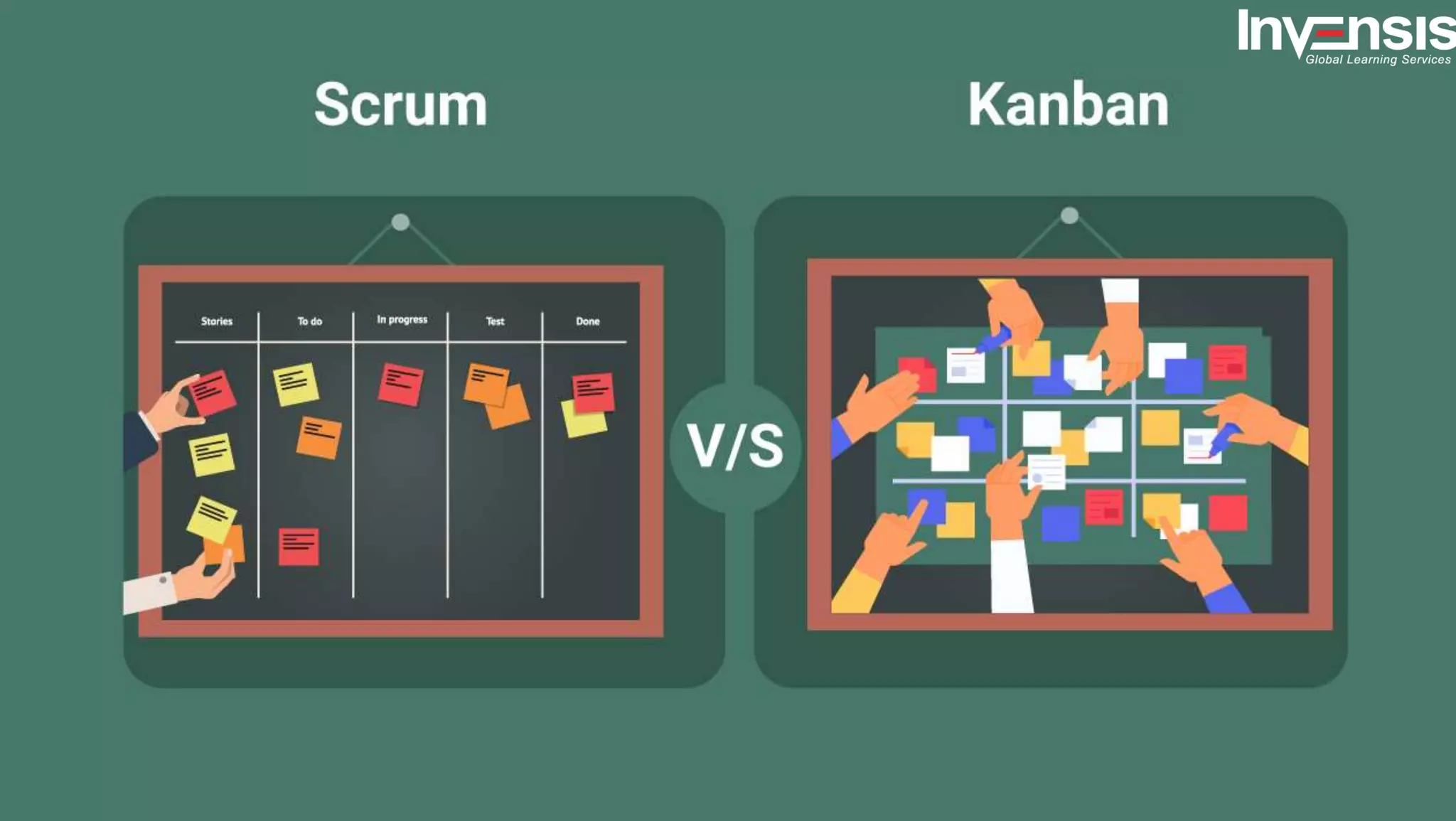
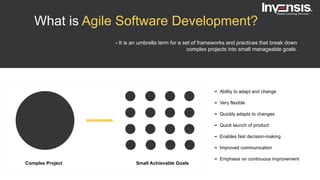
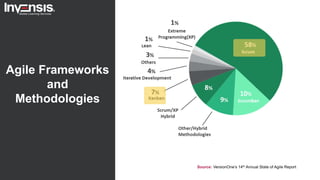
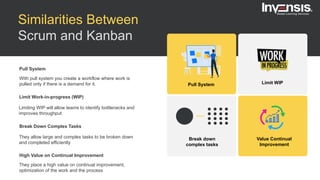
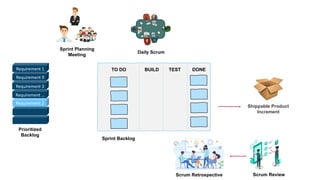
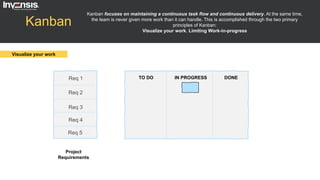
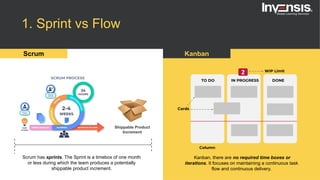
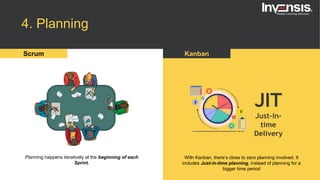
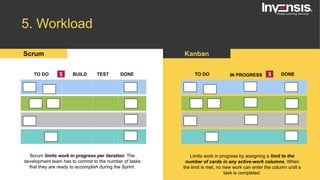
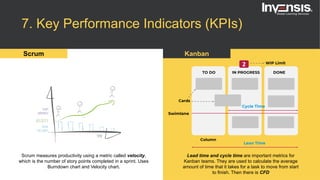
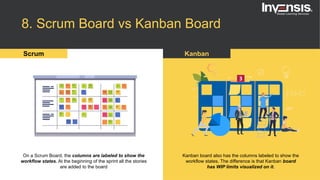
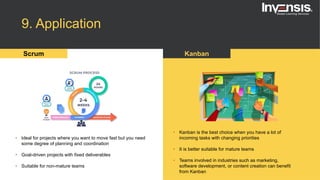
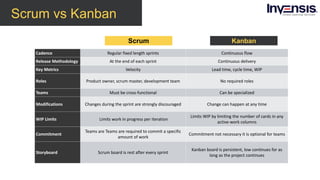
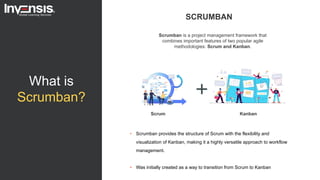
The document discusses the differences between Scrum and Kanban, both of which are agile frameworks for software development. Key distinctions include Scrum's structured approach with defined roles and time-boxed sprints, while Kanban emphasizes continuous flow and visualization without mandatory roles. The document also briefly introduces 'Scrumban', a hybrid of the two methods that combines their advantages.