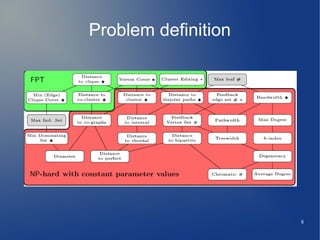
The document summarizes research on the parameterized complexity of the graph MOTIF problem. It begins by defining the problem and providing an example. It then discusses how graph MOTIF can be solved efficiently using different parameters, such as cluster editing, distance to clique, and vertex cover number. The document also analyzes parameters for which graph MOTIF remains NP-hard, such as the deletion set number parameter. In conclusion, it provides references for the algorithms and results discussed.








![10
Some Definitions
•
For any vertex , the set of neighbors of V is
N(v) and for , ,
and .
•
Vertex v dominate S if ,set R dominate
S if .
•
Denote the multiplicity of x in multiset M,
and .
v∈V
S⊂V N (S)=∪
v∈S
N (v)∖ S
S⊆N (v)
S⊆N (R)
mM x
∣M∣= ∑
x∈M
mM x
N [v]=N (v)∪{v}
N [S ]=N (S)∪S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150723180440-lva1-app6892/85/parameterized-complexity-for-graph-Motif-10-320.jpg)







![18
Cluster editing
• Theorem: graph MOTIF can be solved in on graph with
neighborhood diversity K [1].
➢ Compute neighborhood diversity:
- G is input graph, G' graph obtained after k edition on G.
- let X is set of vertices that are endpoints of the edit edges.
- Then
- Let is L cliques of G'.
- ,so number of neighborhood
diversity of G is bounded by .
- applying the above theorem , Graph MOTIF can be solved in
O
∗
(2
k
)
∣x∣≤2k
C1,. .. ,C L
∀i∈[L]∀v∈Ci ∖ X , N [v]=Ci
∣x∣+ l≤2k+ k=3k
O∗
(23k
)=O∗
(8k
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150723180440-lva1-app6892/85/parameterized-complexity-for-graph-Motif-18-320.jpg)

![20
Distance to clique
• Theorem: graph MOTIF can be solved in
where k is distance of input graph to clique.
• Proof: Algorithm:
- Find vertex cover S of size k in in time [2].
- S is also the distance to clique in G.
- let R be solution, trying all subset of S, guess subset of
S, which is in R.
- ,then vertices of the clique C with colors
should complete the solution.
- Problem: finding a minimal (inclusion wise) set such
that and G[ ] is connected.
O
∗
(2
klogk
)
G 1.2738k
2k
S '=S∩R
c(S ')⊆M ∣M∣−∣S '∣
M '=M ∖c(S ')
R'⊆C
c(R')⊆M ' R'∪S '](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150723180440-lva1-app6892/85/parameterized-complexity-for-graph-Motif-20-320.jpg)
![21
Distance to clique
• Proof: Algorithm “continue”:
- Let be connected components of G[S'],
- build graph G'=(V',E') from graph G:
+Keep the clique C as it is.
+ contract into single vertex and draw
and edge from to iff and
+ a minimal (inclusion wise) in a dominating
vertex in G',
+ try out all l-partitions of denoted by
st: dominate . note that .
+ number of partitions : “Bell number”.
C1, C2,. .. ,Ck ' k '< k
∀Ci ,i∈[k ' ] Ci vi
vi v∈C ∃u∈Ci {u ,v}∈E
Rd ⊂R∖ S '
Rd =r1 ,... ,rl
{v1 ,... ,vk ' } {A1 ,... , Al }
ri Ai
Bk '
l≤k '≤k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150723180440-lva1-app6892/85/parameterized-complexity-for-graph-Motif-21-320.jpg)
![22
Distance to clique
• Proof: Algorithm “continue”:
- From G' ,build bipartite graph , H=( ,B)
where and where
there is an edge between and all
iff such that c(v)=x, v dominate and there
is no ,v dominate .
- H has vertices and in
can decided if H has perfect matching in
size l if exists [3].
H1∪H2
H1={uAi
,i∈[l]} H2= ∪
x∈M '
{ux
1
,ux
2
,... ,ux
mM ' x
}
uAi {ux
1,
ux
2,.
.. ,ux
mM ' x
}
∃v∈V ' Ai
i≠ j Aj
l+∣M '∣≤k+∣M∣ (k+ M )2.376](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150723180440-lva1-app6892/85/parameterized-complexity-for-graph-Motif-22-320.jpg)

![24
Distance to clique
• Proof: Algorithm “continue”:
- from perfect matching in H, graph MOTIF
solution built:
- there , namely ,
and dominate .
- set , G[Z] is connected and
and then we extend z by adding subset
such that c(Z')=M'c(Z).
∀i∈l {uAi
,ux
ji
}∈B ∃wi ∈V ' c(wi)=x
wi Ai
Z=S '∪∪
i∈l
wi c(Z )⊆M '
Z '⊆C ∖ Z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150723180440-lva1-app6892/85/parameterized-complexity-for-graph-Motif-24-320.jpg)














![39
Refrences
● [1] “R. Ganian. Using neighborhood diversity to solve hard
problems. CoRR, abs/1201.3091,2012.”.
● [2]M. Mucha and P. Sankowski. Maximum Matchings via
Gaussian Elimination. In 45th Sym-posium on Foundations of
Computer Science (FOCS 2004), pages 248–255. IEEE
ComputerSociety, 2004.
● [3] “J. Chen, I. A. Kanj, and G. Xia. Improved upper bounds for
vertex cover. Theoretical Computer Science, 411(4042):3736 –
3756, 2010.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpresentation-150723180440-lva1-app6892/85/parameterized-complexity-for-graph-Motif-39-320.jpg)
