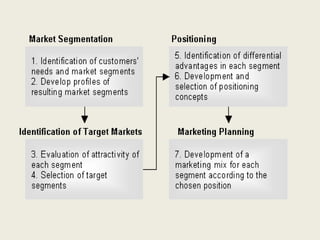
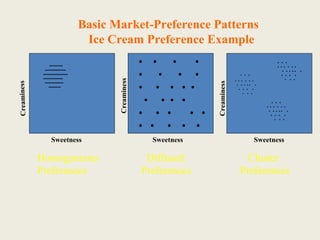
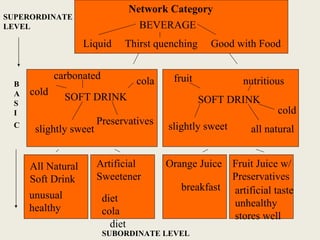
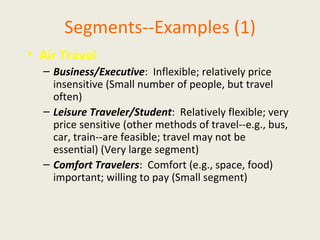
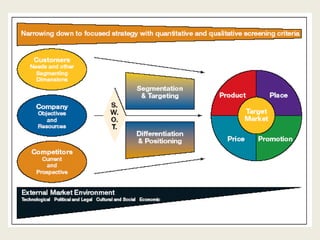
The document discusses market segmentation, which involves dividing a market into subgroups with distinct needs, characteristics, or behaviors that would benefit from targeted marketing efforts. It outlines different ways to segment markets, such as by demographics, psychographics, behaviors, or other variables. Effective segmentation requires groups that are measurable, accessible, substantial, and allow for tailored marketing strategies. Examples of market segments for various industries are provided.