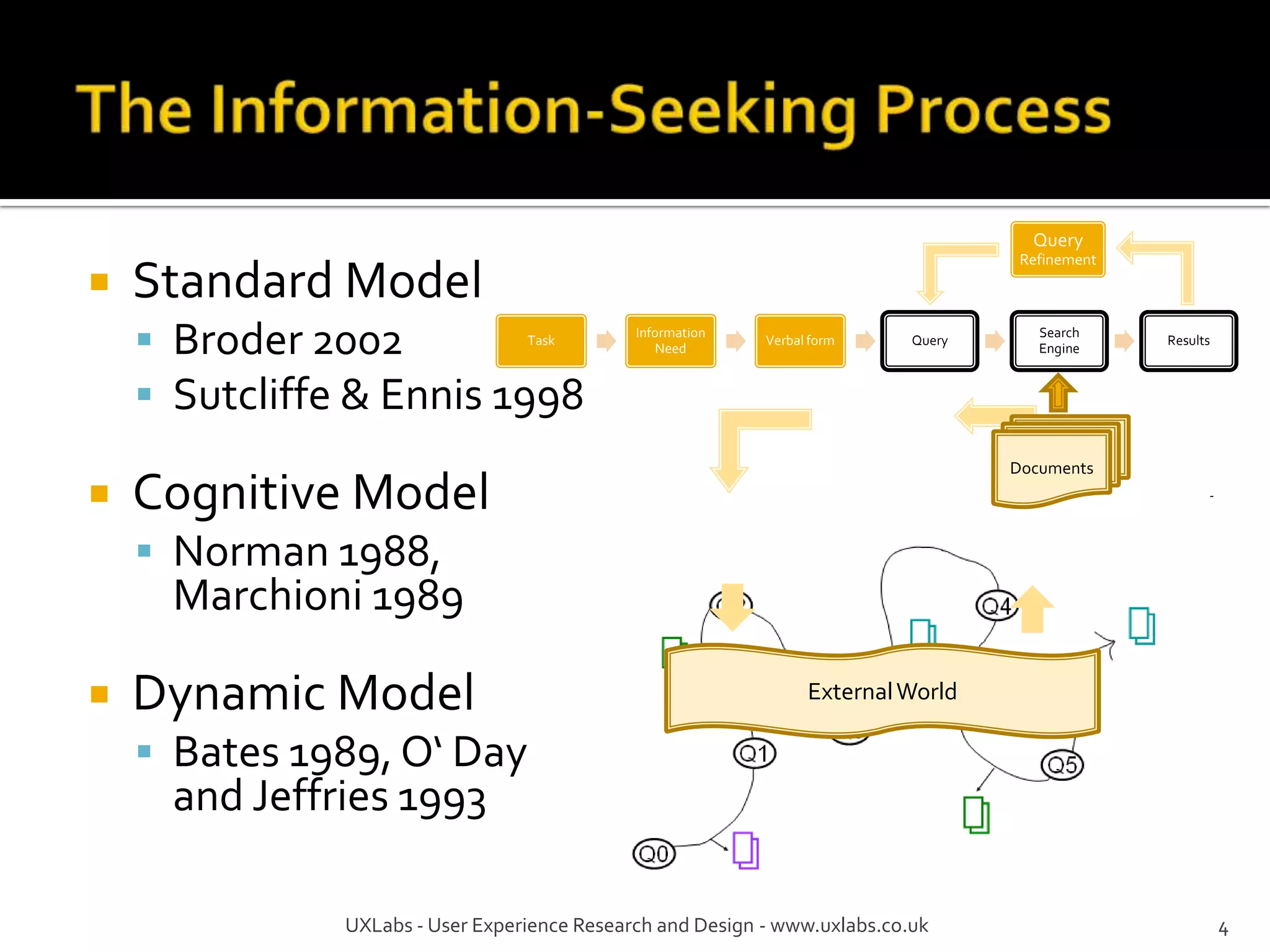
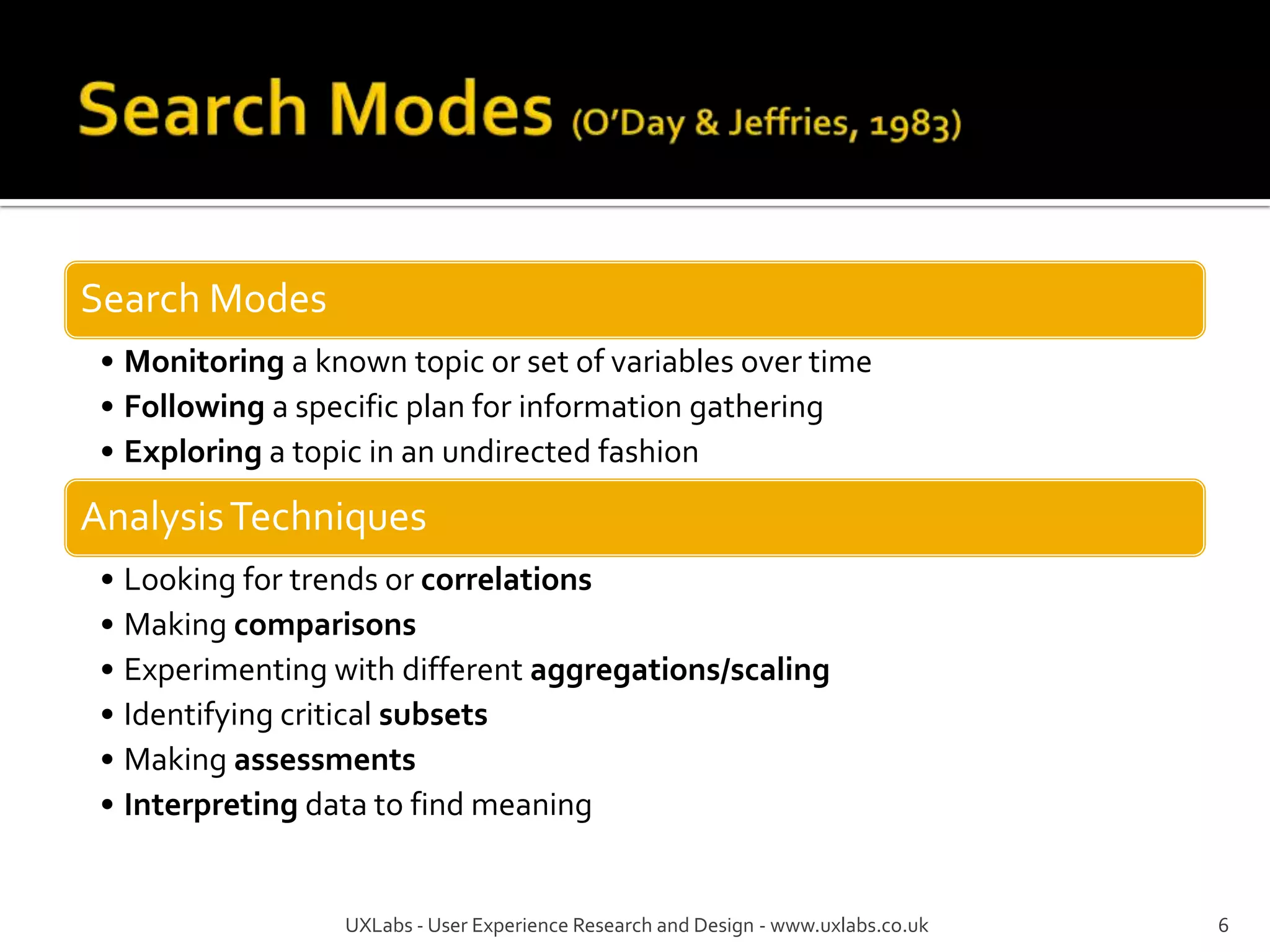
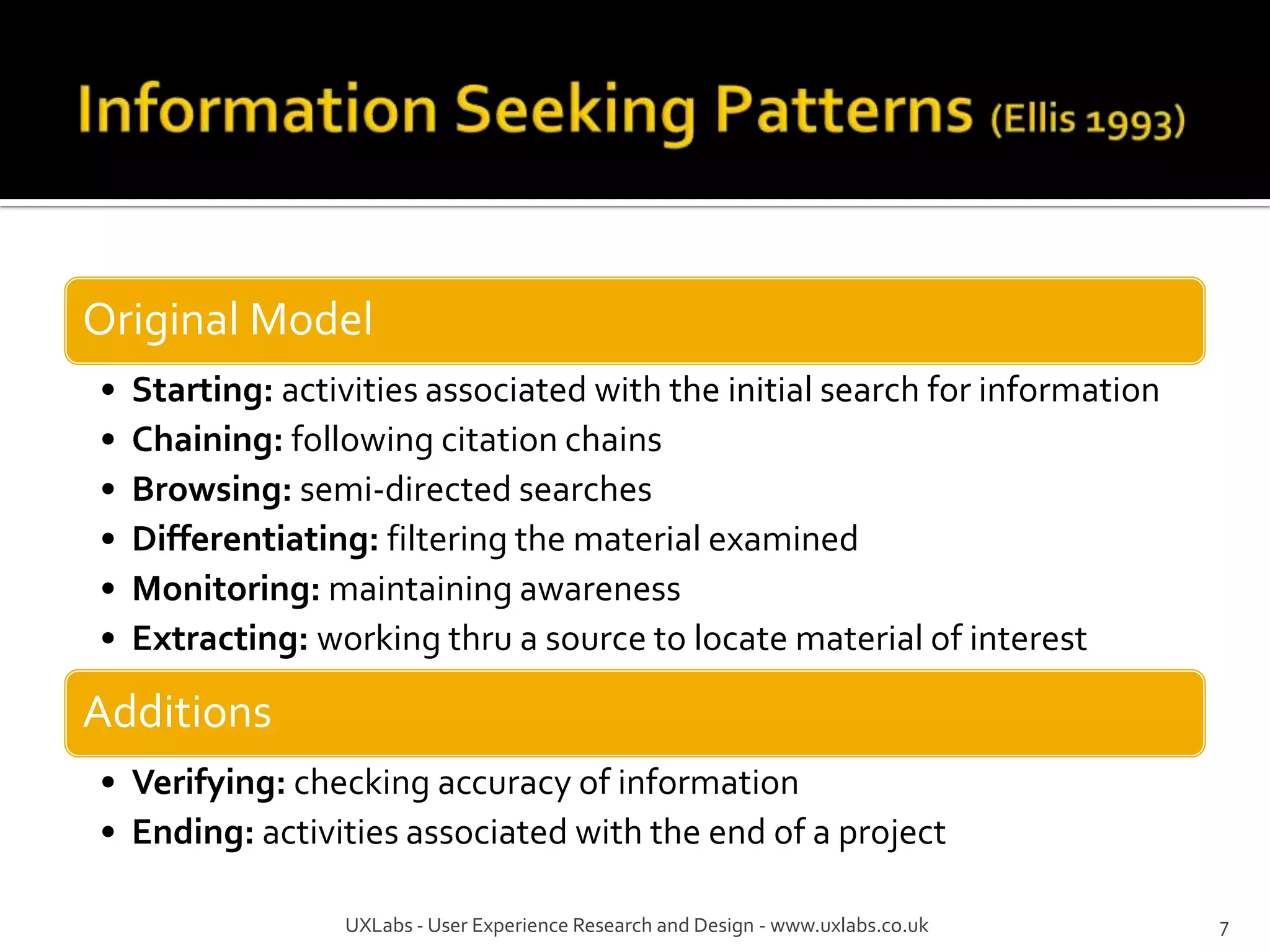
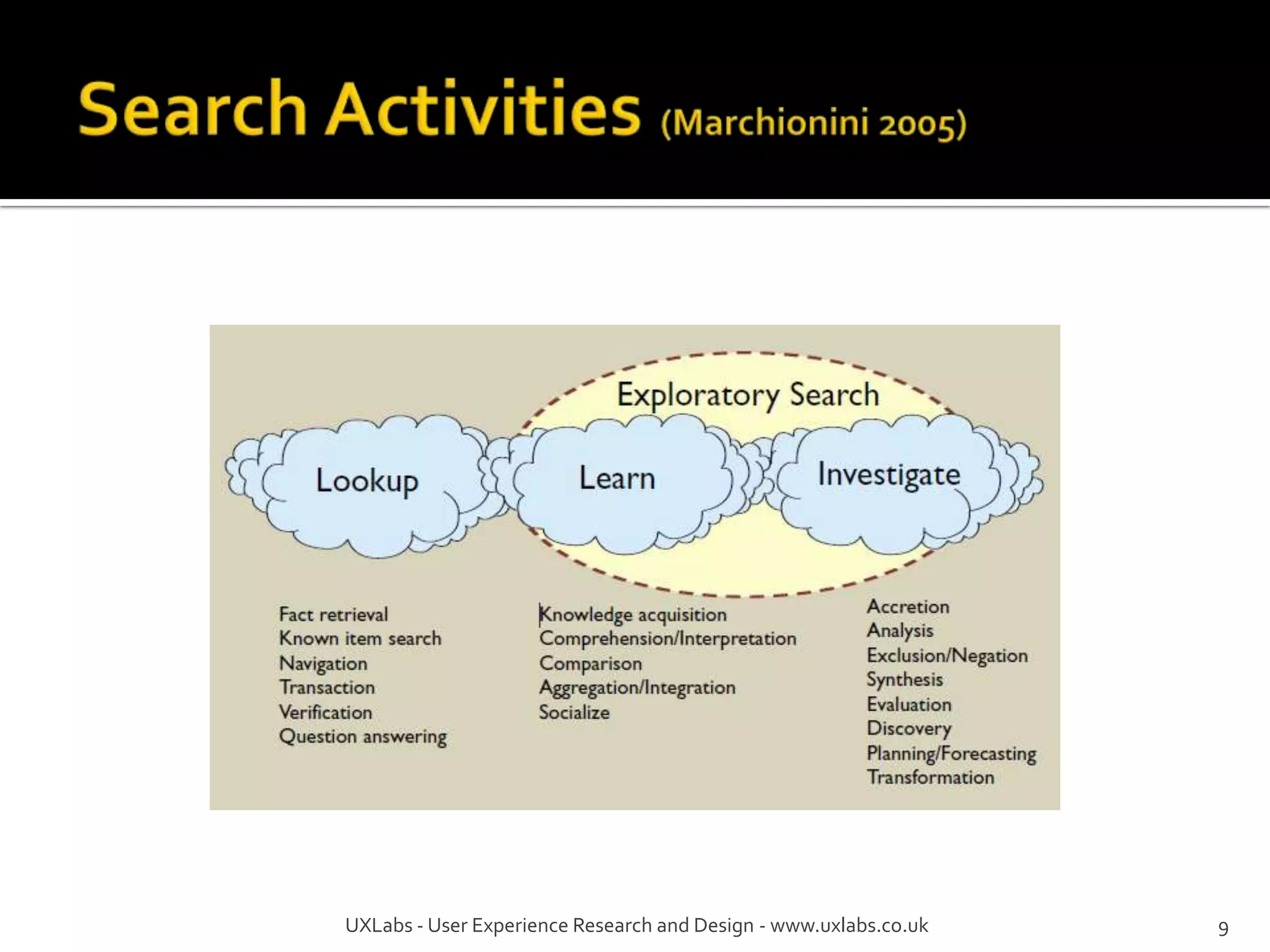
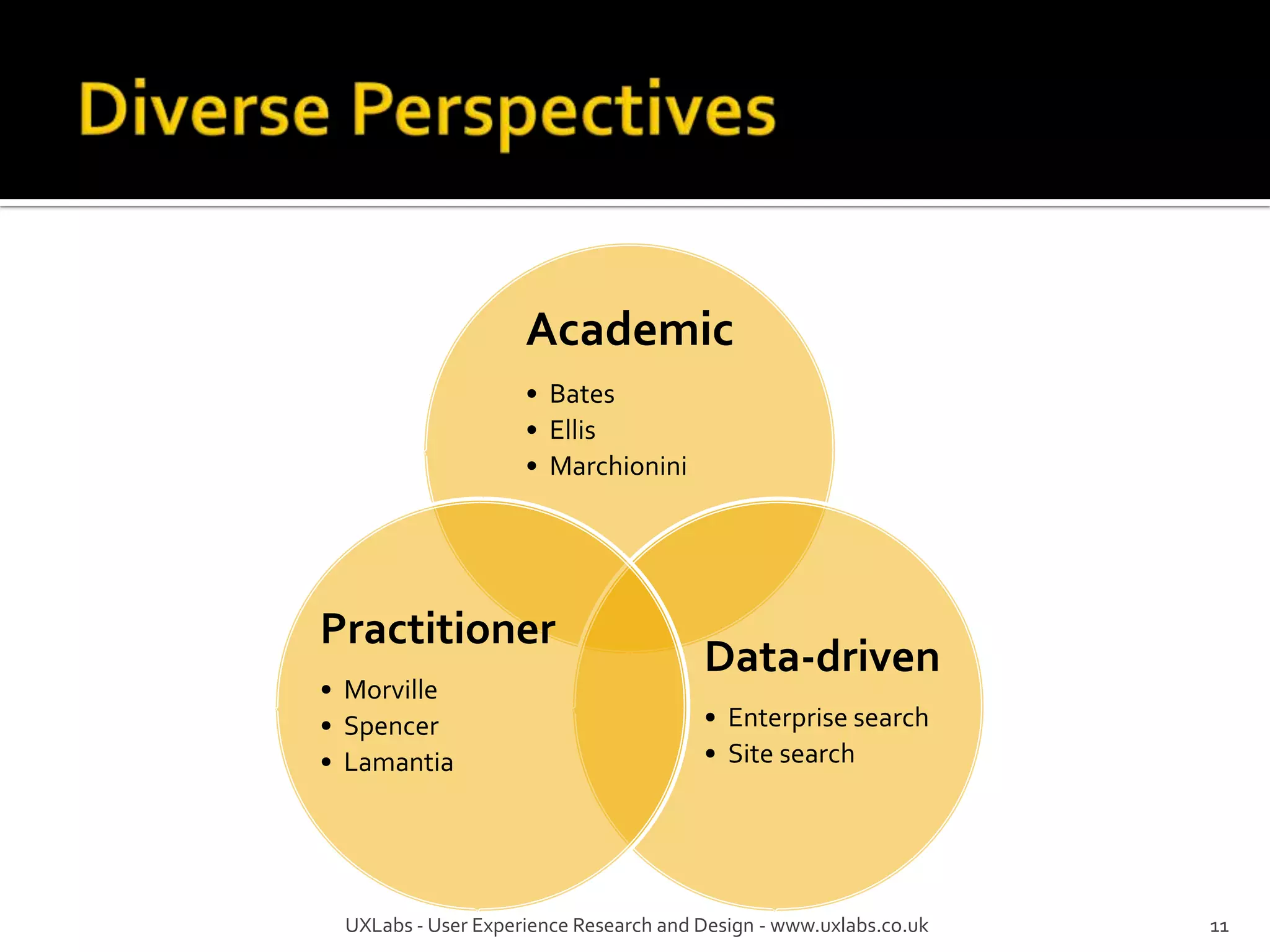
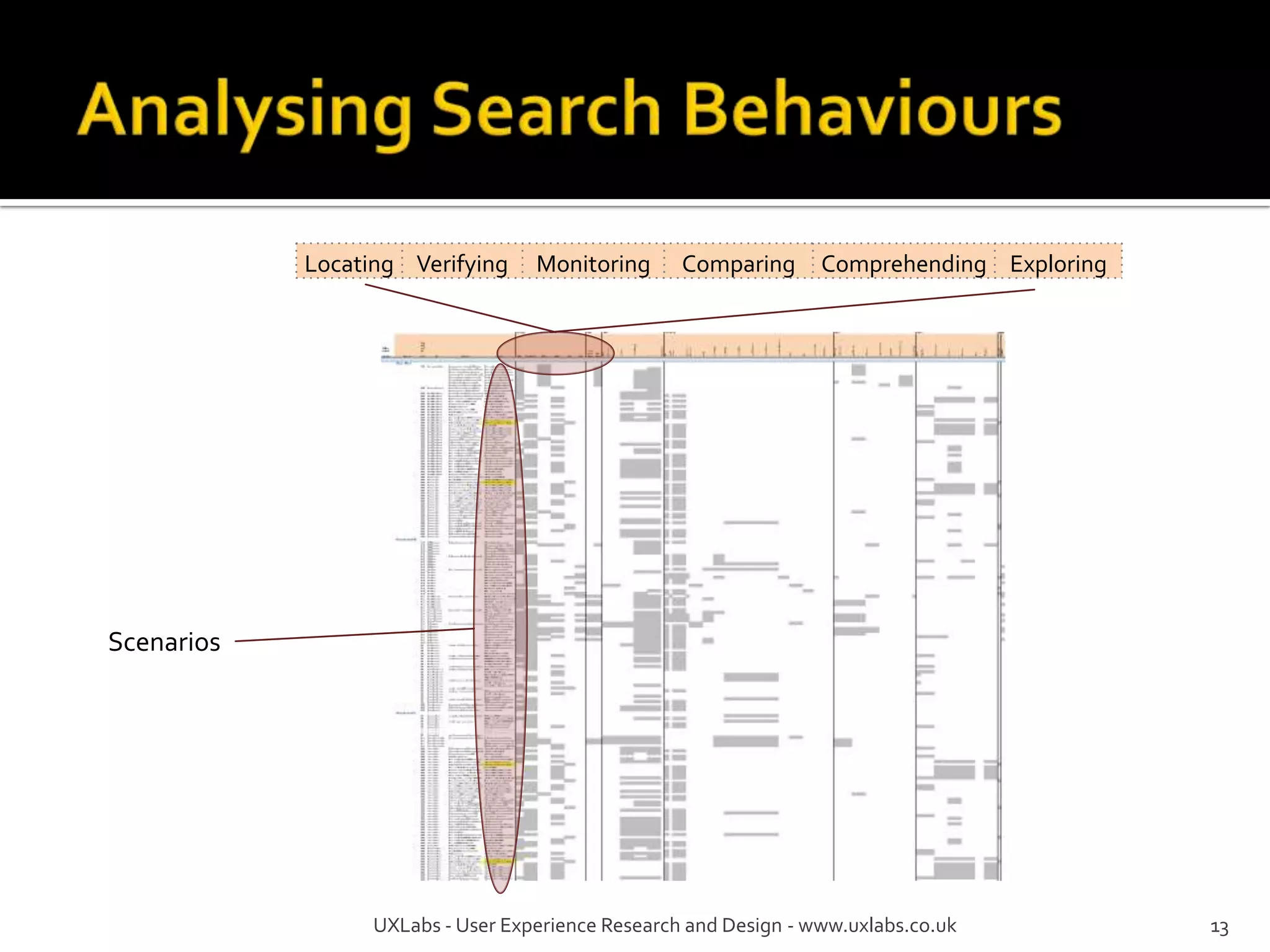
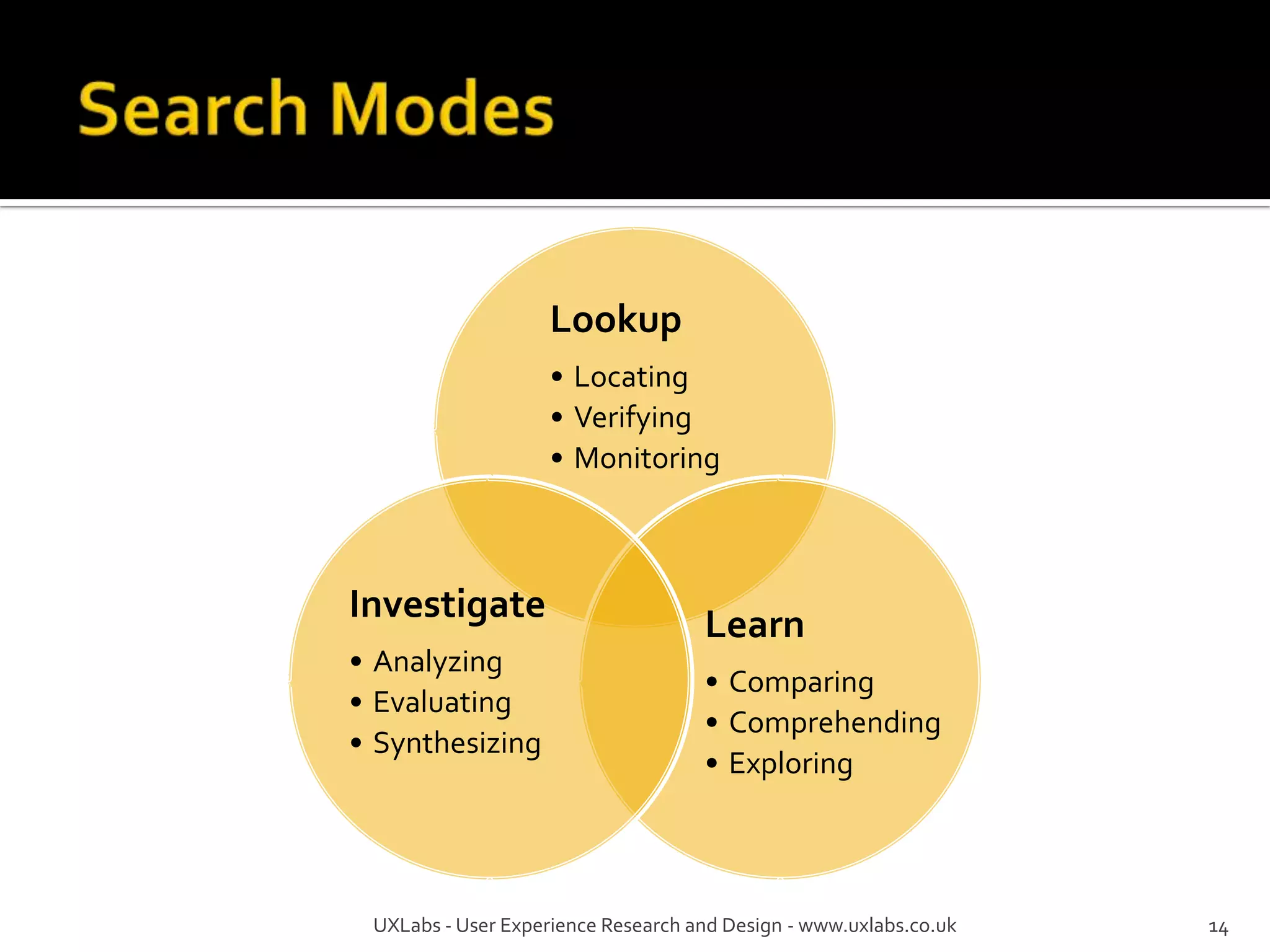
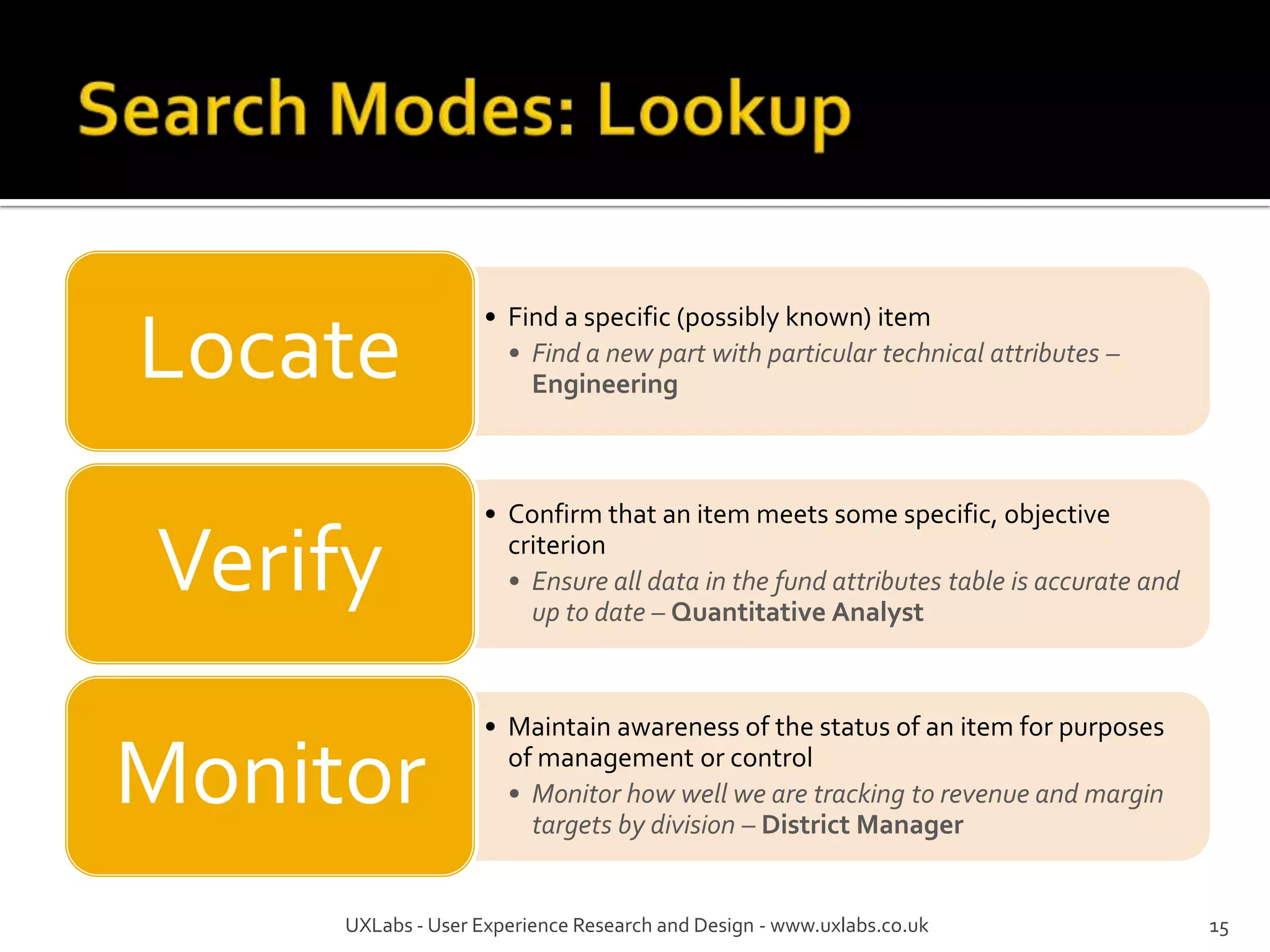
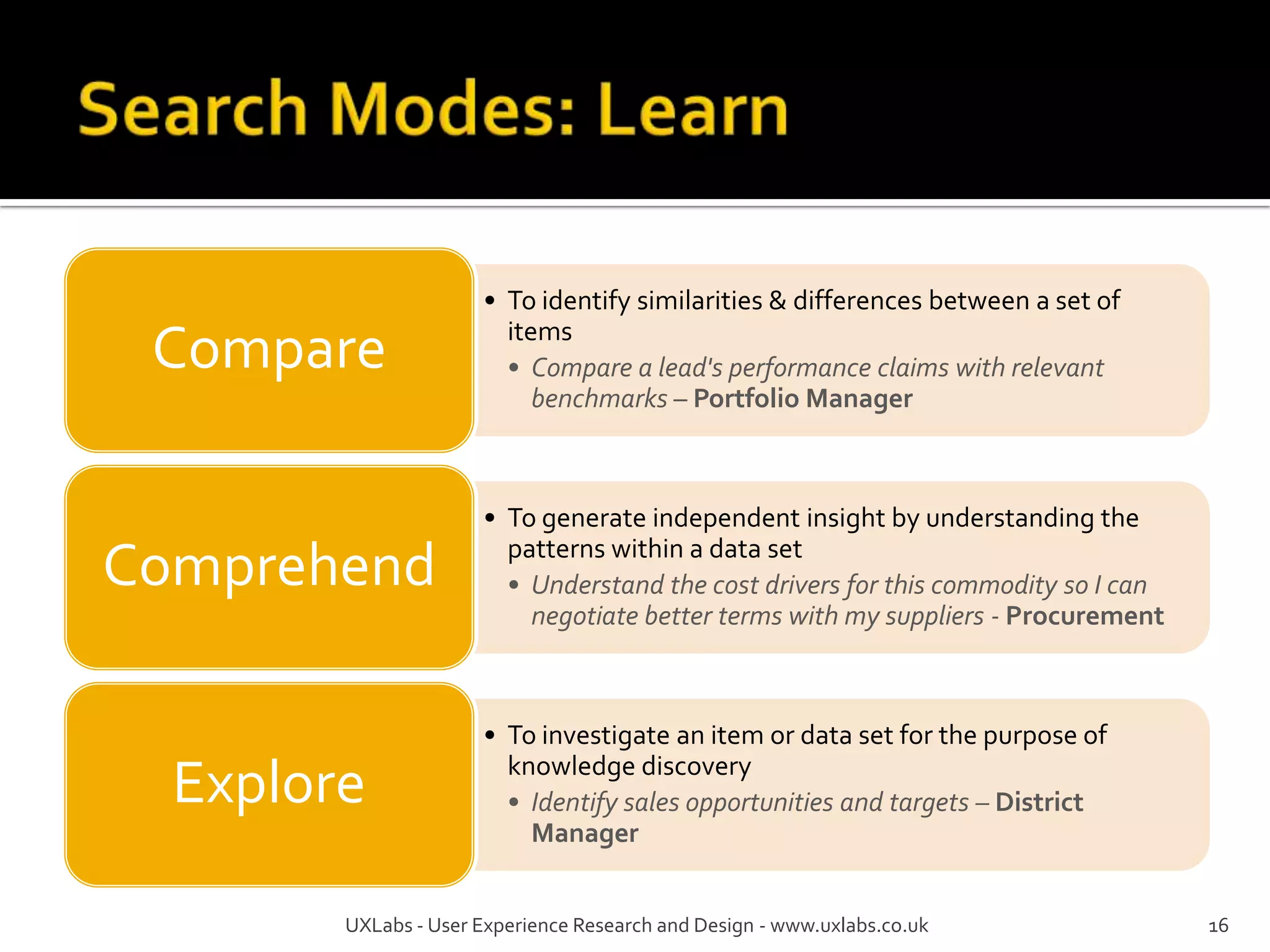
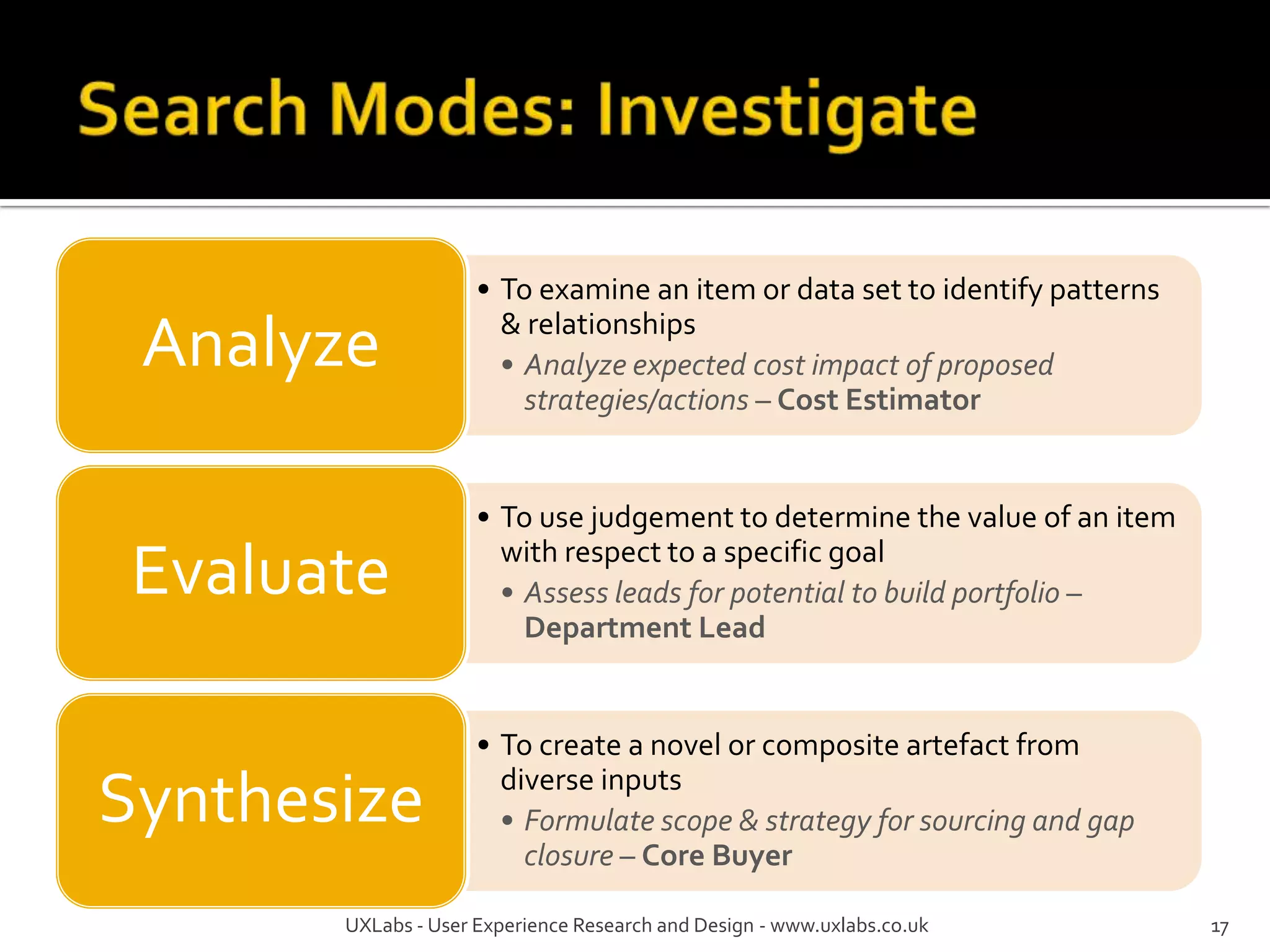
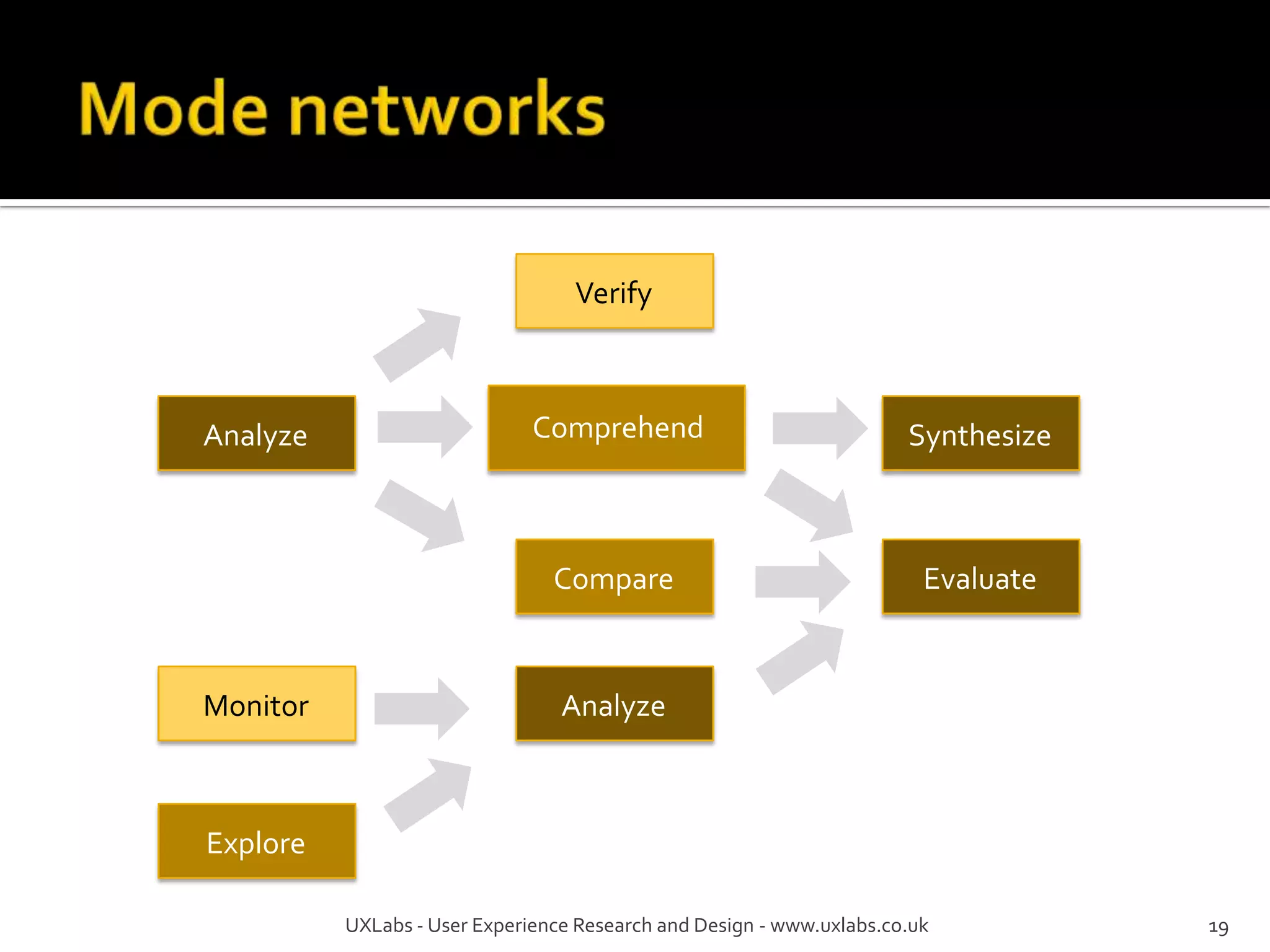
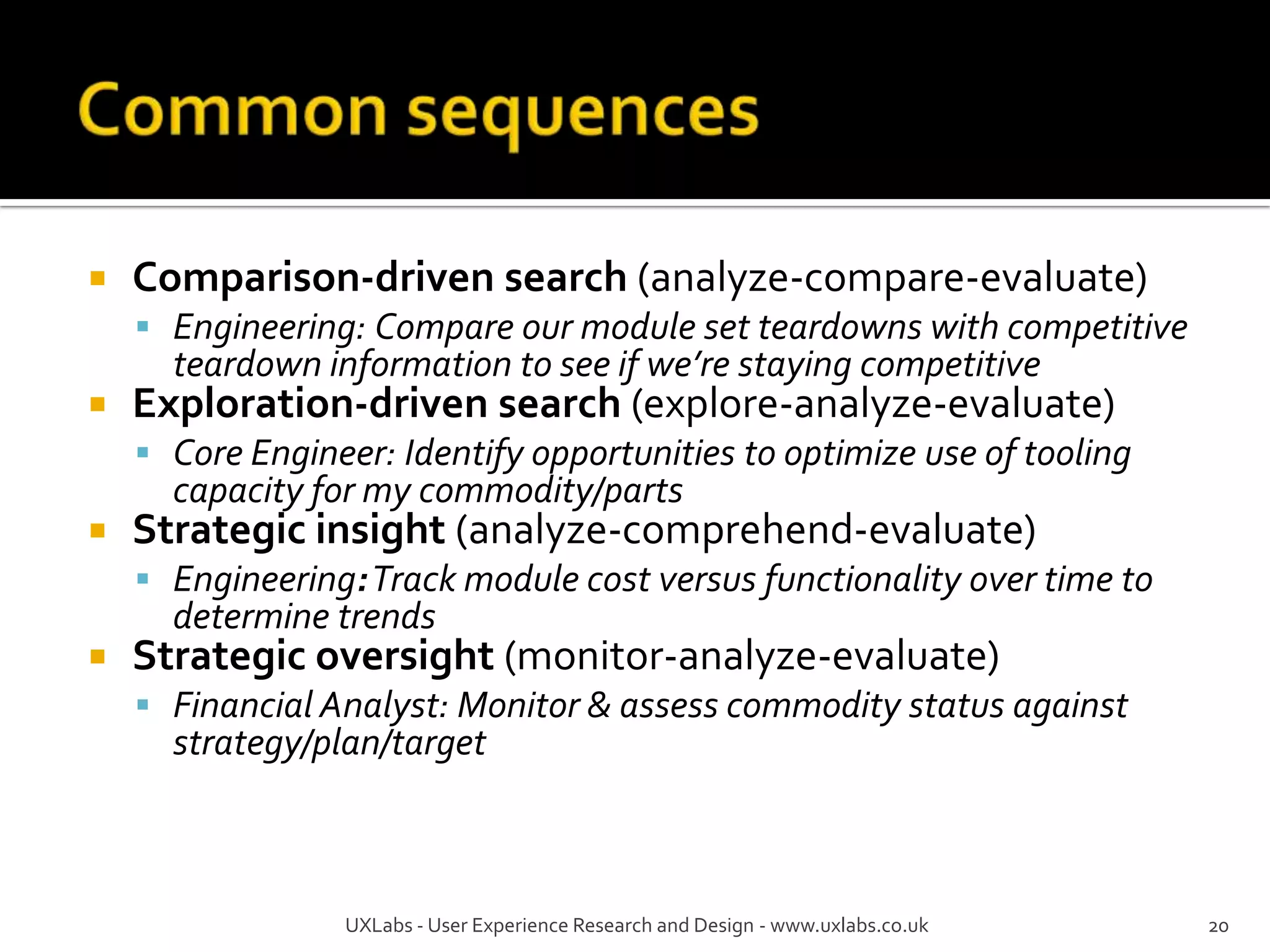
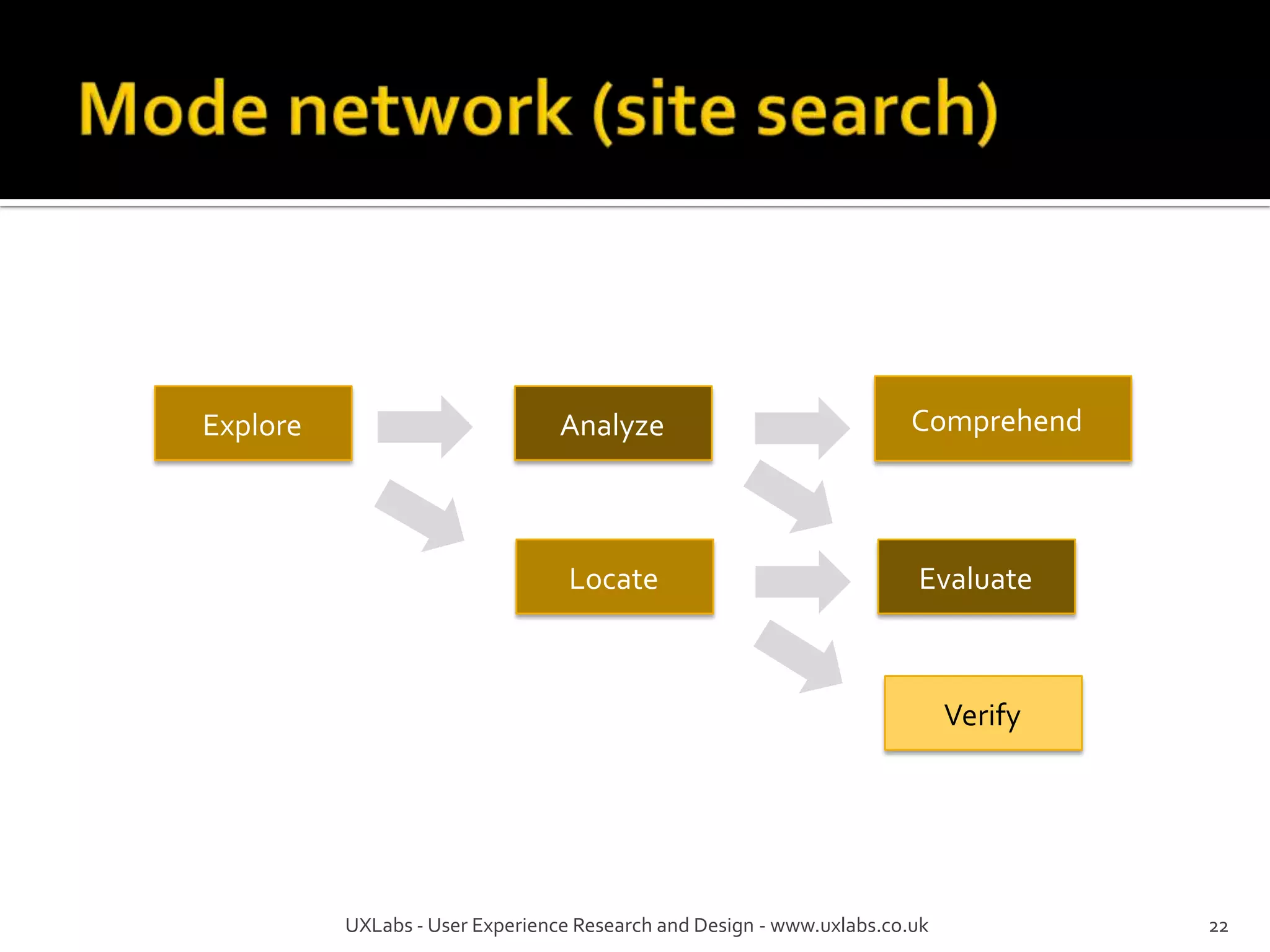
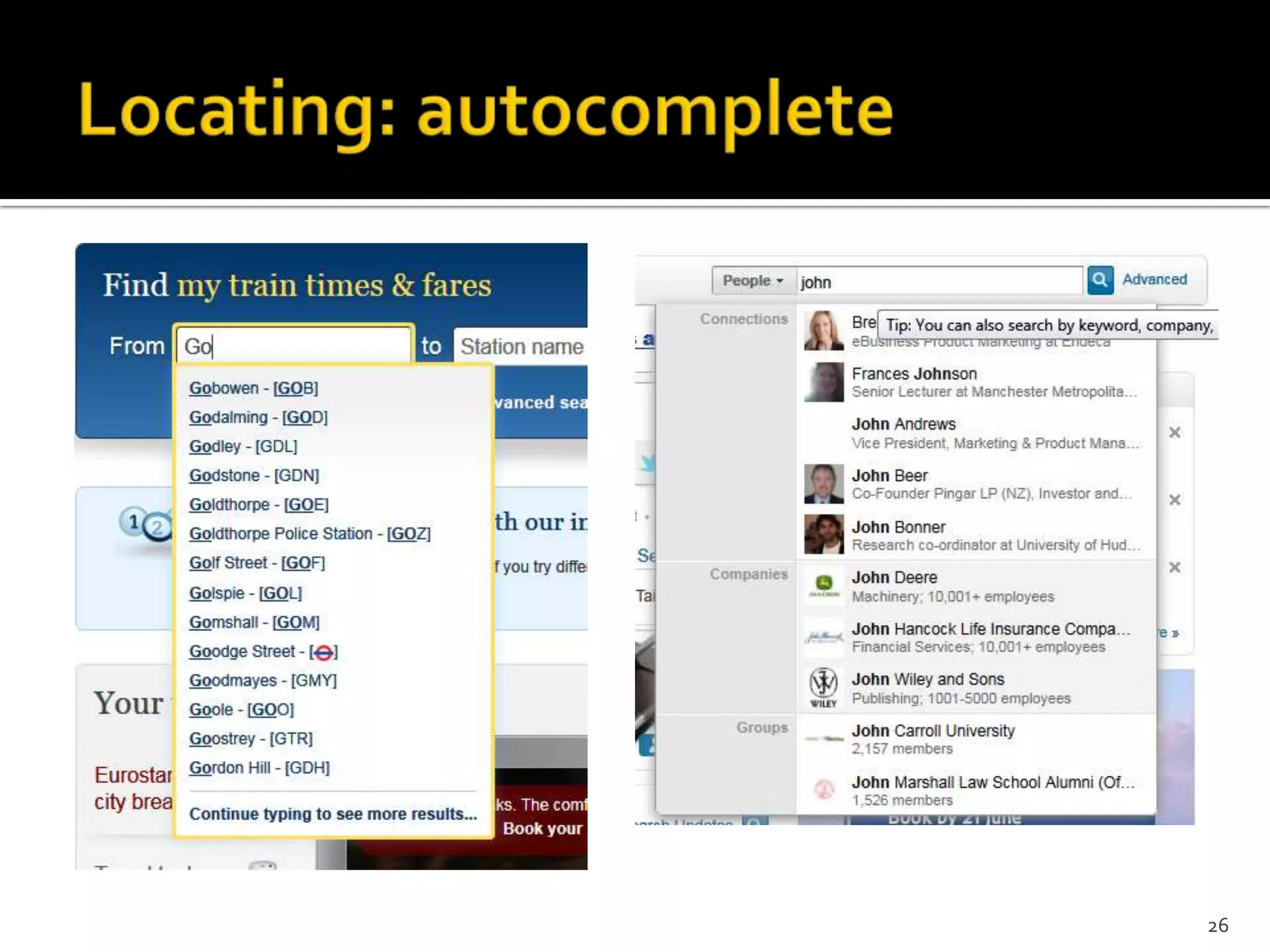
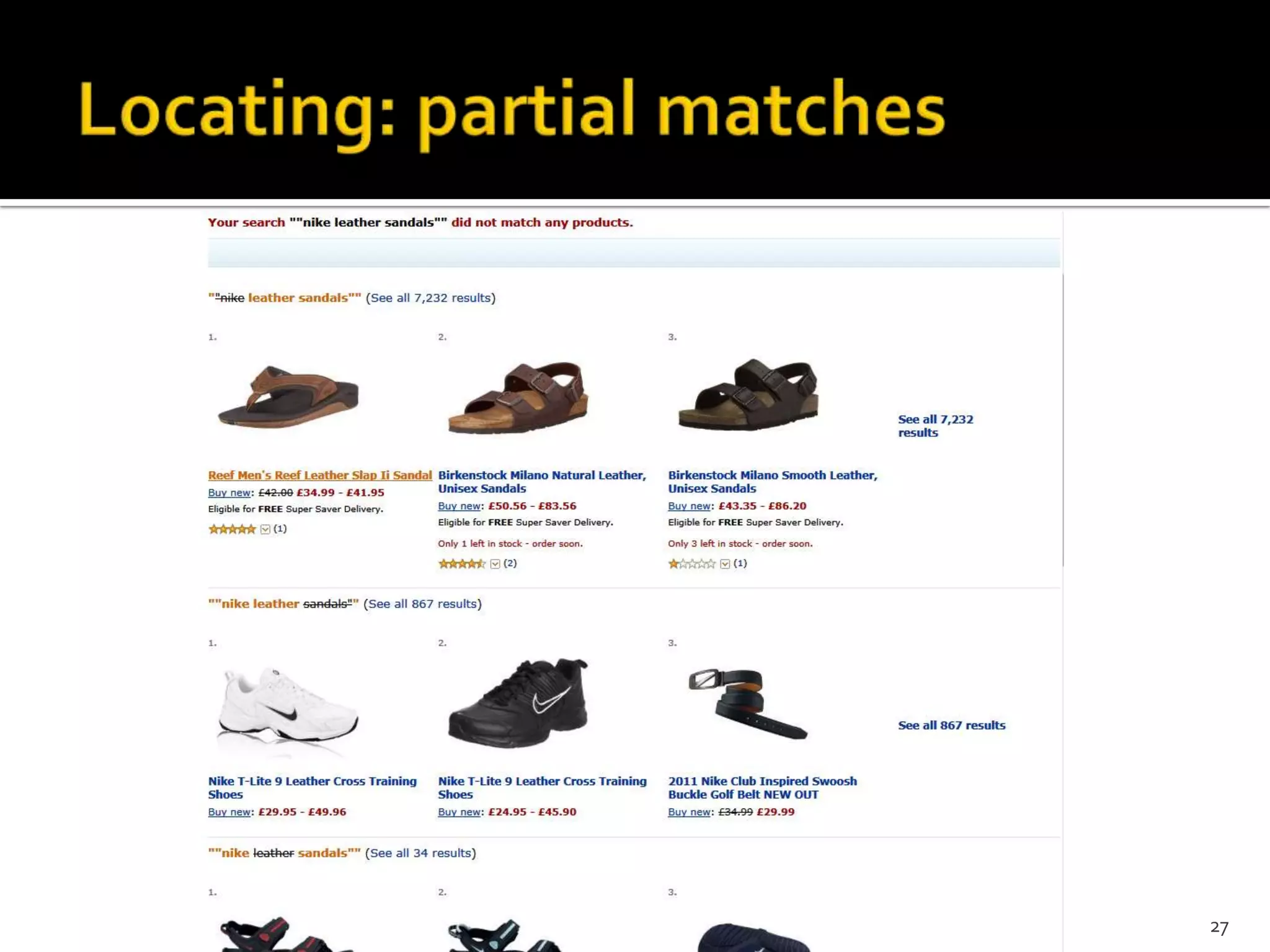
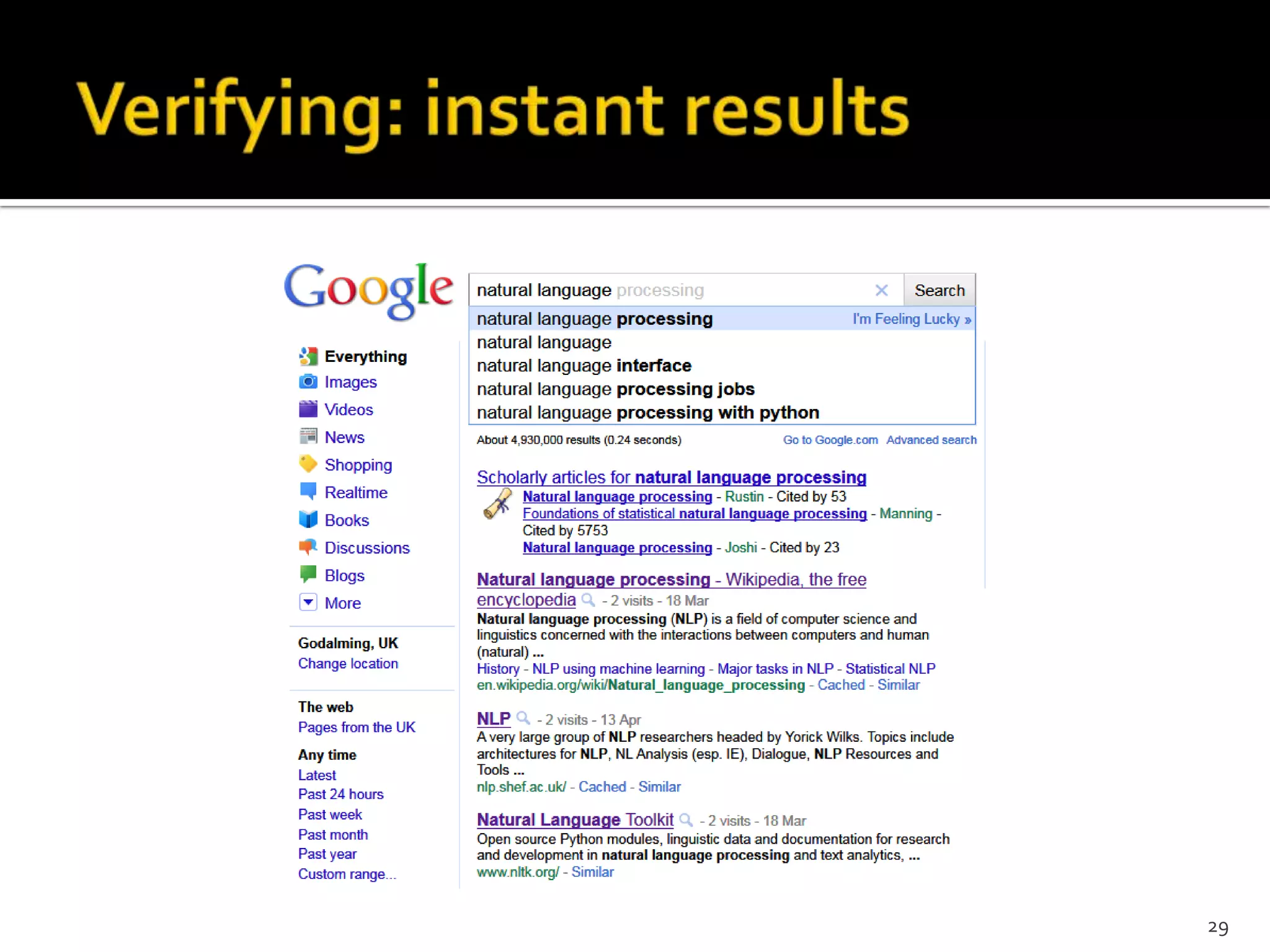
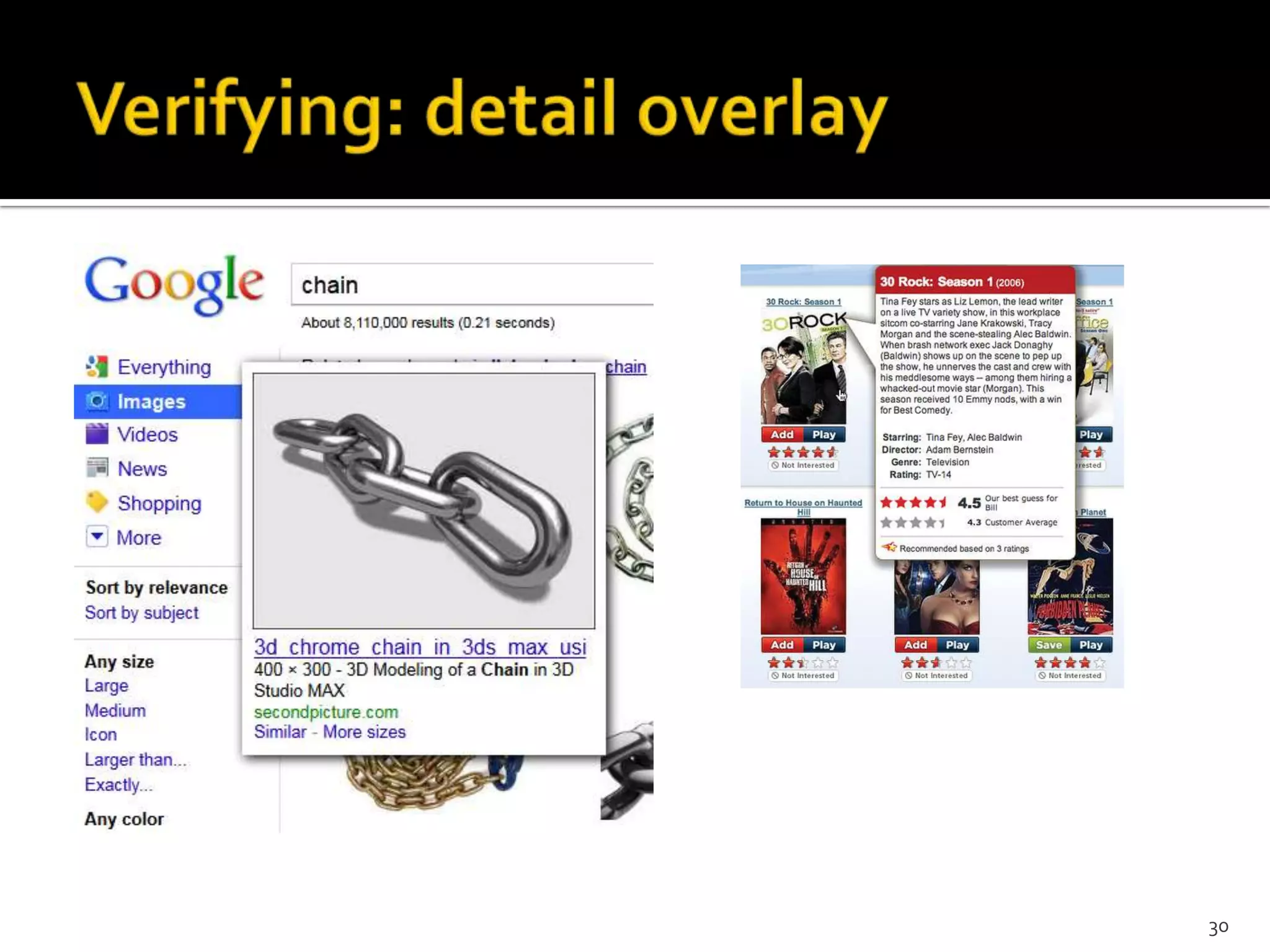
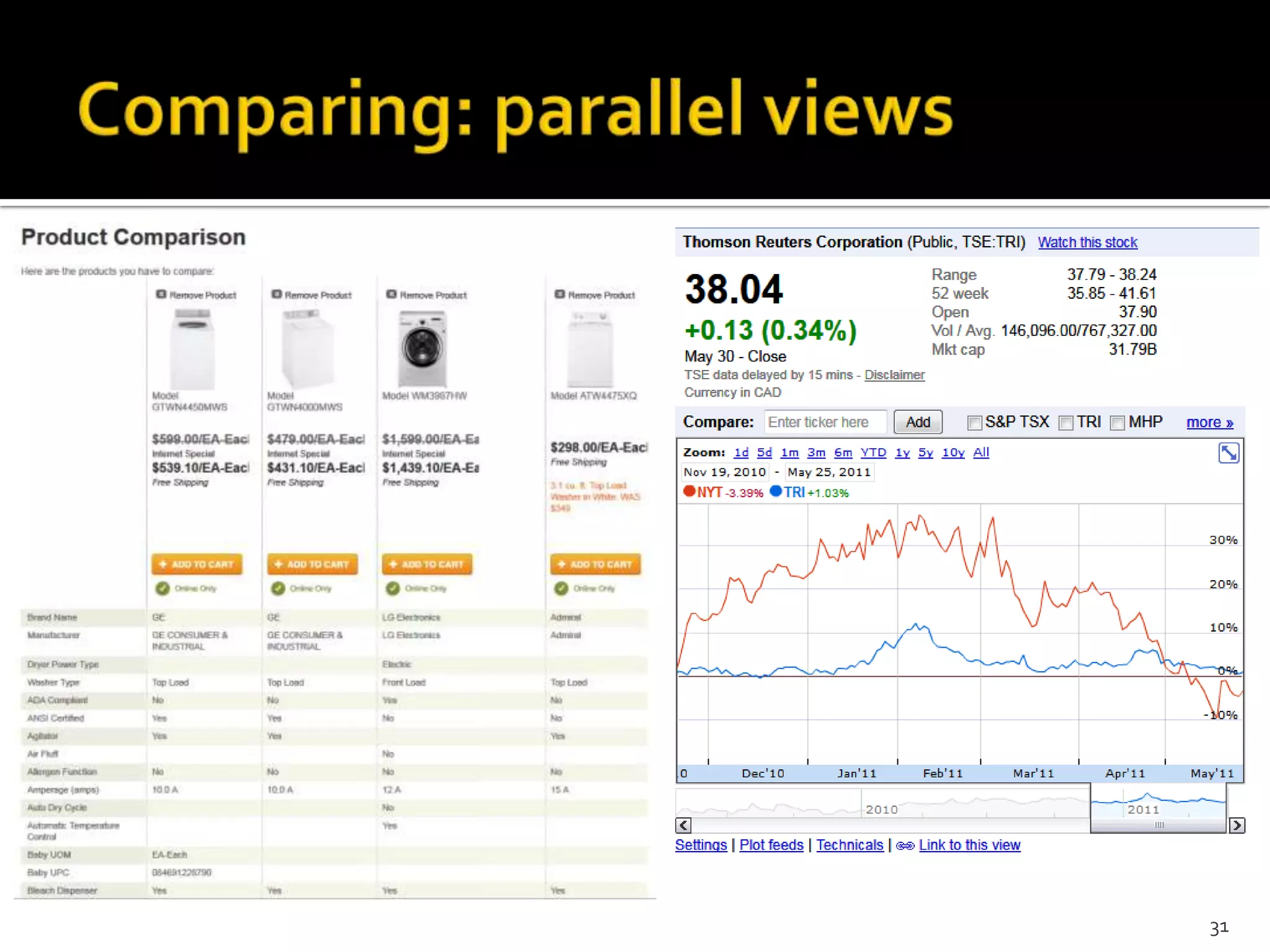
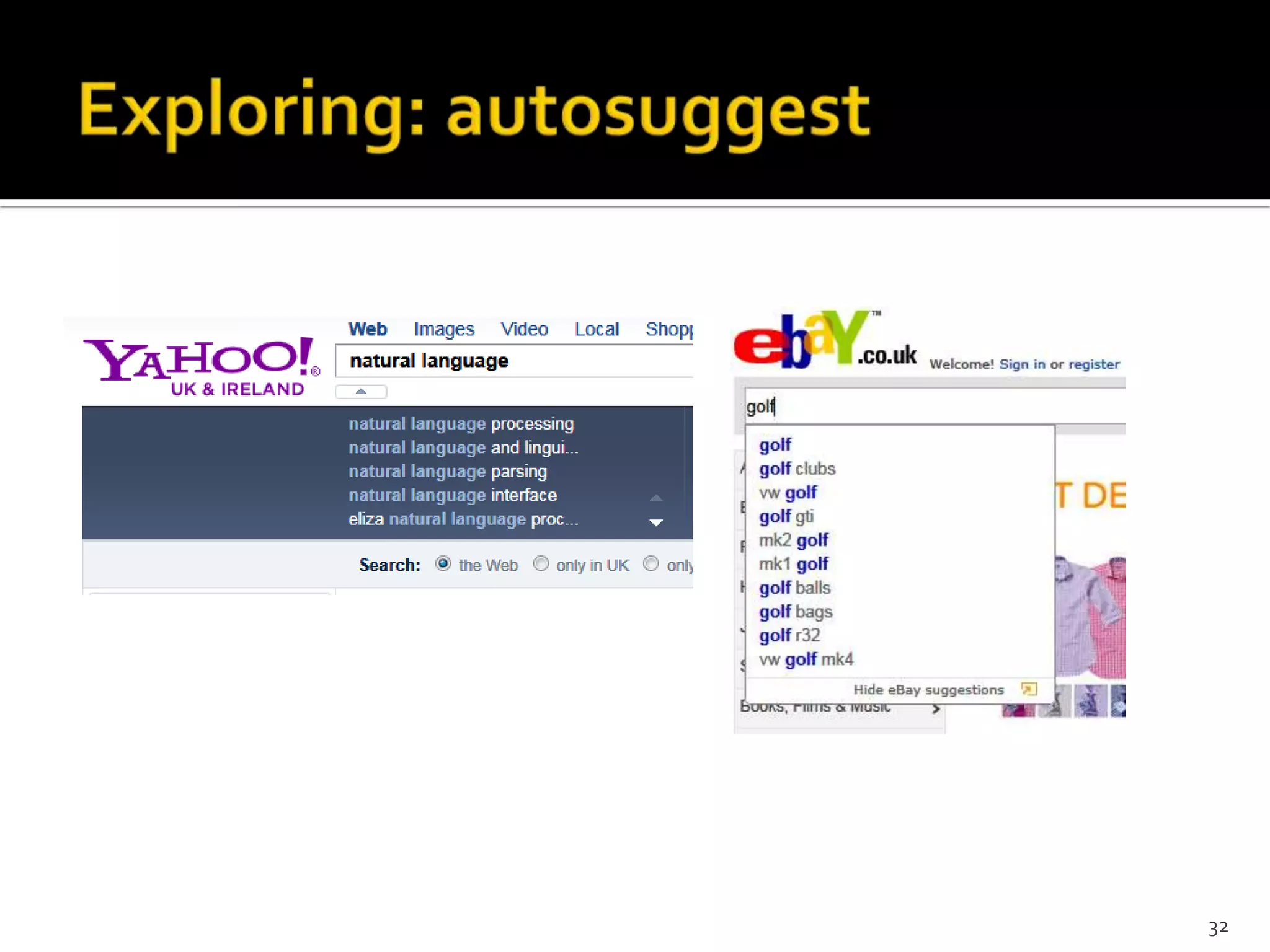
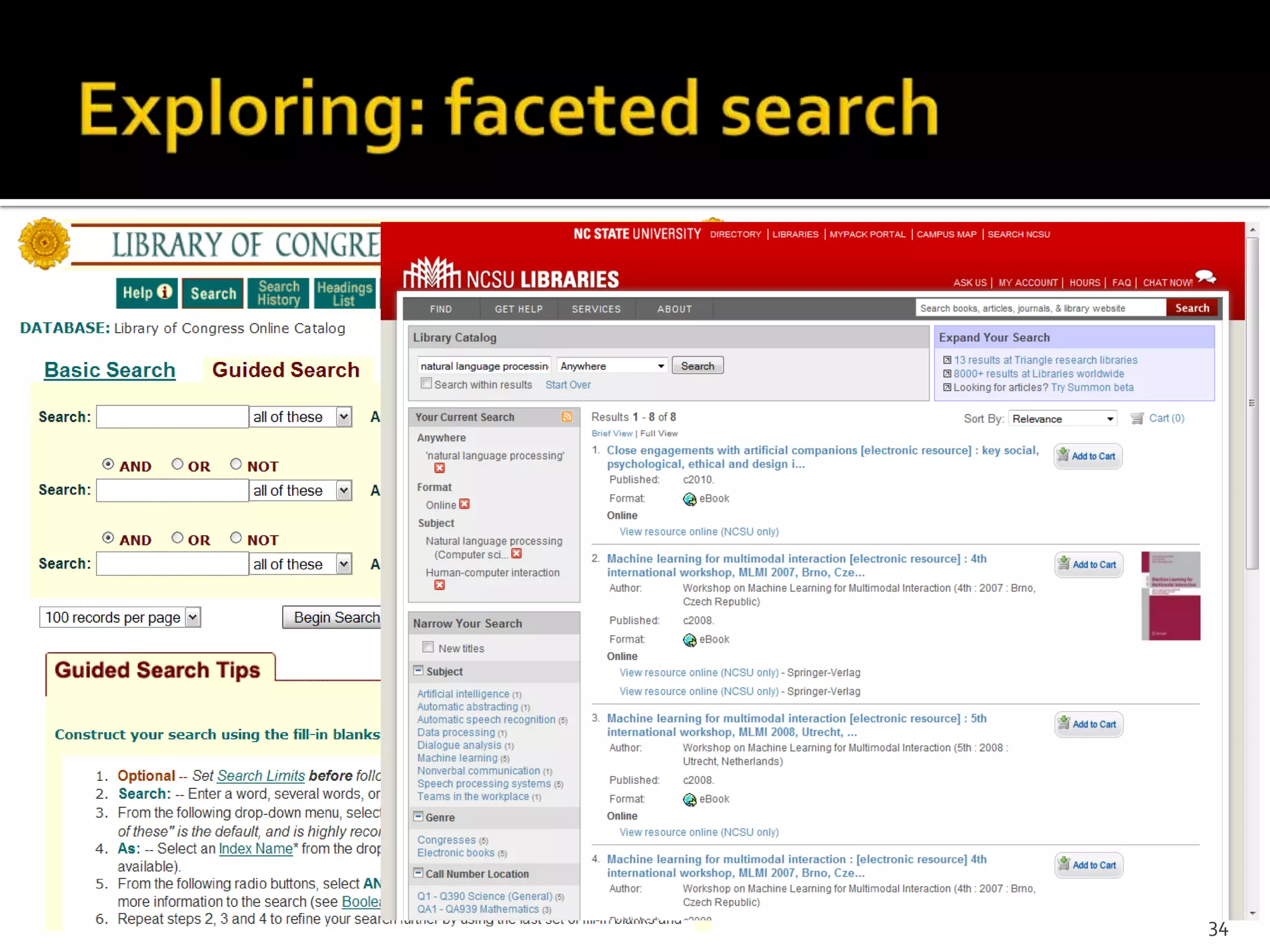
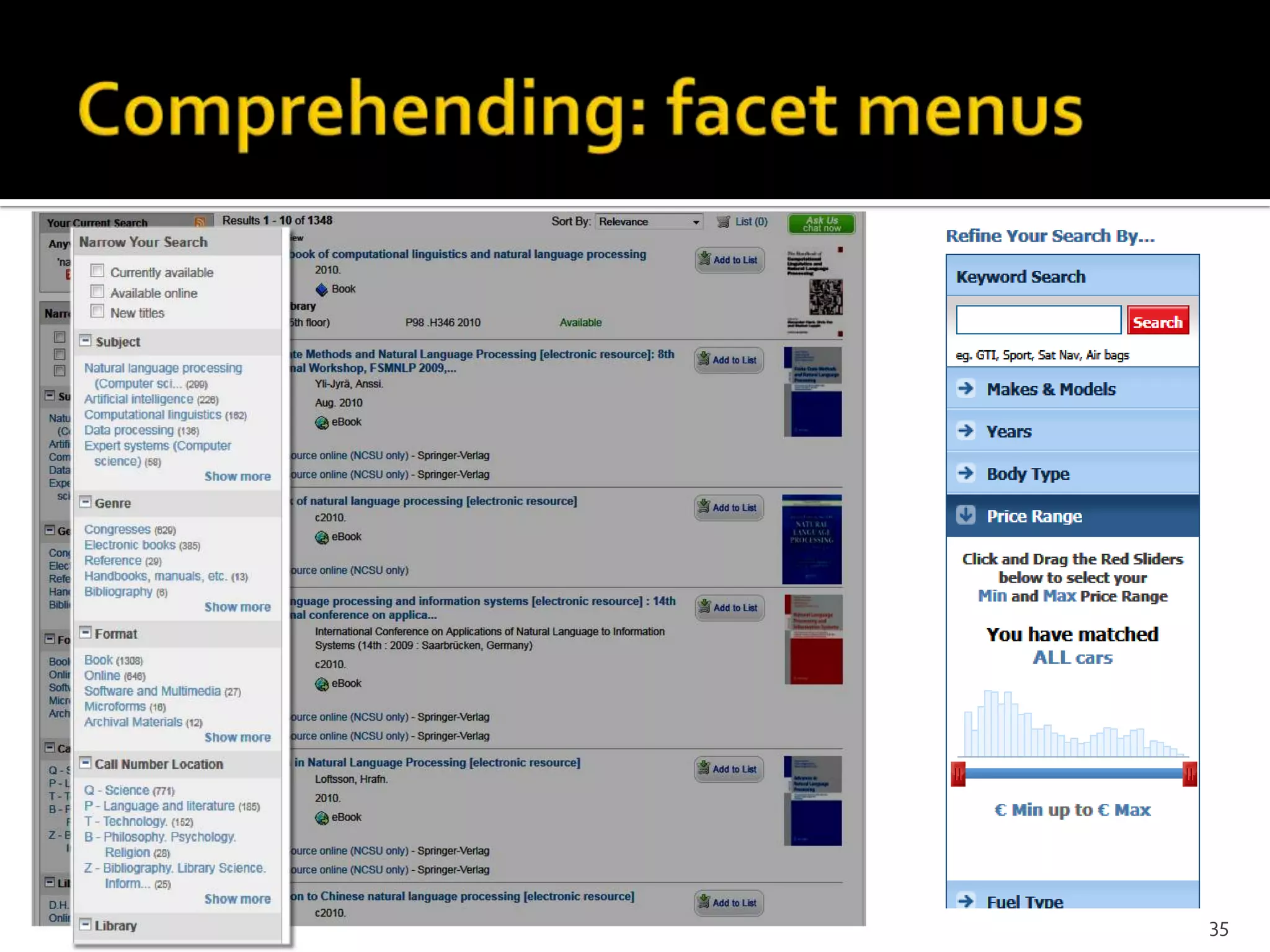
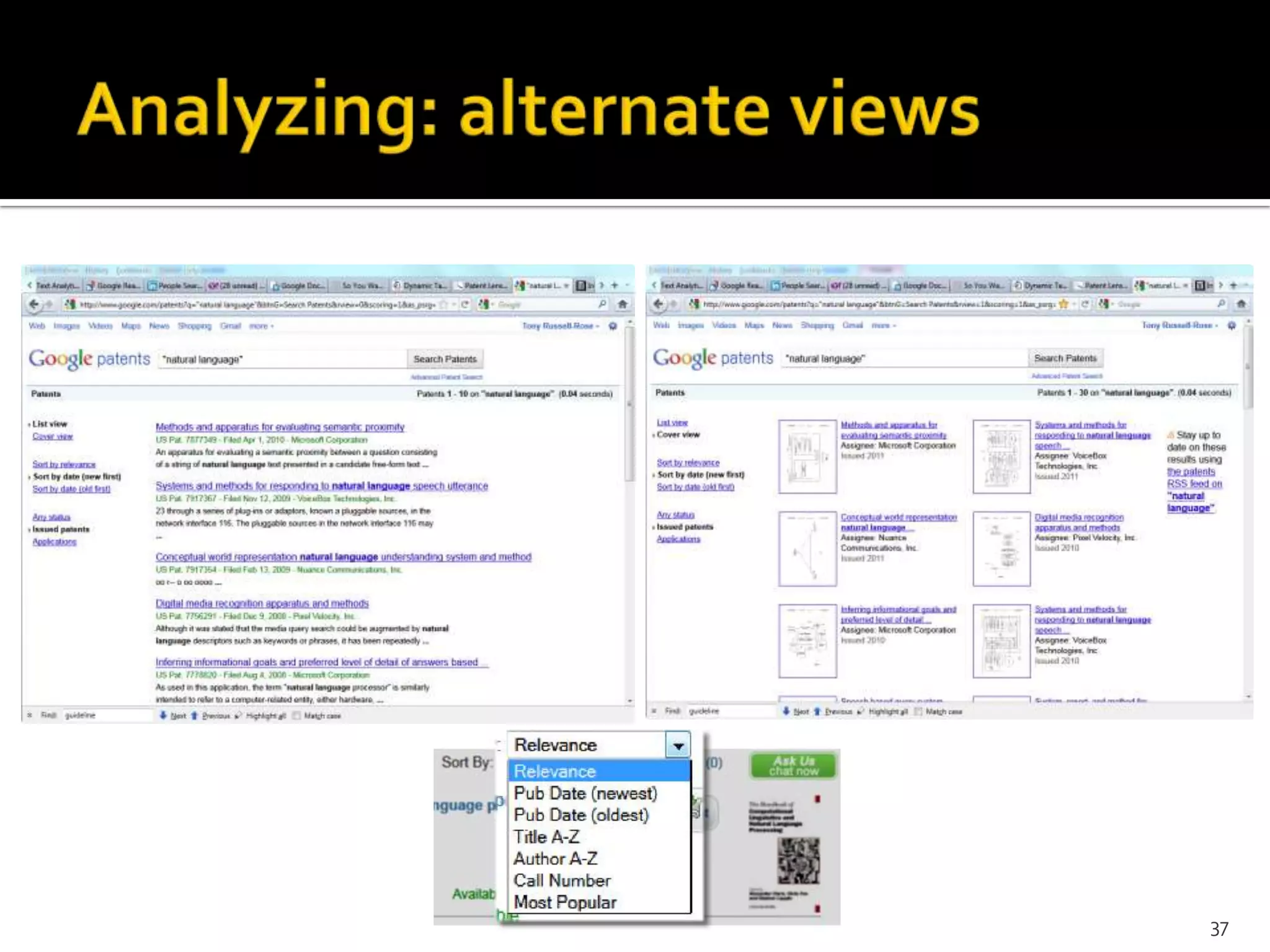
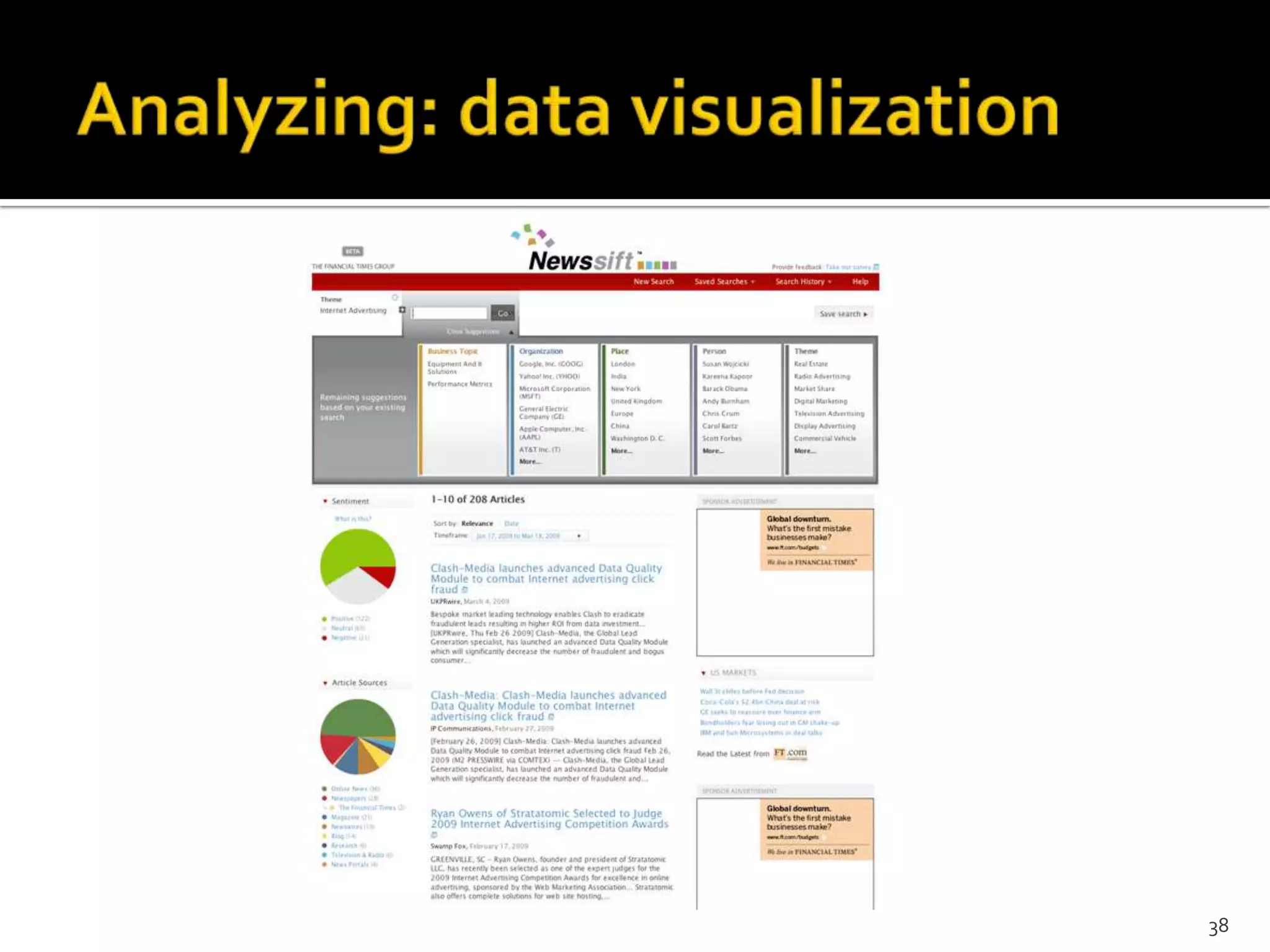
The document discusses the information-seeking process, emphasizing various models, frameworks, and search strategies. It categorizes search behaviors into different modes and highlights user needs based on gathered scenarios, showcasing the distinction between site search and enterprise search. The document concludes with suggestions for refining the search framework and extending it to other data sources.