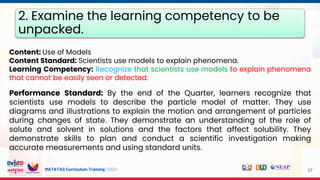
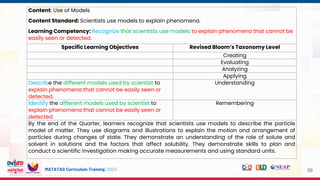
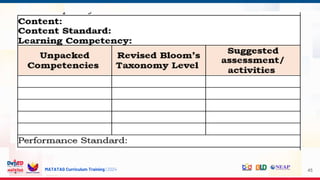
The document outlines the structure and content of the Matatag Curriculum training for grade 4/7 science, focusing on instructional design, curriculum standards, and assessment practices. It includes details on various sessions aimed at unpacking learning competencies, integrating 21st-century skills, and promoting inclusion for special needs learners. The training emphasizes collaborative expertise, classroom management, and enhancing professional development for school leaders.


![MATATAG Curriculum Training | 2024
Grade 4/7 Learning Journey
3
Day 1
Pretest
Opening Program
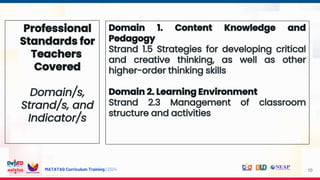
Session 1
The General Shape of the
MATATAG Curriculum
Session 2
21st Century Skills in the
MATATAG Curriculum
Session 3
Walkthrough of [Learning
Area] Shaping Paper
Day 2
Session 4
Quarter 1 Curriculum
Standards and
Unpacking/Clustering of
Learning Competencies
Session 5
Quarter 2 Curriculum
Standards and
Unpacking/Clustering of
Learning Competencies
Day 3
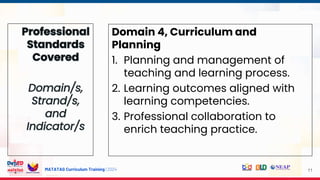
Session 6
MATATAG Curriculum:
Instructional Design
Framework
Session 7A
MATATAG (Learning Area)
Instructional Design
Framework
(IDF): Pedagogy and
Assessment
Session 7B
MATATAG (Learning Area)
Walkthrough of Learning
Resources
Day 4
Session 8
Integrating 21st Century
Skills in Classroom-based
Assessment
Session 9
Classroom Practices
to Promote
Inclusion for Special Needs
Education Learners (SNED)
Session 10
Collaborative Expertise
Session 11
Class Observation in the
Context of MATATAG
Curriculum
Day 5
Session 12
Management of School-
based Professional
Development Programs
Session 13
Facilitation Skills
Posttest
Closing Program
*For School Leaders Only](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdscience7session4-240728011645-4b906a68/85/SD-Science-7-Session-4-Quarter-1-Curriculum-3-320.jpg)
![MATATAG Curriculum Training | 2024
Grade 4/7 Learning Journey
4
Day 1
Pretest
Opening Program
Session 1
The General Shape of the
MATATAG Curriculum
Session 2
21st Century Skills in the
MATATAG Curriculum
Session 3
Walkthrough of [Learning
Area] Shaping Paper
Day 2
Session 4
Quarter 1 Curriculum
Standards and
Unpacking/Clustering of
Learning Competencies
Session 5
Quarter 2 Curriculum
Standards and
Unpacking/Clustering of
Learning Competencies
Day 3
Session 6
MATATAG Curriculum:
Instructional Design
Framework
Session 7A
MATATAG (Learning Area)
Instructional Design
Framework
(IDF): Pedagogy and
Assessment
Session 7B
MATATAG (Learning Area)
Walkthrough of Learning
Resources
Day 4
Session 8
Integrating 21st Century
Skills in Classroom-based
Assessment
Session 9
Classroom Practices
to Promote
Inclusion for Special Needs
Education Learners (SNED)
Session 10
Collaborative Expertise
Session 11
Class Observation in the
Context of MATATAG
Curriculum
Day 5
Session 12
Management of School-
based Professional
Development Programs
Session 13
Facilitation Skills
Posttest
Closing Program
*For School Leaders Only](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdscience7session4-240728011645-4b906a68/85/SD-Science-7-Session-4-Quarter-1-Curriculum-4-320.jpg)