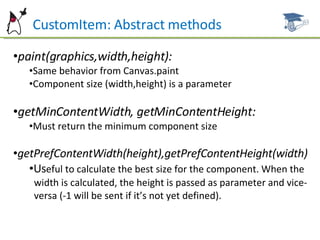
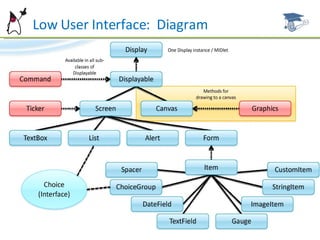
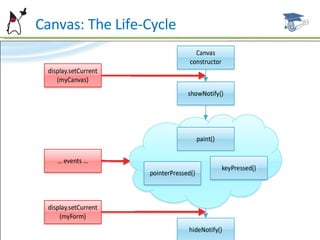
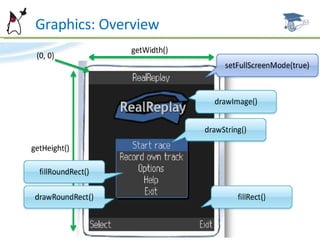
The document discusses the user interface capabilities in MIDP, including custom items which allow custom rendering and input handling, and the canvas API which provides low-level graphics and event handling capabilities. It describes the key methods and features of custom items and the canvas, such as painting, sizing, and handling input events from touchscreens and keyboards. Examples are provided and future topics are outlined.





![CustomItem: Callback methods Transverse(dir,viewportWidth,viewportHeight,visRect_inout[]): Notifies that a navigation event happened on an item Parameters: dir : Canvas.UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT or NONE (None: User clicked with a touchscreen) viewportWidth, viewportHeight: Size of the visible area visRect inout: In/Out parameter. Array of int[4] with [x, y,w, h], where x, y is the distance from the origin, and w, h are the size of the rectangle. State may be kept on the component (and used at paint method). It may be easier to ignore this parameter Returns true when the navigation happened internally, and false when the focus shall be lost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter06-1217728755700457-9/85/Scmad-Chapter06-7-320.jpg)











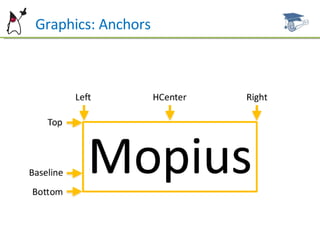


![Can Graphics: methods translate(x,y): Translates the reference point (origin). To return to the original reference, you may call g.translate(ax – g.getTranslateX() , ay – g.getTranslateY()) setClip(x,y,width,height): Sets a clip area to limit painting (like “framing” the image). Paints outsides of this area are ignored. drawRGB(data[],offset,scanlength,x,y,w,h,procAlpha): Renders an integer array with format: 0xAARRGGBB, where AA stands for transparency. Offset: first index on the array. Scanlength: number of elements that define a “line”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter06-1217728755700457-9/85/Scmad-Chapter06-24-320.jpg)

![References ALVES F. Eduardo. SCMAD Study Guide, 27/04/2008. JAKL Andreas, Java Platform, Micro Edition Part 01 slides, 12/2007. Sun Certification Mobile Application Developer Website: [http://www.sun.com/training/certification/java/scmad.xml].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter06-1217728755700457-9/85/Scmad-Chapter06-28-320.jpg)