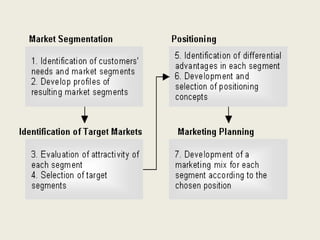
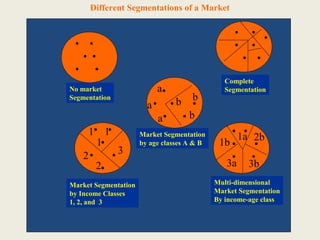
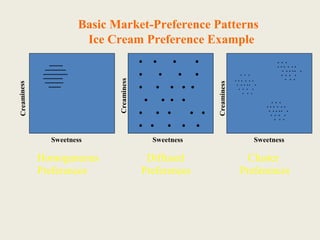
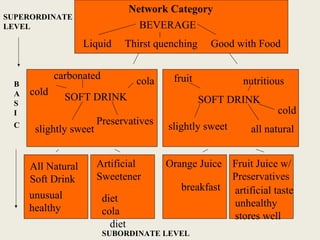
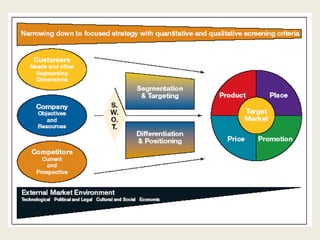
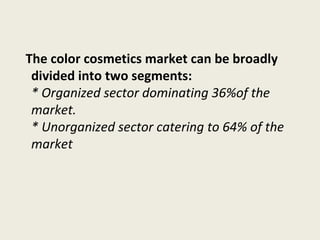The document discusses market segmentation, which involves dividing a market into subgroups with distinct needs, characteristics, or behaviors that would benefit from targeted marketing efforts. It provides definitions and principles of segmentation, including aggregating buyers into groups that have common needs and will respond similarly to marketing actions. The document also outlines various ways to segment markets, such as by geography, demographics, psychographics, purchase behaviors, and category networks. It emphasizes that effective segmentation requires groups that are measurable, accessible, substantial, and actionable. Examples of market segmentation for air travel and cosmetics are also provided.