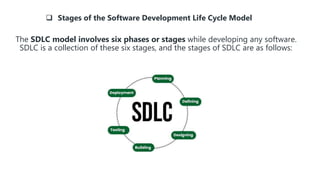
The document outlines the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), emphasizing its structured approach for designing, developing, and testing software while addressing common challenges like inconsistent processes, communication gaps, and resource allocation issues. It details the six stages of SDLC: planning and requirement analysis, defining requirements, designing architecture, developing the product, testing and integration, and deployment and maintenance. Additionally, it compares various SDLC models, such as the waterfall and V-shaped models, highlighting the importance of risk management, quality assurance, and effective collaboration throughout the development process.