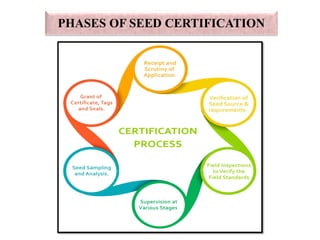
Seed certification is a system for quality control of seed production that identifies superior varieties, provides high quality seeds, and ensures genetic and physical purity. It involves establishing certification standards, inspecting seed fields, testing seed samples, and issuing certificates. The key goals are to identify new varieties, supply quality seeds, and ensure freedom from diseases, weeds, and good germination. Certification is overseen by state Seed Certification Agencies or the National Seed Corporation and involves inspection, testing, labeling, and record-keeping at multiple stages of seed production and processing.