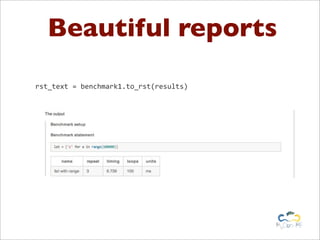
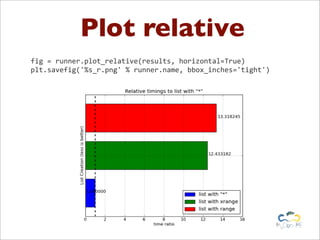
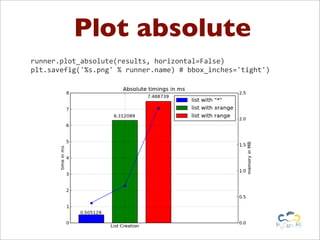
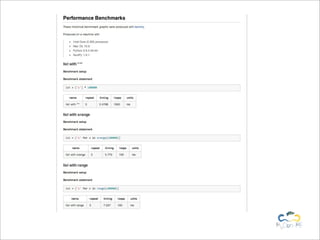
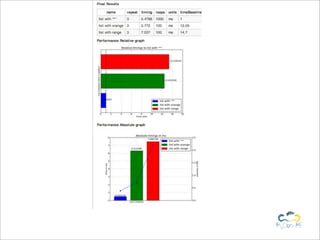
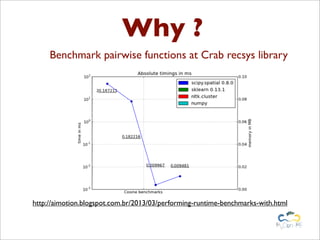
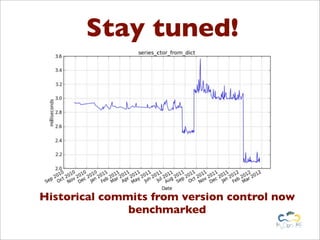
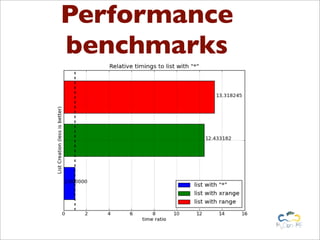
Benchy is a lightweight benchmark framework for Python scripts developed by Marcel Caraciolo, aimed at measuring performance and memory consumption of Python code. It allows users to create and run benchmarks, compare alternative implementations, and generate reports using Matplotlib. The tool promotes performance testing in various programming contexts, particularly focusing on efficient coding practices and optimization.







![Solutions ?
In
[1]:
def
f(x):
...:
return
x*x
...:
In
[2]:
%timeit
for
x
in
range
(100):
f(x)
100000
loops,
best
of
3:
20.3
us
per
loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benchy-130407082806-phpapp02/85/Benchy-Lightweight-framework-for-Performance-Benchmarks-9-320.jpg)


![Writing benchmarks
from
benchy.api
import
Benchmark
common_setup
=
""
statement
=
"lst
=
['i'
for
x
in
range(100000)]"
benchmark1
=
Benchmark(statement,
common_setup,
name=
"range")
statement
=
"lst
=
['i'
for
x
in
xrange(100000)]"
benchmark2
=
Benchmark(statement,
common_setup,
name=
"xrange")
statement
=
"lst
=
['i']
*
100000"
benchmark3
=
Benchmark(statement,
common_setup,
name=
"range")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benchy-130407082806-phpapp02/85/Benchy-Lightweight-framework-for-Performance-Benchmarks-13-320.jpg)
![Use them in your
workflow
[1]:
print
benchmark1.run()
{'memory':
{'repeat':
3,
'success':
True,
'units':
'MB',
'usage':
2.97265625},
'runtime':
{'loops':
100,
'repeat':
3,
'success':
True,
'timing':
7.5653696060180664,
'units':
'ms'}}
Same code as %timeit
and %memit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benchy-130407082806-phpapp02/85/Benchy-Lightweight-framework-for-Performance-Benchmarks-14-320.jpg)