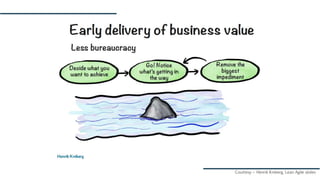
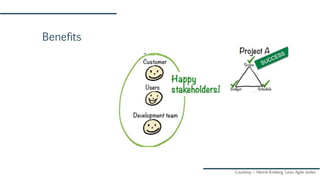
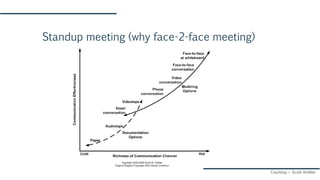
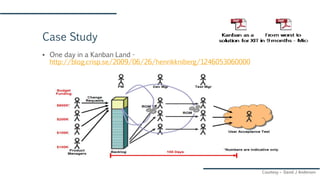
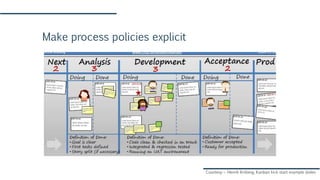
The document discusses Agile and Kanban principles and practices. It defines Agile as focusing on early delivery of business value, continuous improvement, and flexibility. Kanban is introduced as a method for managing knowledge work using visual signals and limiting work in progress. The document outlines Kanban values like transparency and flow, principles like starting with the current process and incremental change, and practices like visualizing work, limiting WIP, and implementing feedback loops. It provides an example of how Kanban could be applied at an organization's support team.