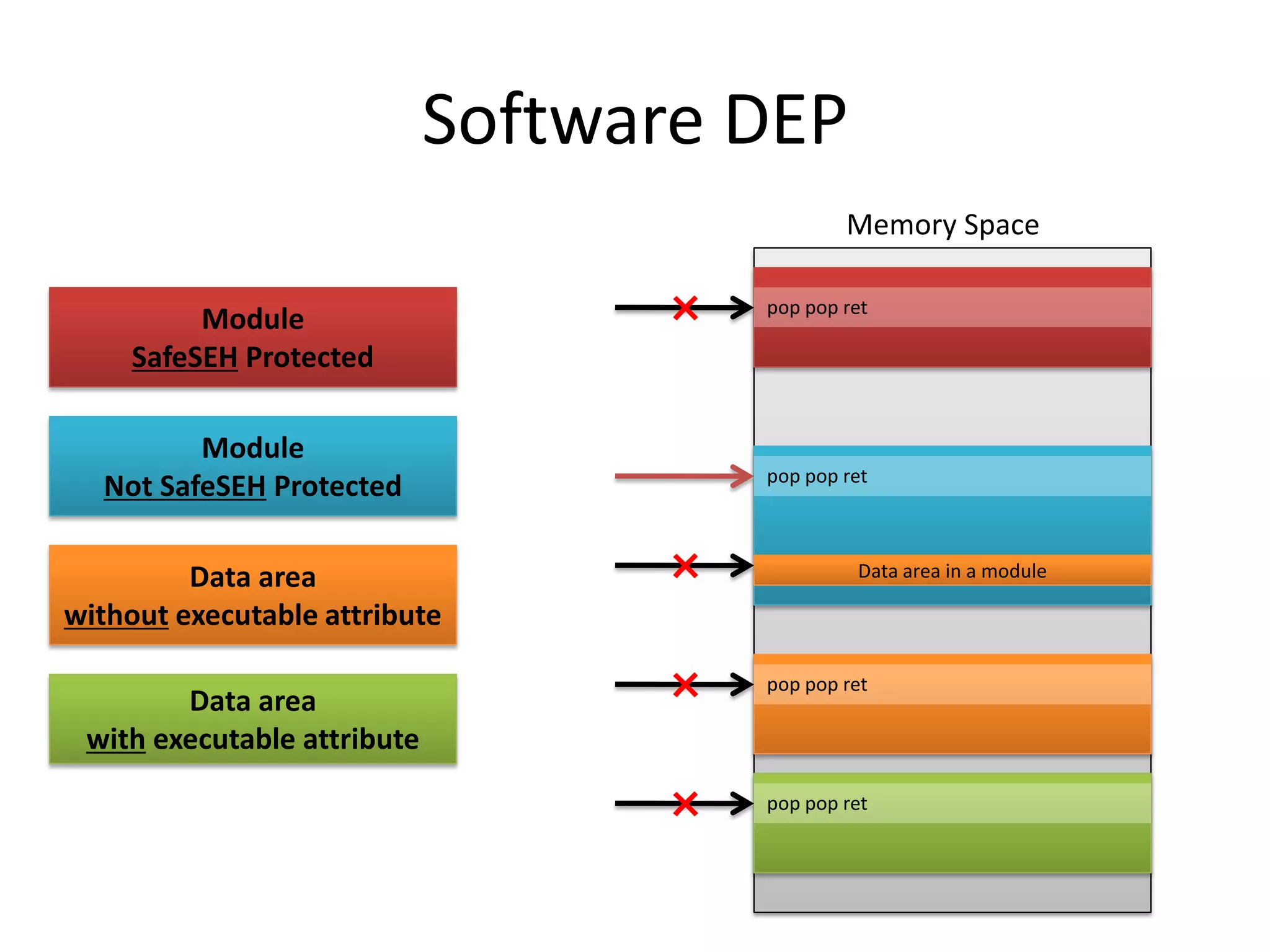
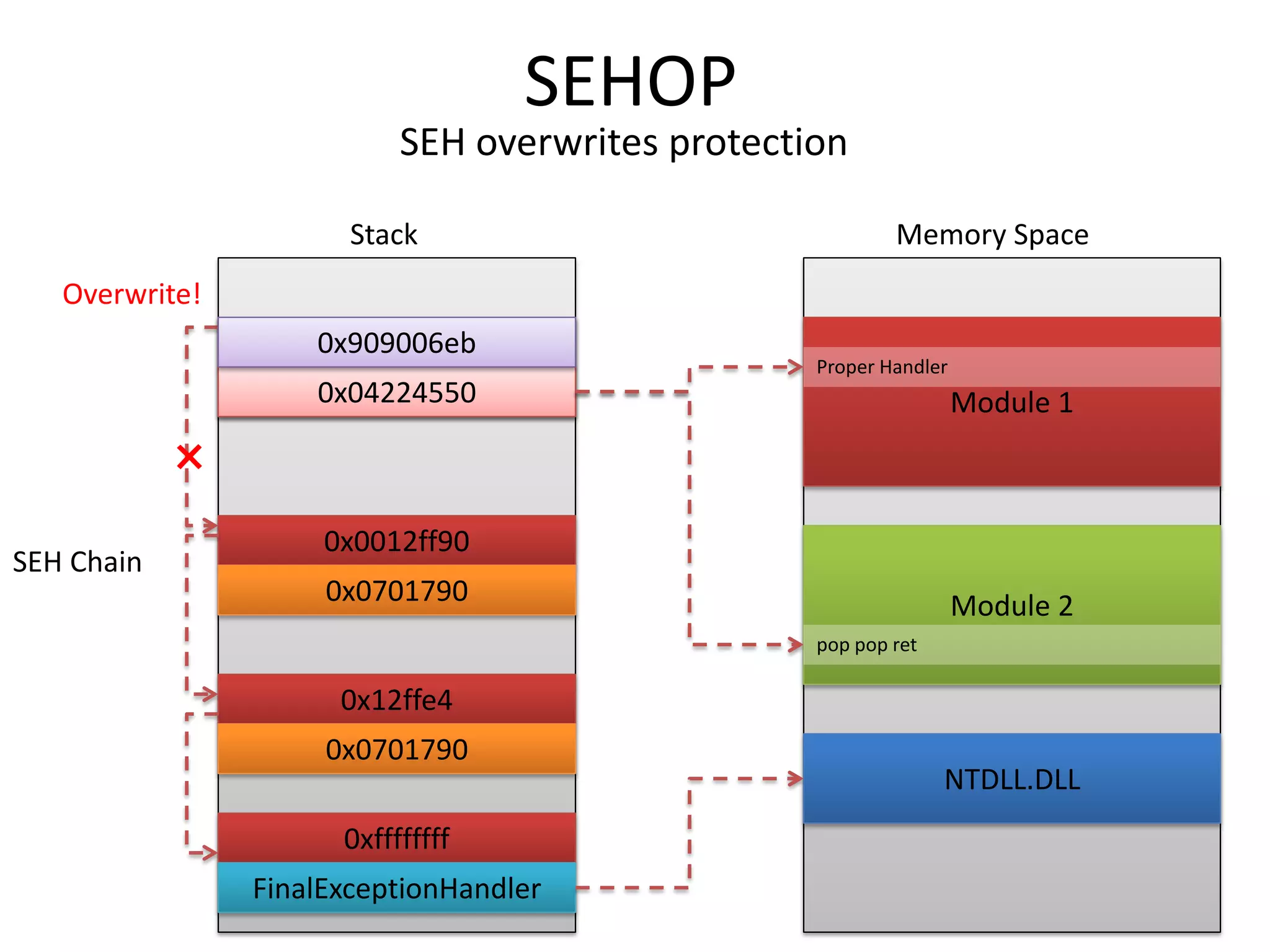
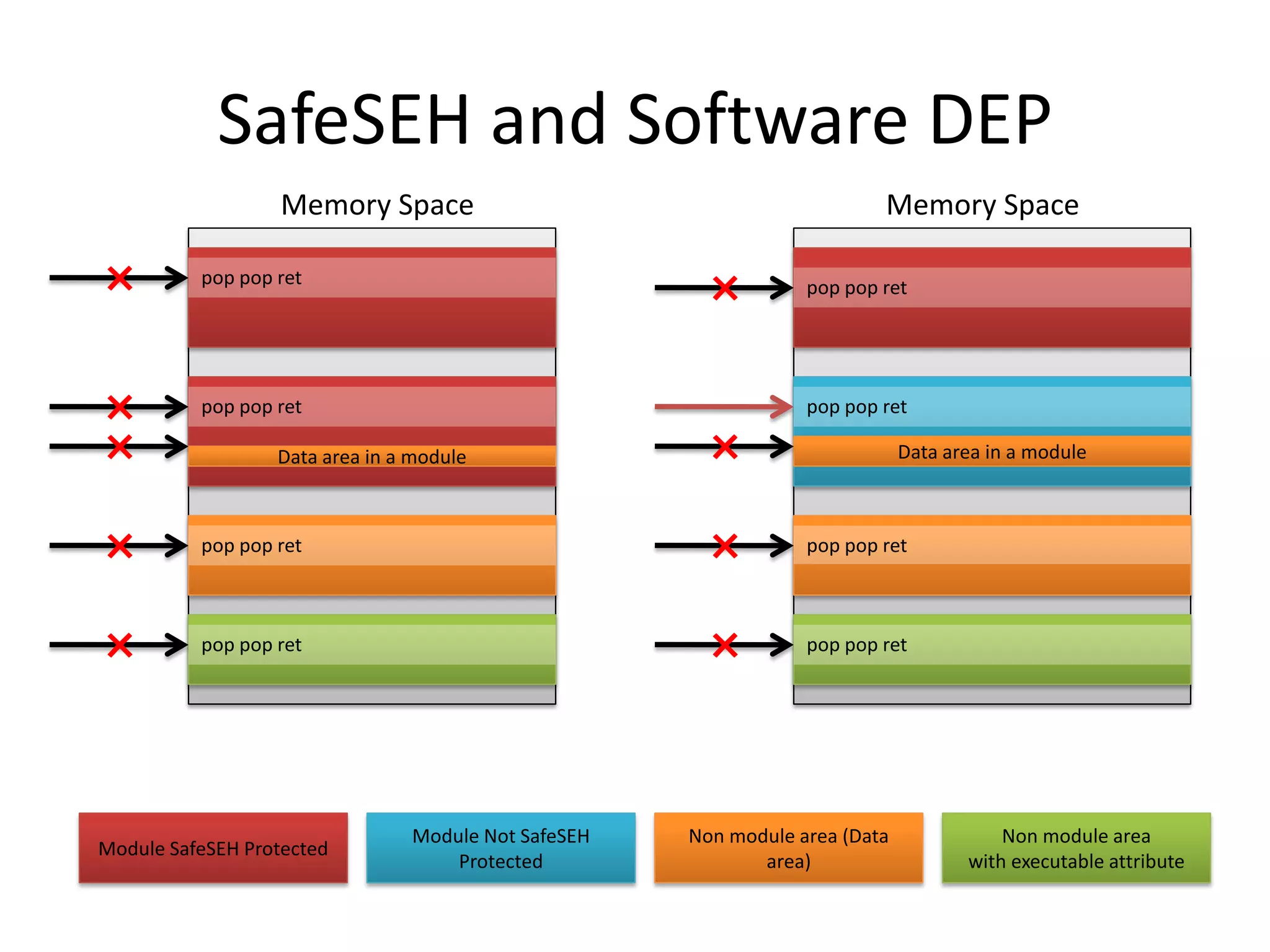
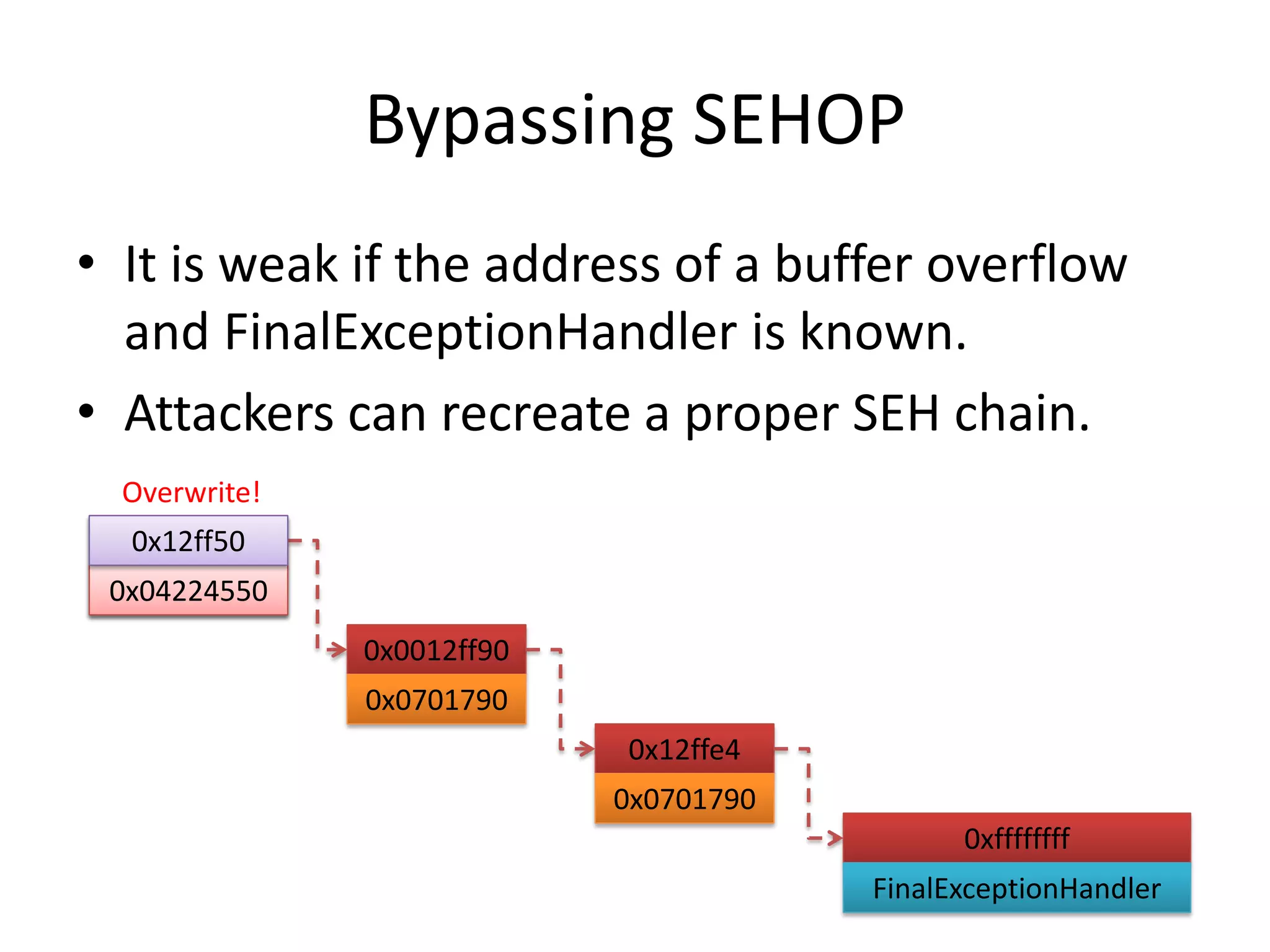
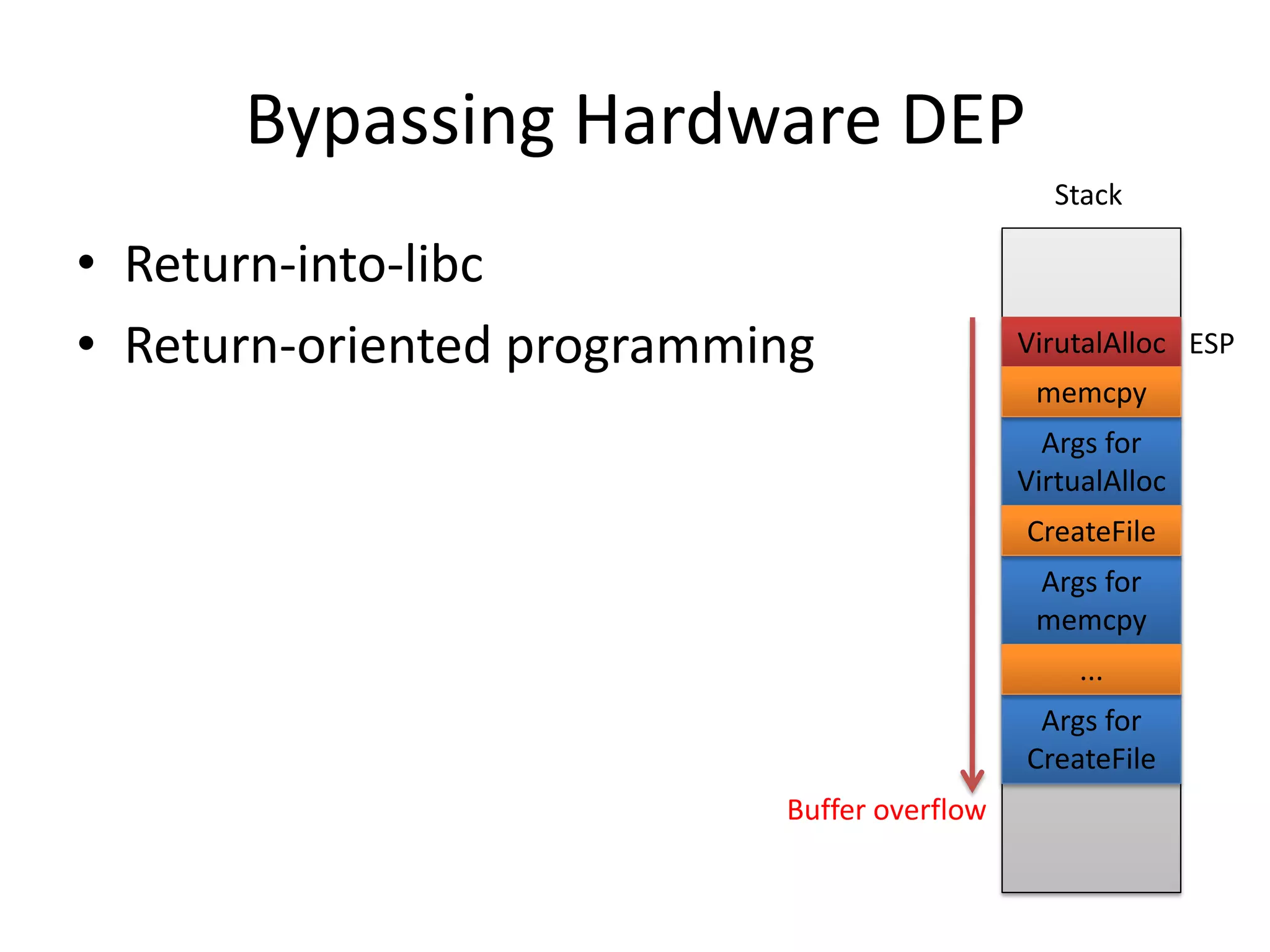
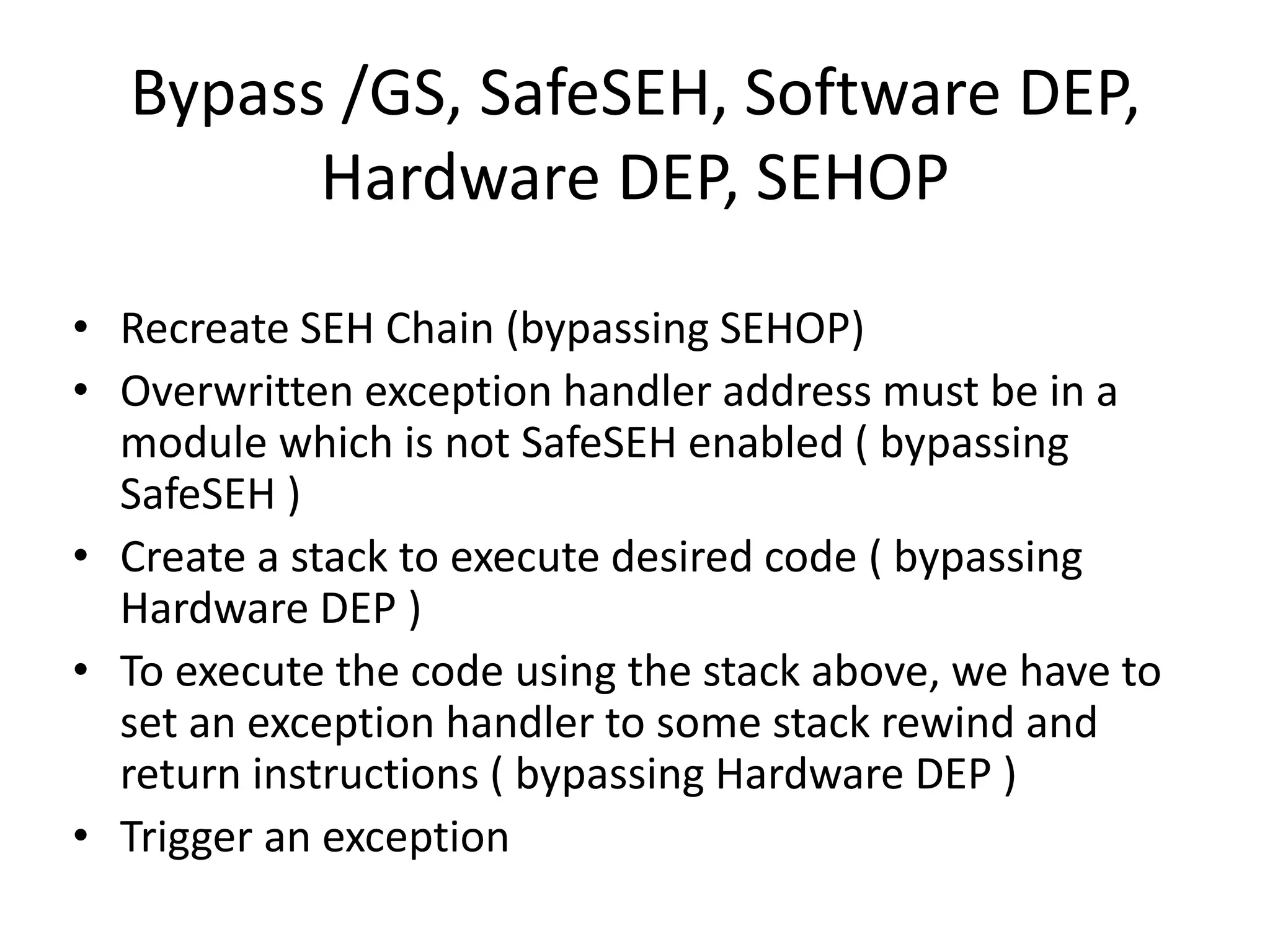
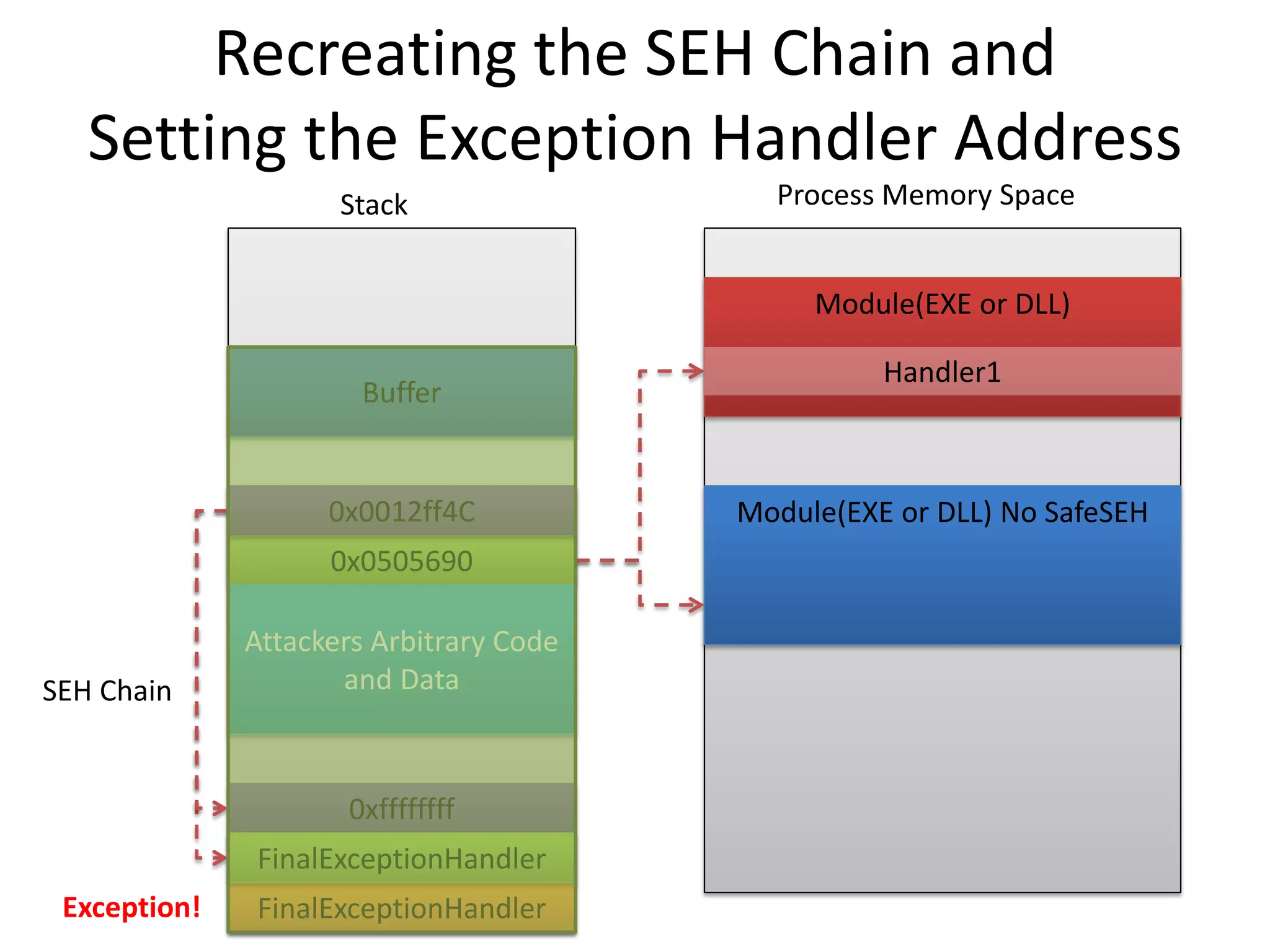
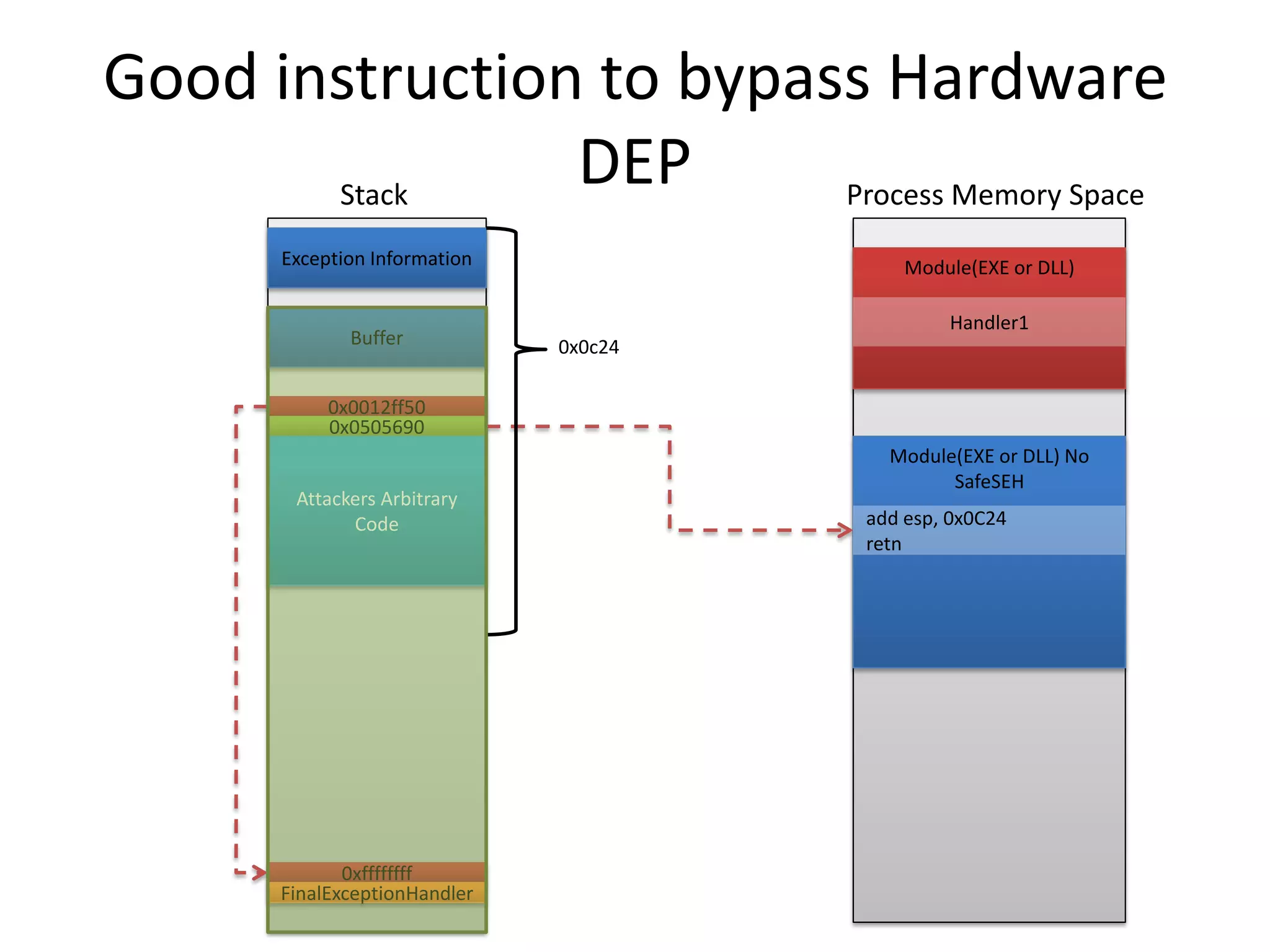
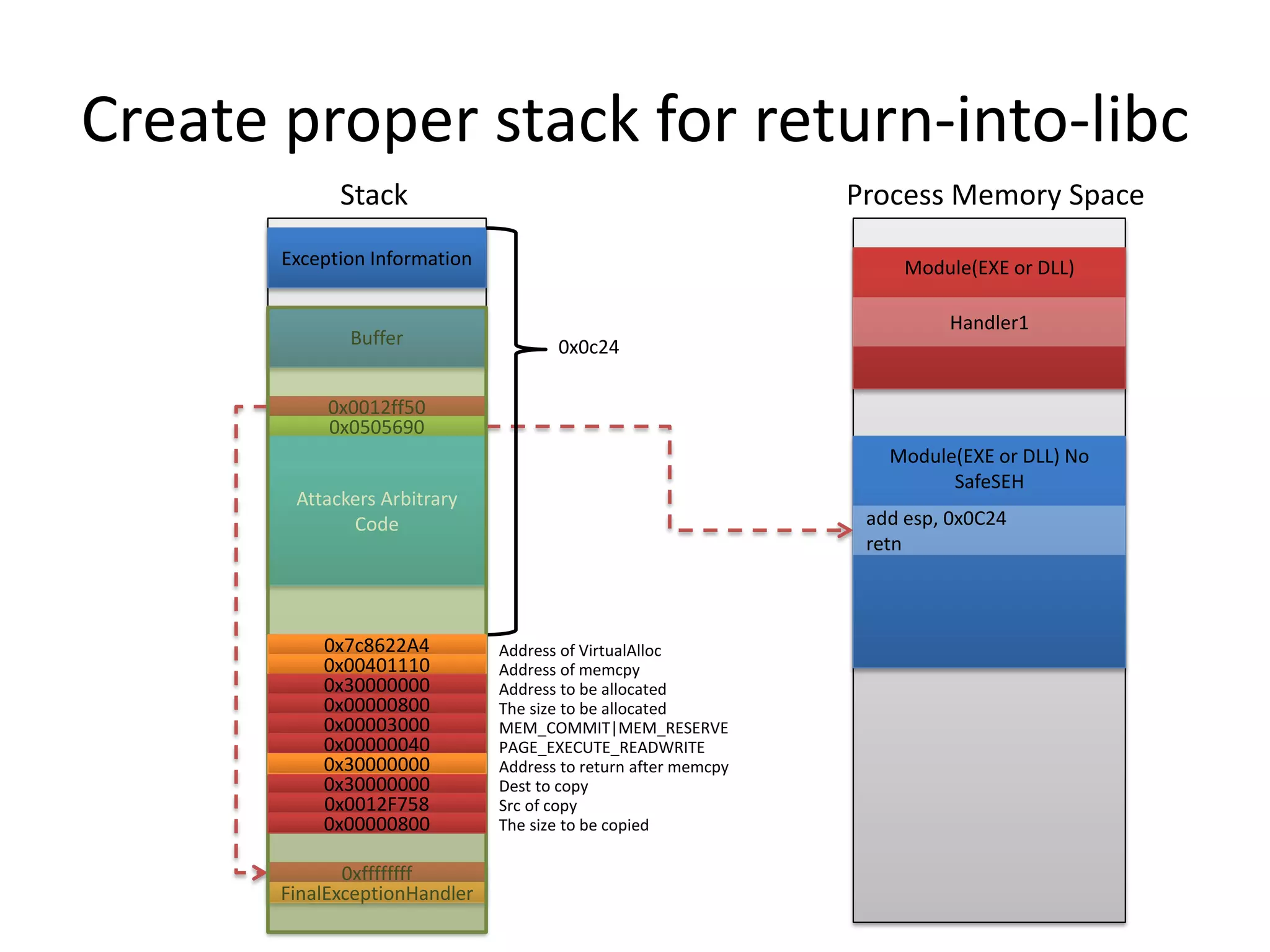
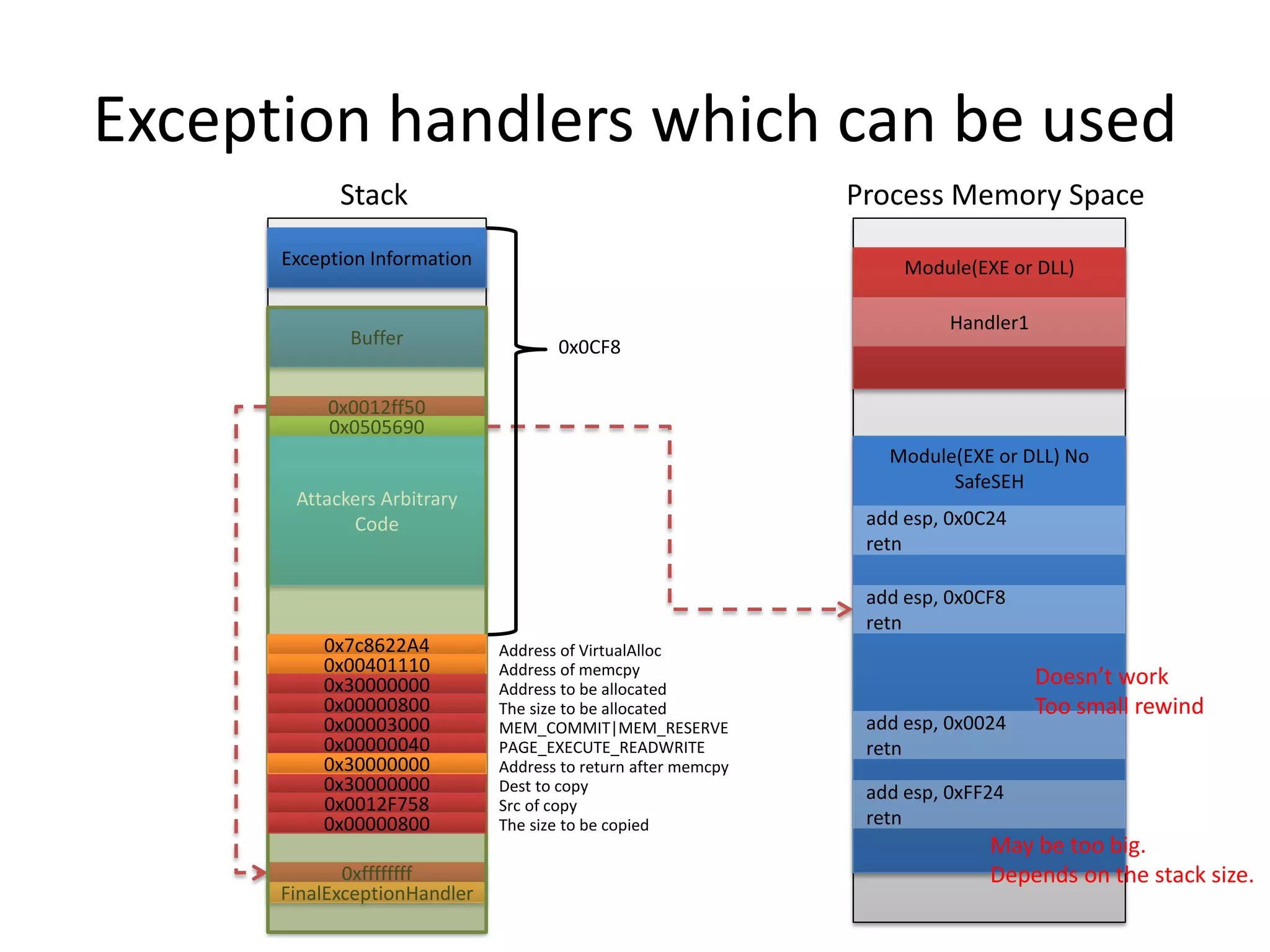
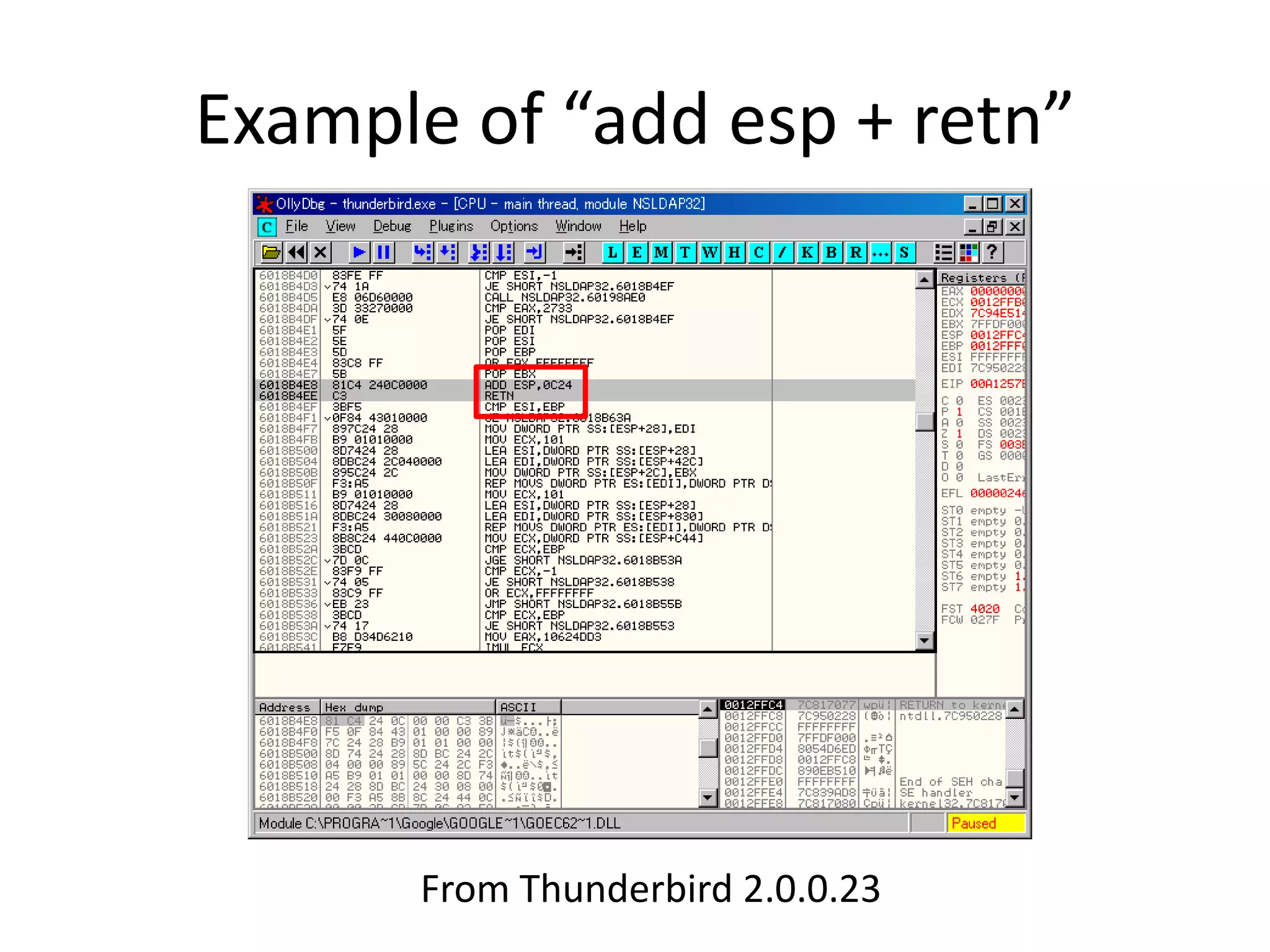
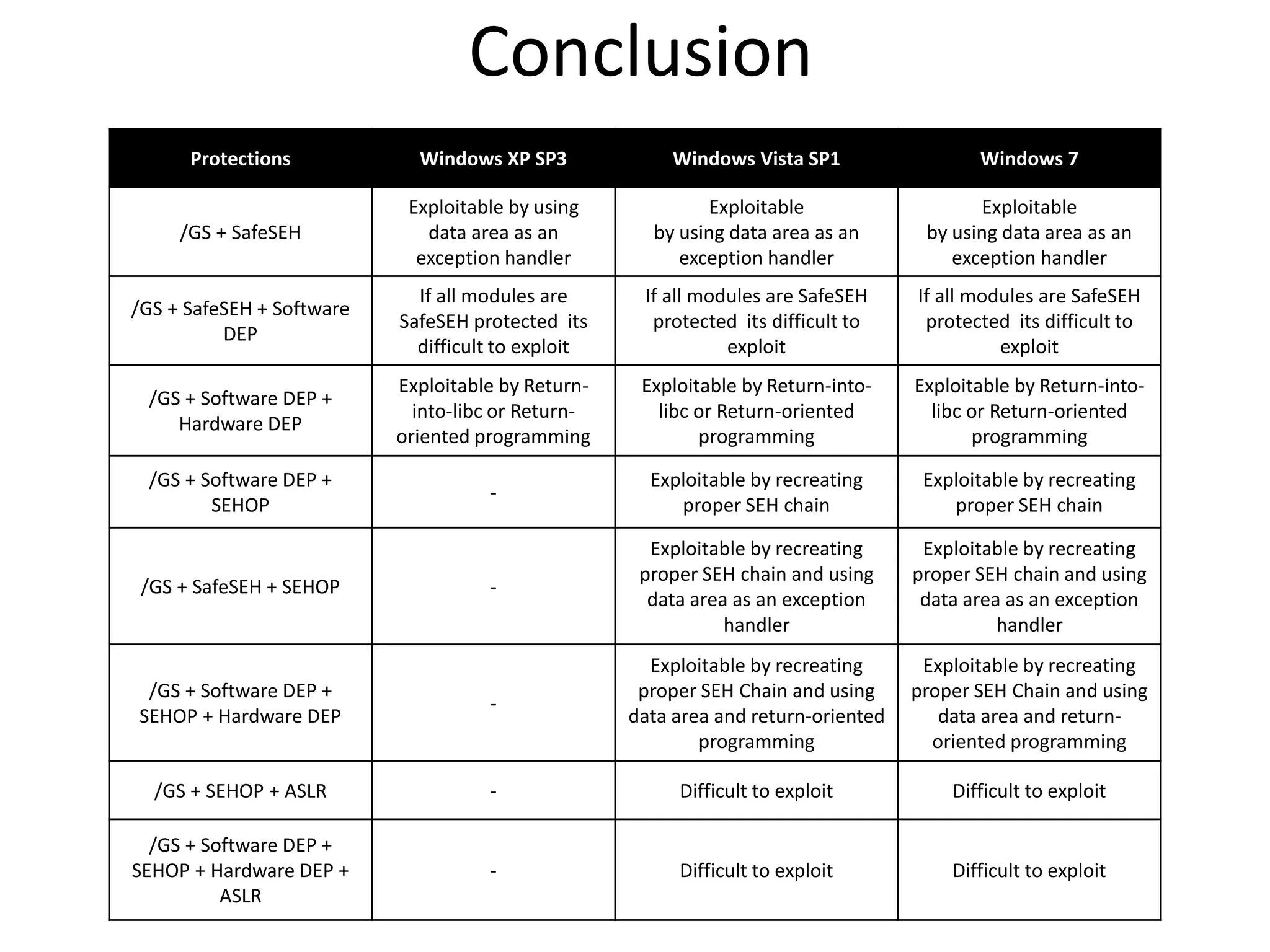
The document discusses SEH (structured exception handling) overwrites and techniques to bypass protections against them. It explains that SEH overwrites can be used to exploit Windows software by overwriting exception handlers. Common protections like SafeSEH, software DEP, hardware DEP, and SEHOP aim to prevent this. However, the document demonstrates that under certain conditions, it is possible to bypass all of these protections simultaneously. Specifically, if an attacker knows addresses needed to recreate the SEH chain and has a non-SafeSEH module containing suitable "add esp, ret" instructions, they can exploit a buffer overflow to execute arbitrary code despite all protections. The document provides a detailed example of this technique on Windows 7.