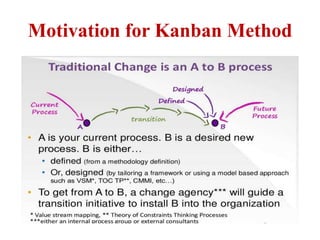
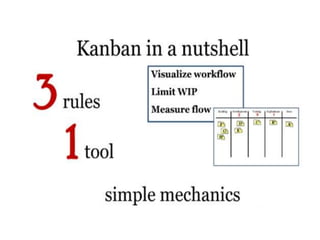
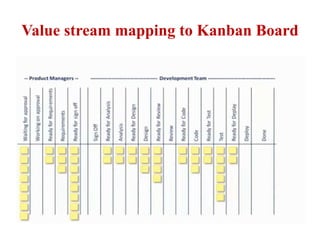
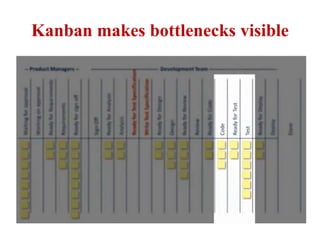
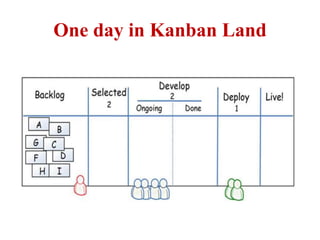
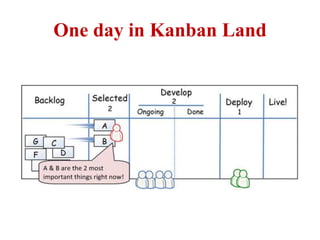
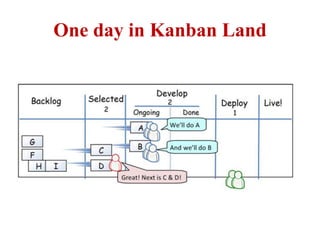
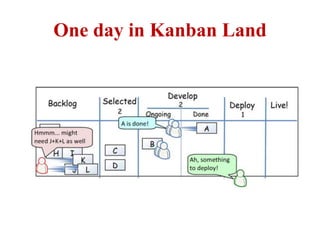
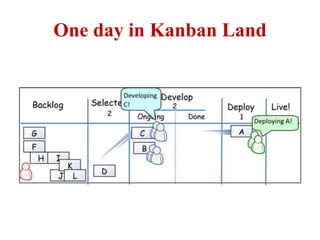
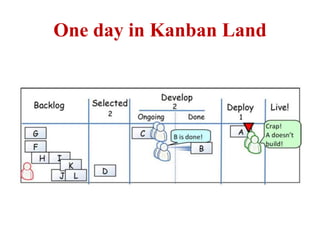
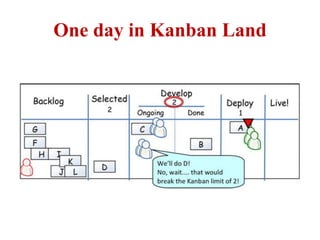
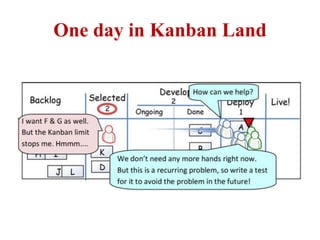
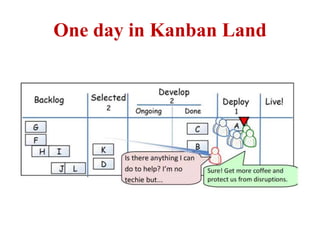
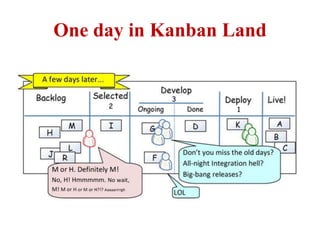
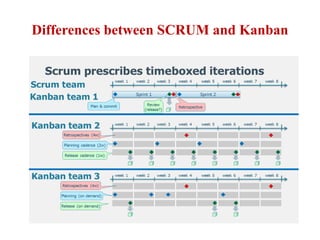
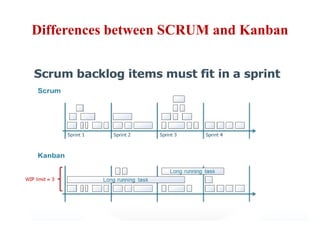
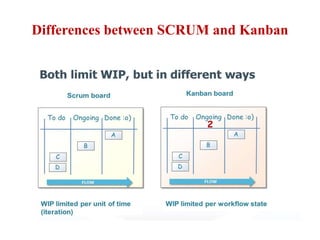
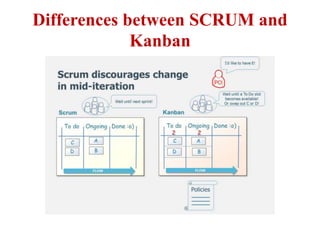
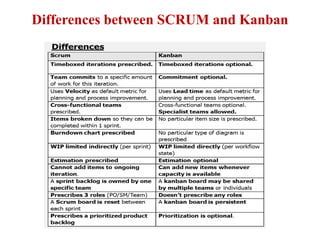
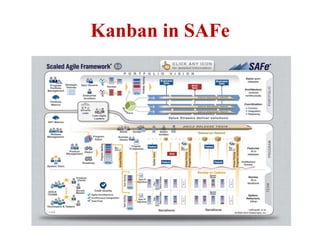
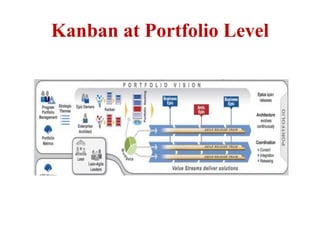
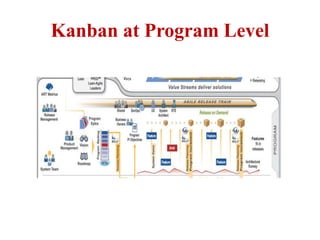
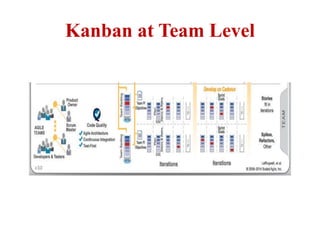
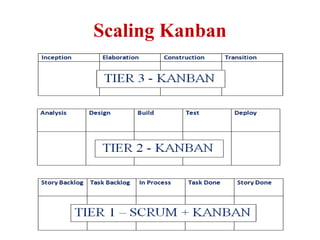
This document discusses blending SCRUM and Kanban approaches. It describes using Kanban at different levels of an organization, including at the portfolio, program, and team levels. Kanban focuses on limiting work in progress to improve flow and make bottlenecks visible. The document compares SCRUM and Kanban methods and suggests using a combination of the two by overlaying Kanban's work in progress limits on top of a SCRUM board at the team level. This allows restricting work in each column to optimal levels to increase throughput and productivity across the entire enterprise.