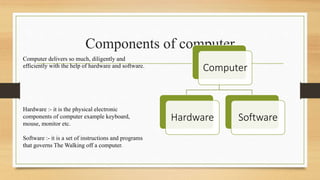
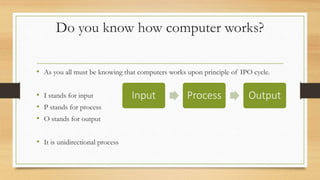
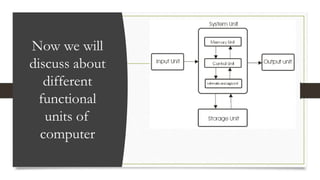
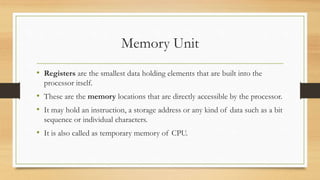
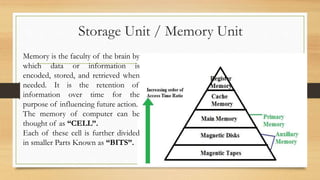
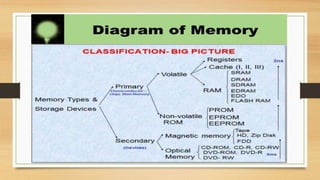
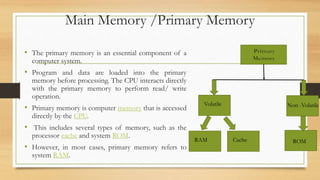
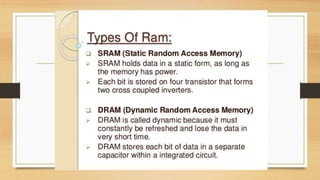
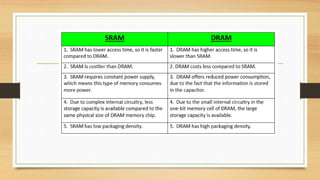
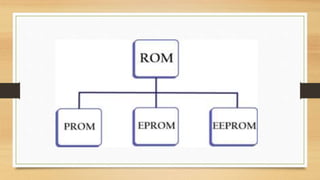
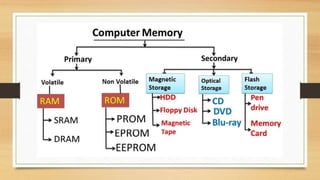
The document discusses the basic components and organization of a computer system. It describes the input and output units that allow for data entry and display. The central processing unit (CPU) is comprised of an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for processing, a control unit for directing operations, and memory units for temporary and permanent storage. The CPU interacts with primary memory like RAM and secondary memory like hard drives for long-term storage. Together, hardware and software work to power computer functions.













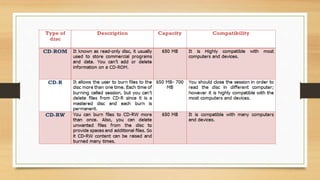
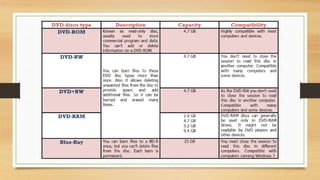
![HDD / Hard Disk Drive
A Hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed
disk[ is an electro-mechanical data storage device that
stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage and
one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with
magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic
heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which
read and write data to the platter surfaces.[2] Data is
accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that
individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any
order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining
stored data even when powered off.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch1notesip-221109161435-52b54617/85/ch1notes-IP-pptx-28-320.jpg)