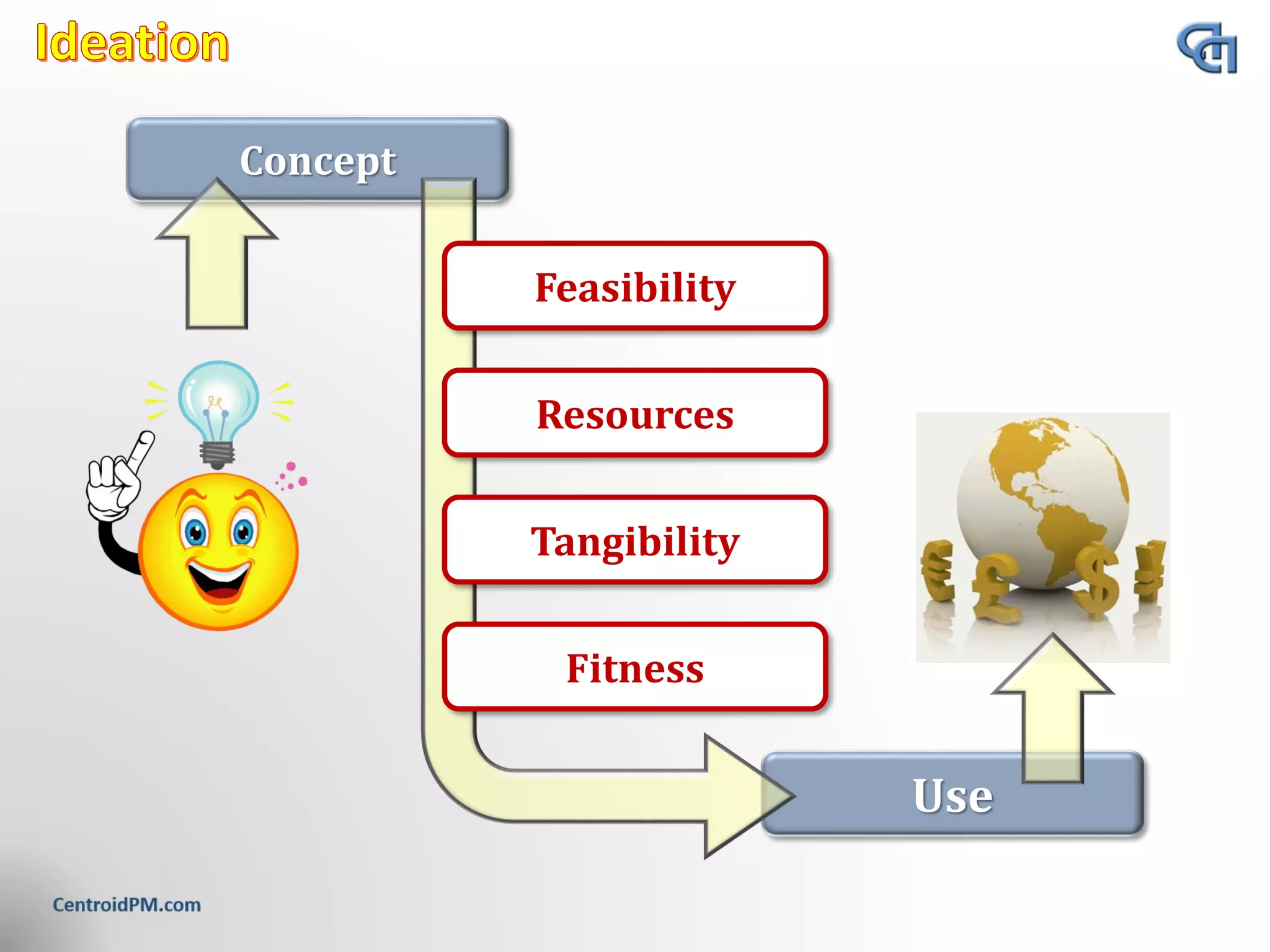
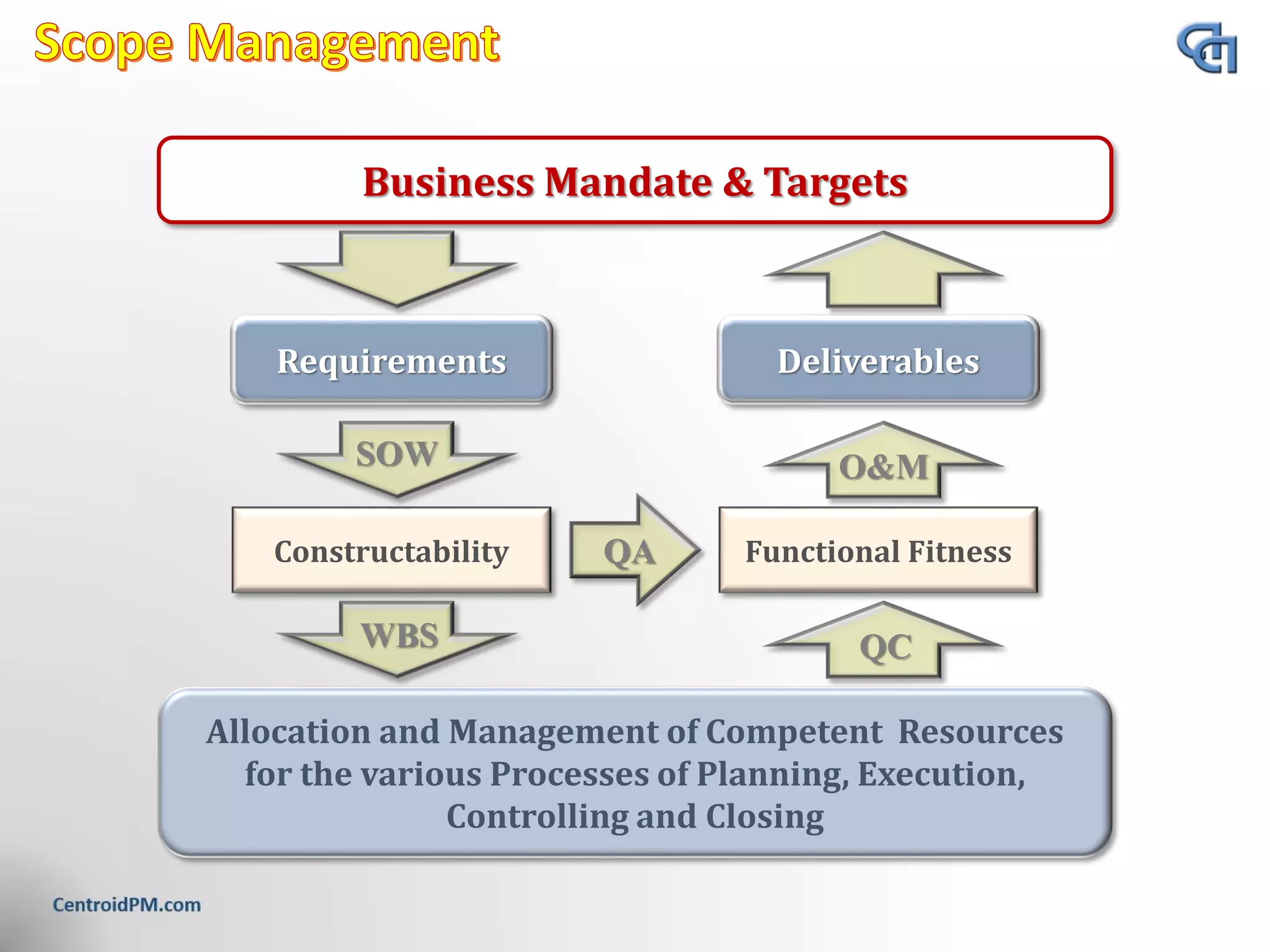
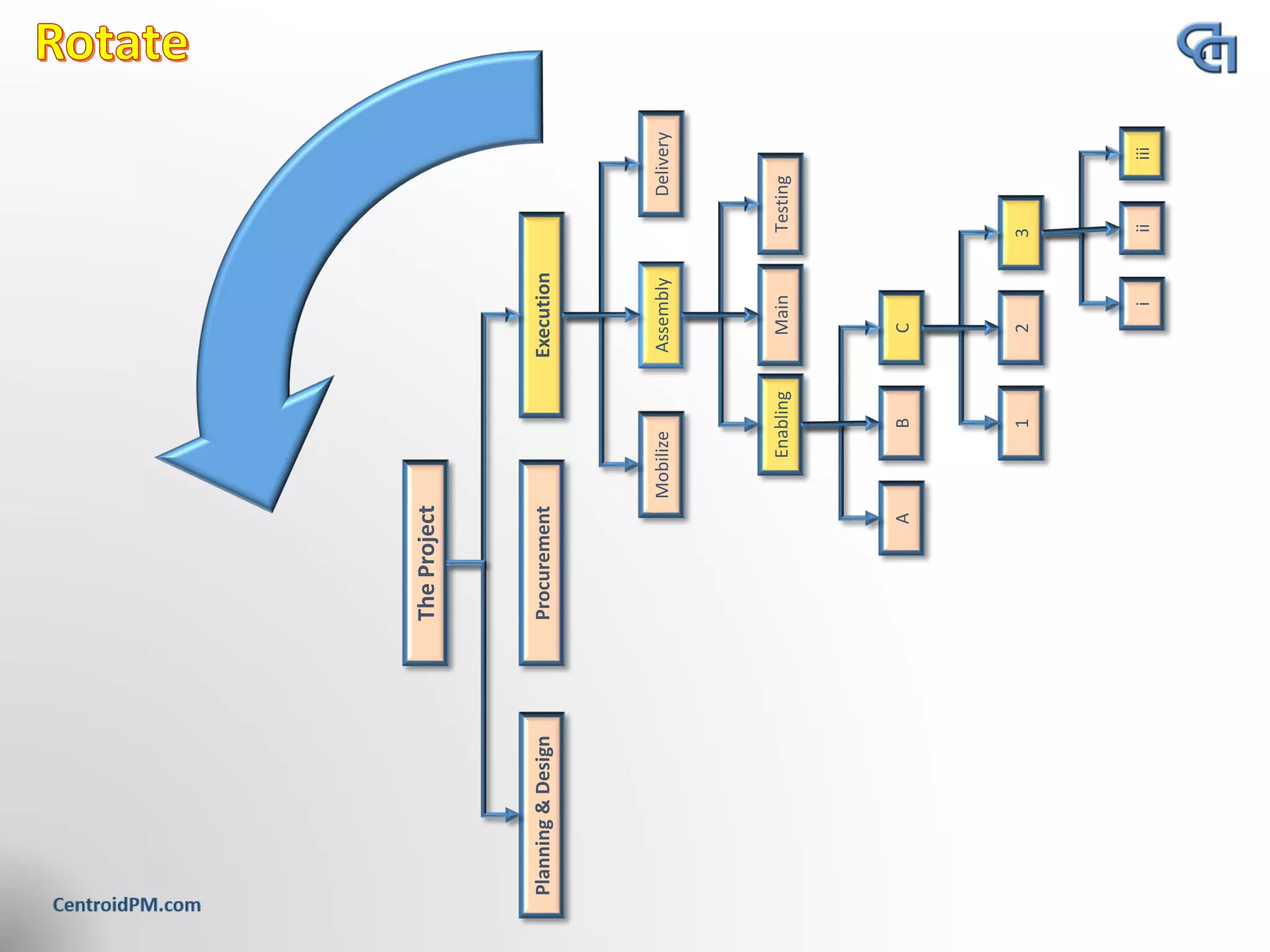
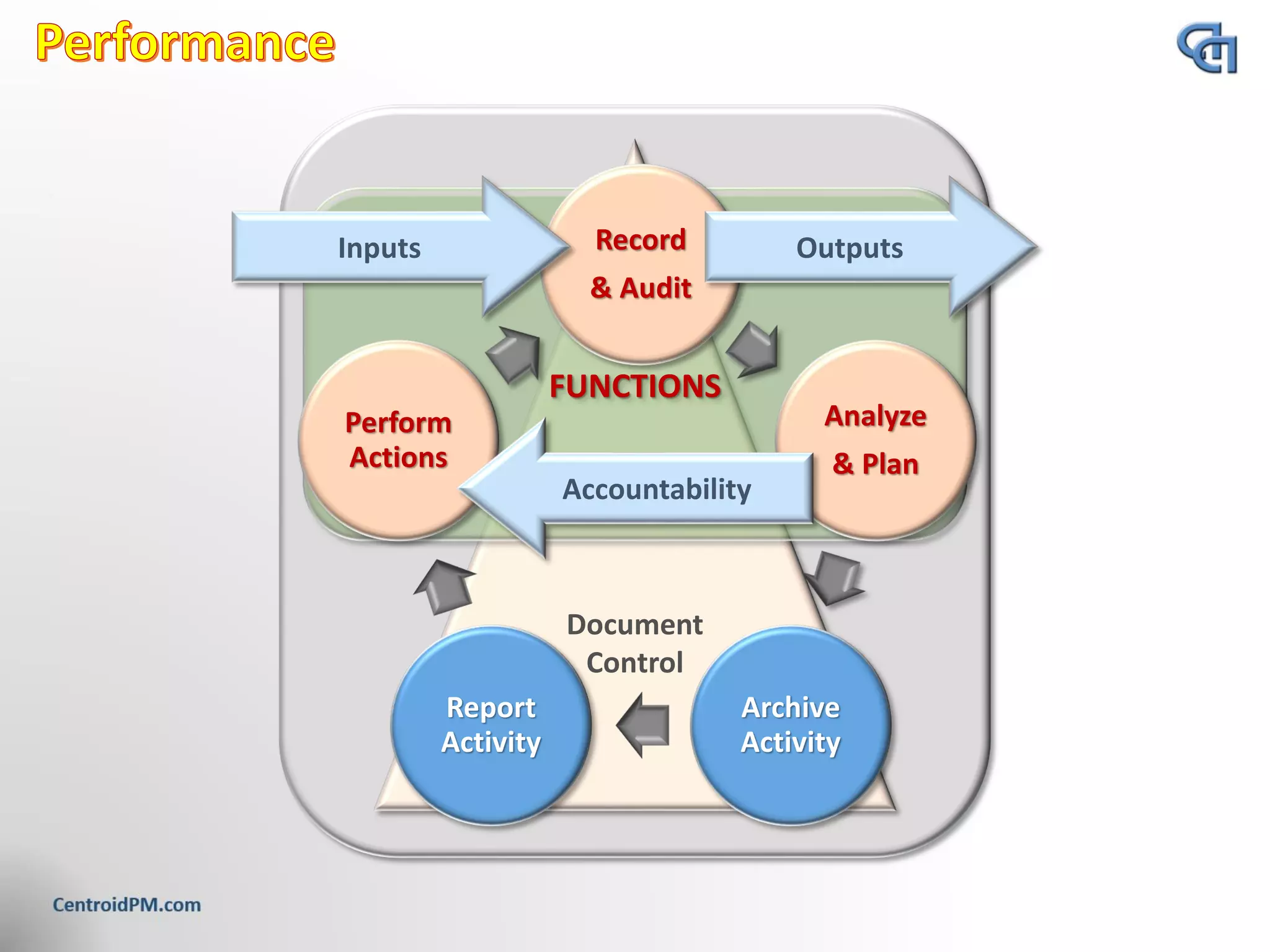
The document discusses the concept of project scope from several perspectives. It defines scope as the extent of the area or subject matter dealt with by a project, as well as the work needed to deliver the specified features and functions. The document emphasizes that clearly defining scope helps establish timelines, goals, and allocate resources. It also stresses the importance of getting client agreement on the scope boundaries.