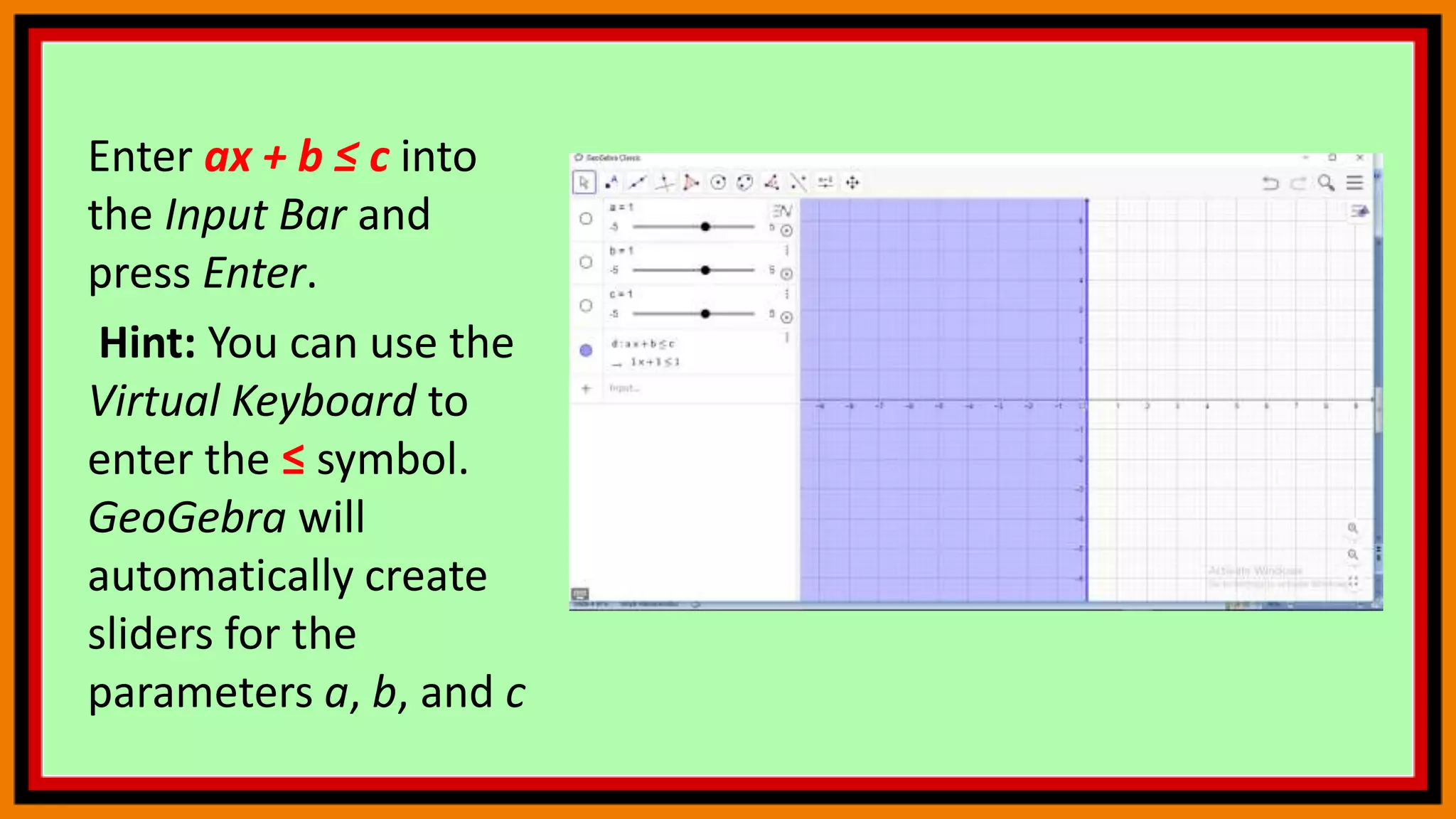
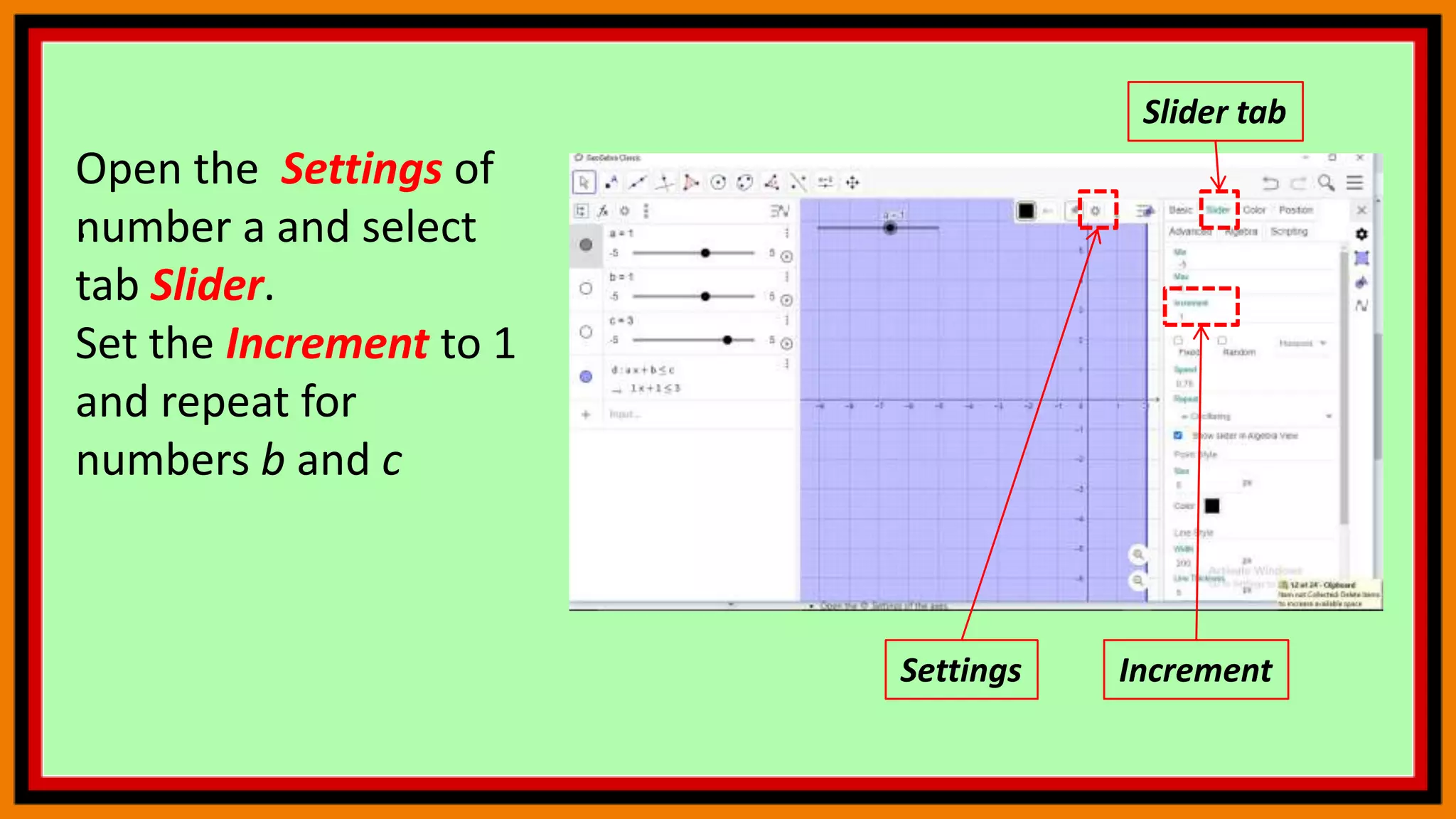
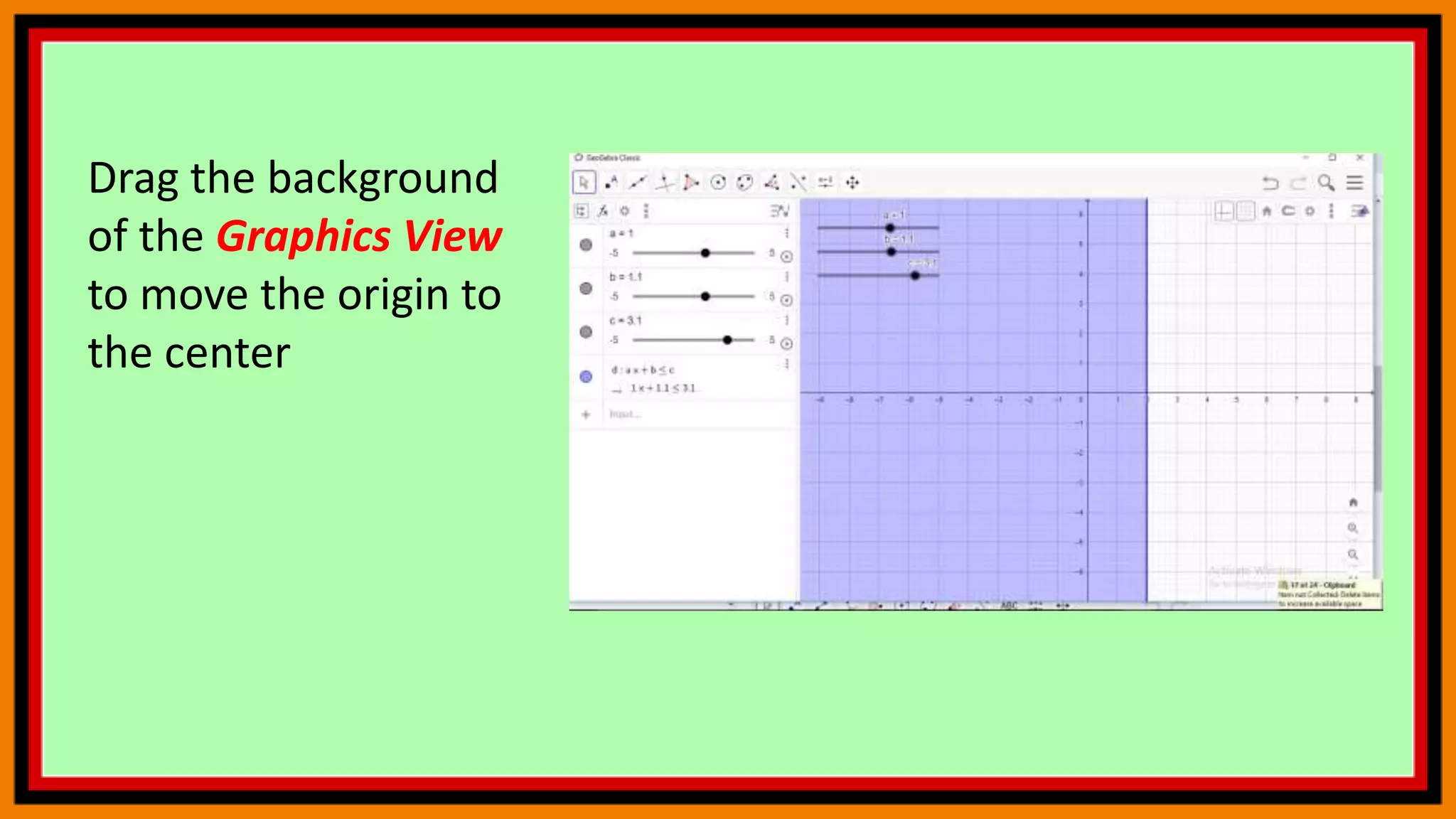
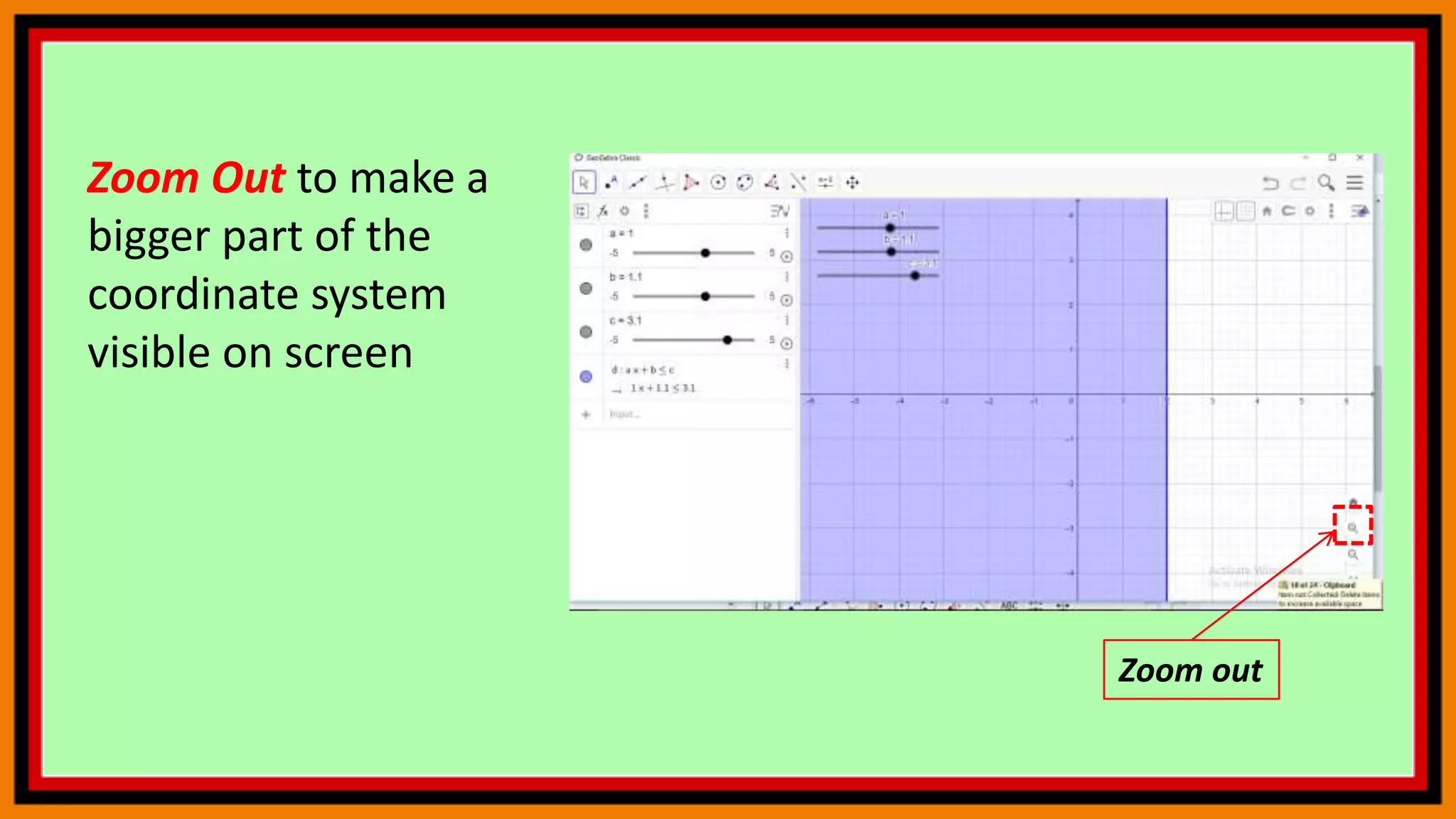
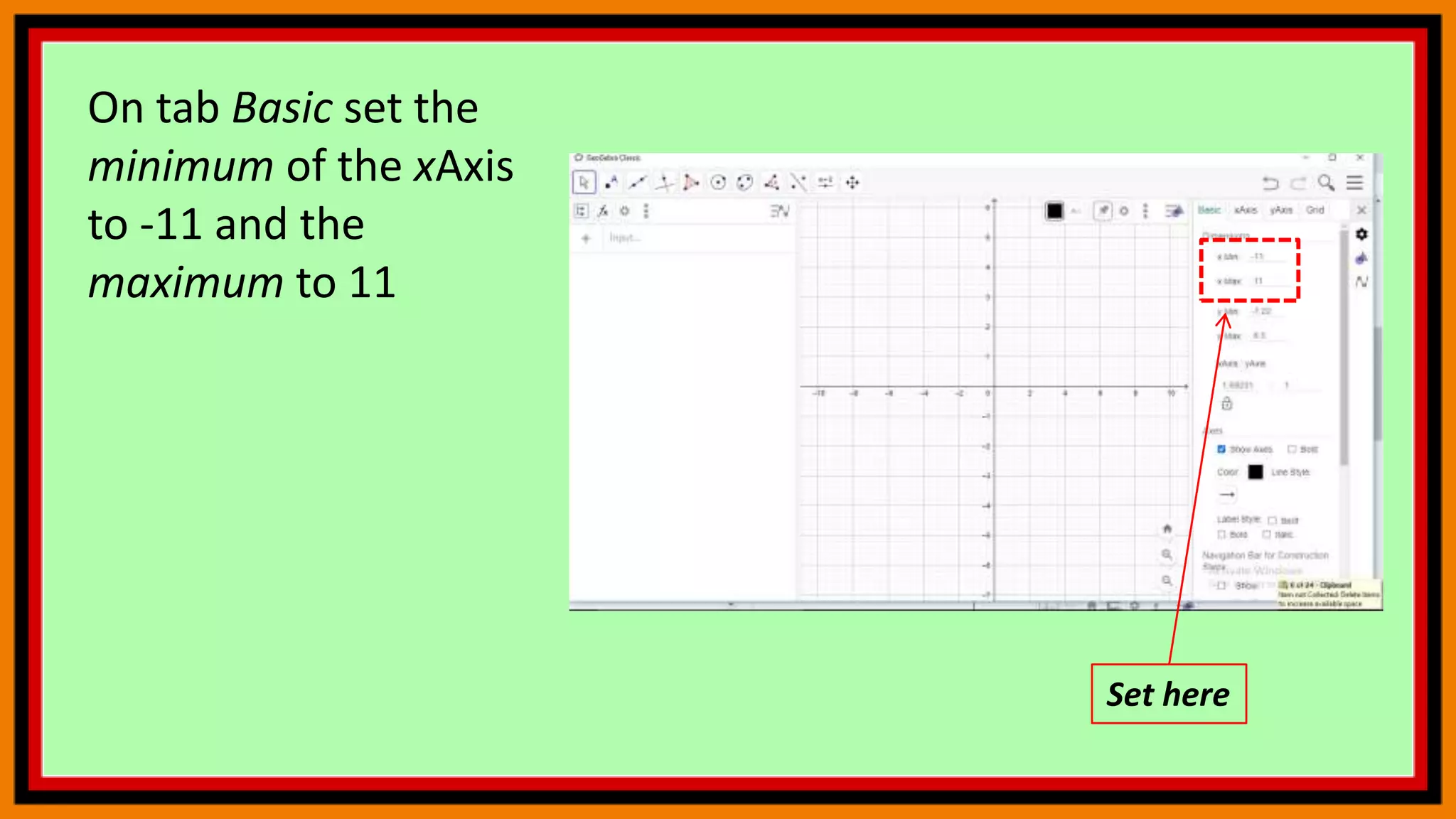
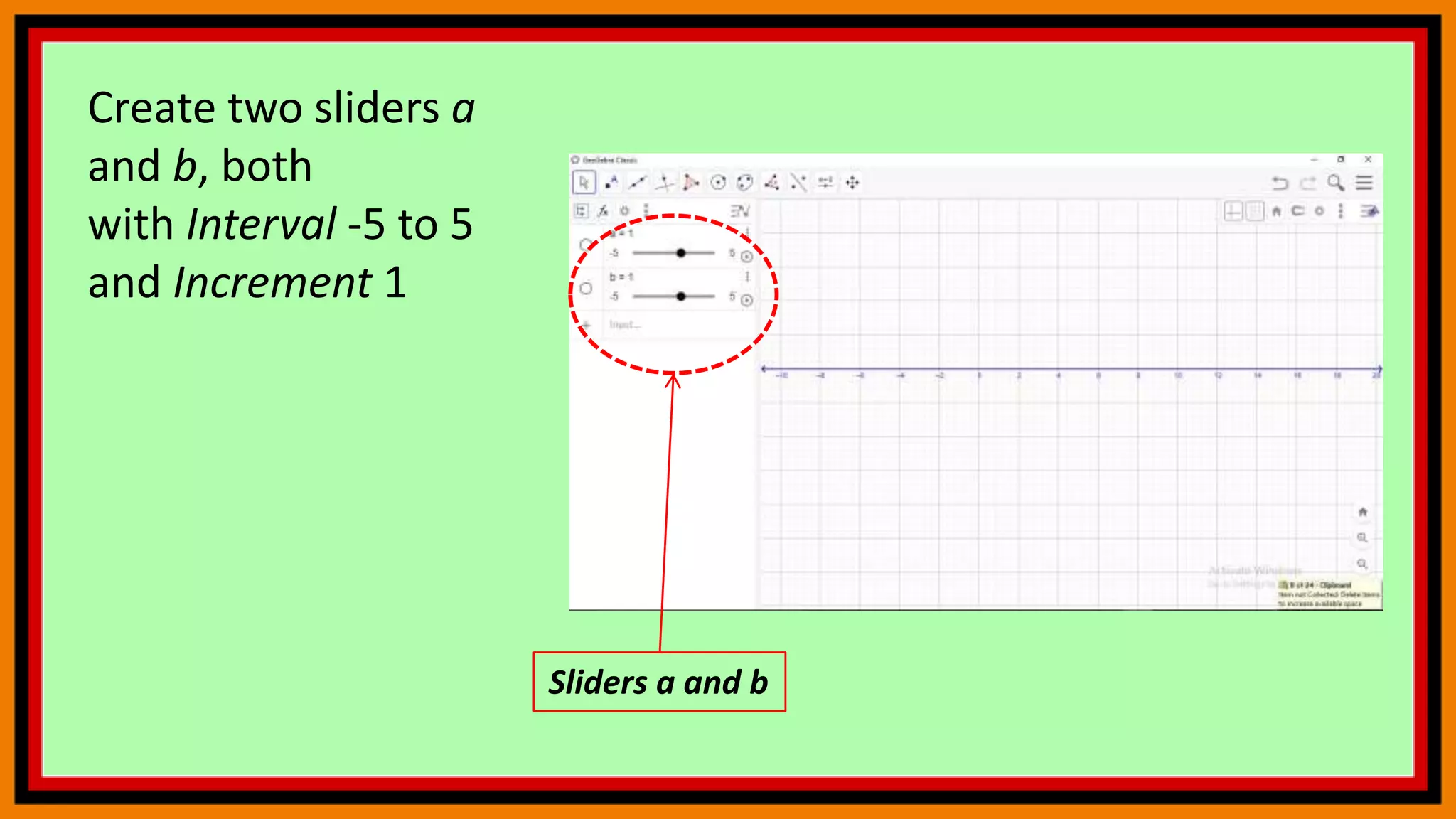
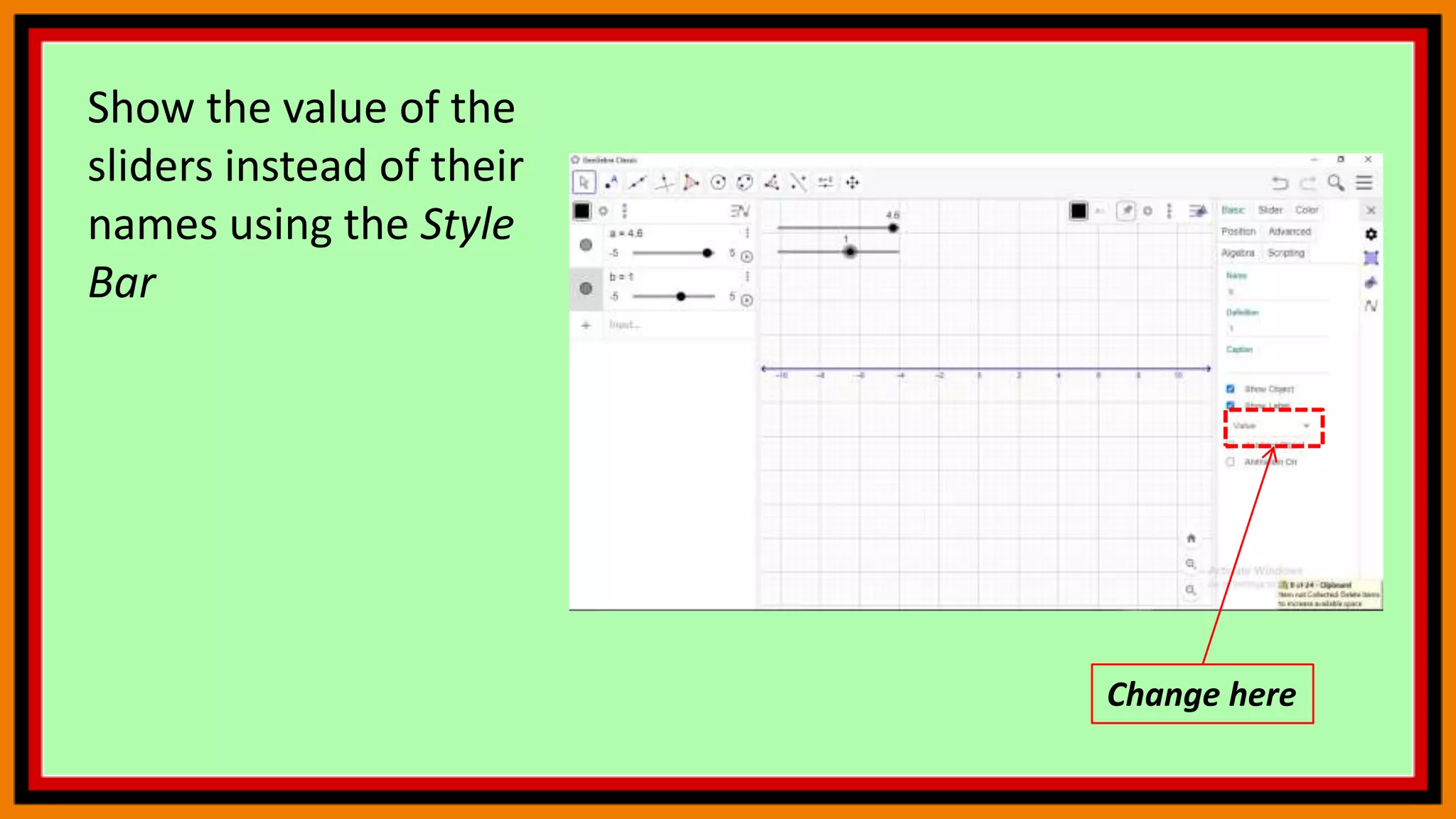
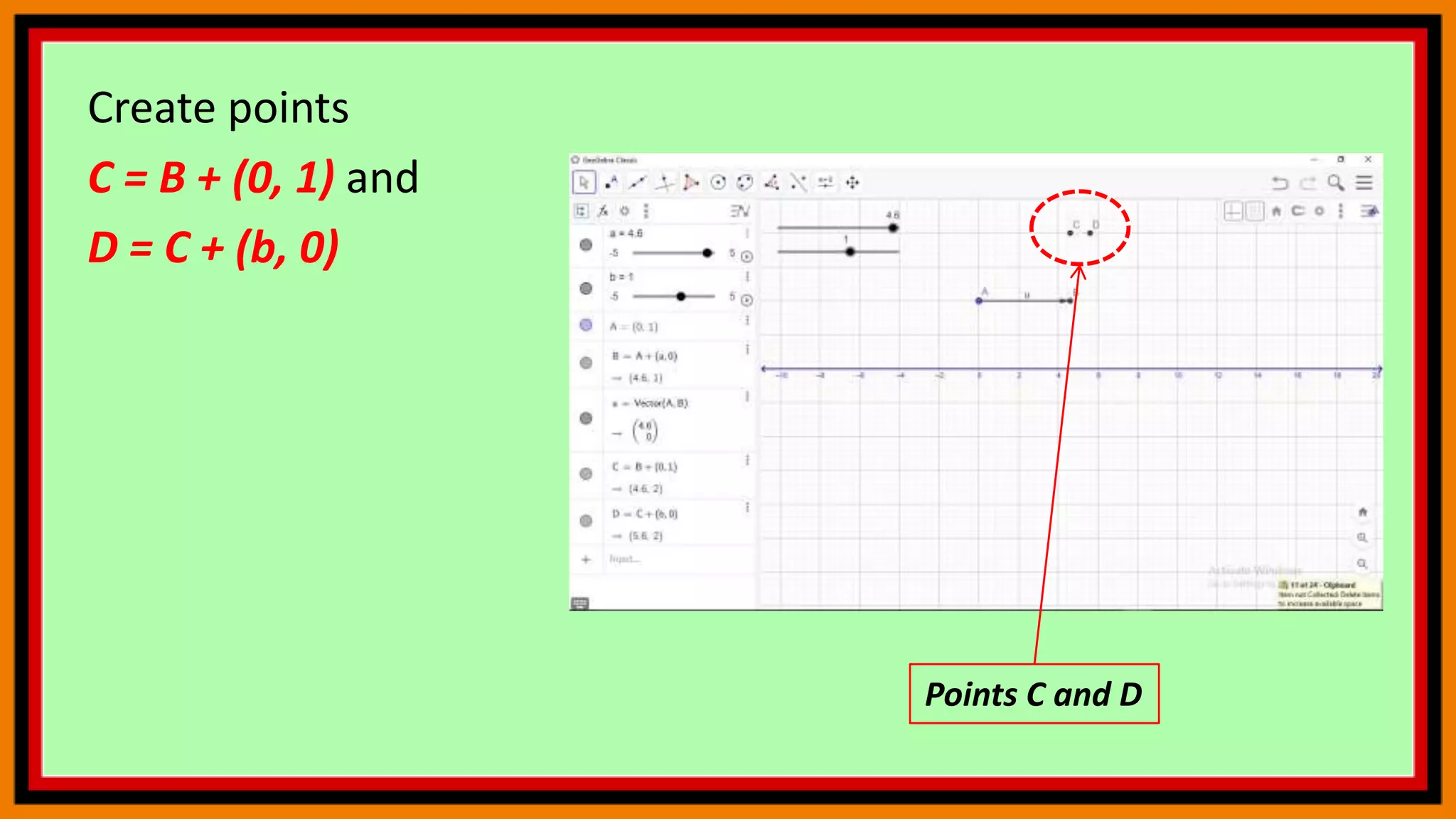
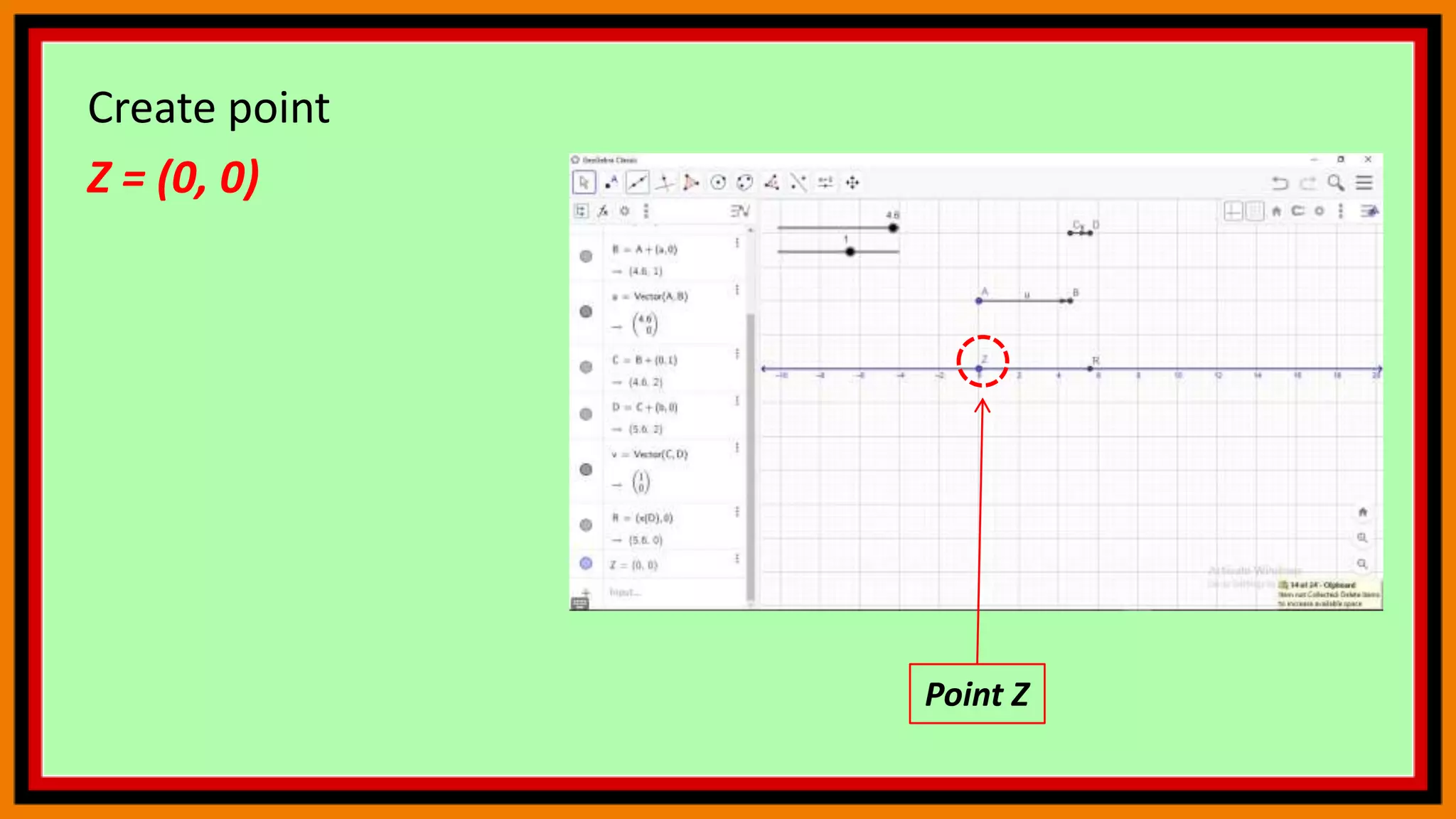
This document provides instructions for using a graphing calculator to explore linear inequalities and integer addition visually. It guides the user to create sliders and points on a number line to represent linear expressions and the addition of integers. Adjusting the sliders allows observation of how changing the variables affects the linear inequality and integer sum. The final construction enhances understanding through an interactive visualization of these mathematical concepts.