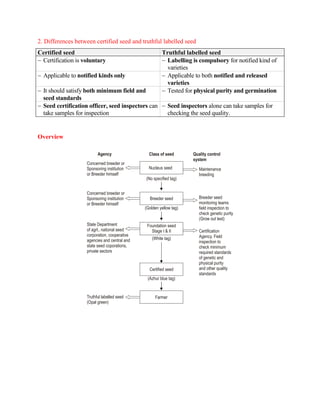
This document outlines the seed generation system for producing different classes of seeds. It discusses 6 classes - nucleus seed, breeder seed (stage I and II), foundation seed (stage I and II), registered seed, certified seed (stage I and II), and truthful labelled seed. The classes represent successive generations of seed production, with nucleus seed being the initial generation and certified seed being the final generation made available to farmers. The document also provides details on genetic and physical purity standards for each class and how they are stored and tagged.